How To Install Odoo on openSUSE

Installing Odoo on openSUSE can transform your business operations by providing a comprehensive enterprise resource planning (ERP) solution. This open-source business management software offers modules for accounting, inventory management, customer relationship management, and project tracking. openSUSE, with its robust package management and enterprise-grade stability, provides an excellent foundation for Odoo deployment.
Whether you’re a system administrator setting up Odoo for the first time or an experienced Linux user exploring different installation methods, this guide covers everything you need to know. We’ll explore multiple installation approaches, from package-based installations to Docker containers, ensuring you find the method that best suits your environment and requirements.
Prerequisites and System Requirements
Before diving into the installation process, ensuring your openSUSE system meets the necessary requirements is crucial for optimal Odoo performance.
System Requirements
Your openSUSE system should have a dual-core CPU as the minimum processor requirement. For RAM, allocate at least 2 GB, though 4 GB or more is recommended for production environments. Storage requirements include a minimum of 10 GB of available hard disk space, with SSD storage recommended for improved database performance.
openSUSE Leap 15.x versions provide the most stable foundation for Odoo installations. openSUSE Tumbleweed can also work but may introduce compatibility challenges due to its rolling release nature. Network connectivity should include a stable, high-speed internet connection for downloading packages and accessing the web interface.
Pre-installation Setup
Start by updating your openSUSE system to ensure all packages are current:
sudo zypper refresh
sudo zypper updateCreate a dedicated user account for Odoo operations, which enhances security by following the principle of least privilege:
sudo useradd -m -d /opt/odoo -U -r -s /bin/bash odooConfigure the firewall to allow HTTP traffic on port 8069, which is Odoo’s default port:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=8069/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadMethod 1: Package Installation via Zypper
The package management approach offers the simplest installation method, though it may have limitations regarding version control and dependency management.
Repository Setup
Adding the official Odoo repository enables direct installation through zypper. Configure the repository with the appropriate version URL:
sudo zypper ar https://nightly.odoo.com/18.0/nightly/rpm/ odoo-repo
sudo zypper refreshImport the GPG key to verify package authenticity:
sudo rpm --import https://nightly.odoo.com/odoo.keyInstallation Process
Install Odoo using zypper, which will automatically handle most dependencies:
sudo zypper install odooThe package manager will resolve dependencies and install the required components. However, some dependencies might not be available in the standard openSUSE repositories.
Service Configuration
Enable and start the Odoo service using systemd:
sudo systemctl enable odoo
sudo systemctl start odooVerify the service status:
sudo systemctl status odooCommon Issues with Package Method
Users often encounter dependency issues, particularly with babel and pychart packages. The babel package can sometimes be installed from openSUSE Leap 15 repositories, but pychart may not be available. These dependency conflicts can prevent successful installation or cause runtime issues.
Version limitations represent another challenge, as the repository might not always contain the latest Odoo release. Repository maintenance can also be inconsistent, potentially leading to outdated packages or broken dependencies.
Method 2: Source Installation from GitHub
Source installation provides maximum flexibility and access to the latest features, though it requires more manual configuration.
Dependency Installation
Install essential build tools and libraries required for Odoo compilation:
sudo zypper install python3-devel python3-pip python3-virtualenv
sudo zypper install gcc gcc-c++ make
sudo zypper install libxml2-devel libxslt-devel
sudo zypper install libjpeg8-devel libpng16-devel
sudo zypper install nodejs npmInstall additional Python dependencies:
sudo zypper install python3-lxml python3-Pillow python3-psycopg2PostgreSQL Database Setup
PostgreSQL serves as Odoo’s primary database backend. Install and configure PostgreSQL:
sudo zypper install postgresql postgresql-server postgresql-contrib
sudo systemctl enable postgresql
sudo systemctl start postgresqlCreate a database user for Odoo:
sudo -u postgres createuser --createdb --username postgres --no-createrole --no-superuser --pwprompt odooConfigure PostgreSQL to accept connections from the Odoo user by editing /var/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.conf:
local all odoo md5Restart PostgreSQL to apply configuration changes:
sudo systemctl restart postgresqlOdoo User and Directory Setup
Create the necessary directory structure:
sudo mkdir /opt/odoo
sudo chown odoo:odoo /opt/odooSwitch to the odoo user account:
sudo su - odooSource Code Installation
Clone the official Odoo repository from GitHub:
cd /opt/odoo
git clone https://www.github.com/odoo/odoo --depth 1 --branch 16.0 --single-branch .Create a Python virtual environment:
python3 -m venv odoo-venv
source odoo-venv/bin/activateInstall Python dependencies:
pip3 install wheel
pip3 install -r requirements.txtInstall wkhtmltopdf for PDF report generation:
sudo zypper install wkhtmltopdfConfiguration File Setup
Create the Odoo configuration file:
sudo mkdir /etc/odoo
sudo nano /etc/odoo/odoo.confAdd the following basic configuration:
[options]
admin_passwd = admin
db_host = False
db_port = False
db_user = odoo
db_password = your_password
addons_path = /opt/odoo/addons
logfile = /var/log/odoo/odoo.log
log_level = infoCreate the log directory:
sudo mkdir /var/log/odoo
sudo chown odoo:odoo /var/log/odooMethod 3: Docker Installation (Recommended)
Docker installation offers the most reliable and portable deployment method, eliminating dependency conflicts and simplifying maintenance.
Why Docker is Recommended
Docker containers provide isolated environments that eliminate compatibility issues between different system configurations. The official Odoo Docker images include all necessary dependencies, reducing installation complexity. Container isolation enhances security by preventing interference between Odoo and other system services.
Docker Setup Process
Install Docker on openSUSE:
sudo zypper install docker docker-compose
sudo systemctl enable docker
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo usermod -aG docker $USERLog out and log back in to apply group membership changes.
Pull the official Odoo and PostgreSQL images:
docker pull odoo:16.0
docker pull postgres:13Docker Compose Configuration
Create a docker-compose.yml file for multi-container orchestration:
version: '3.1'
services:
web:
image: odoo:16.0
depends_on:
- db
ports:
- "8069:8069"
environment:
- HOST=db
- USER=odoo
- PASSWORD=myodoo
volumes:
- odoo-web-data:/var/lib/odoo
- ./config:/etc/odoo
- ./addons:/mnt/extra-addons
restart: always
db:
image: postgres:13
environment:
- POSTGRES_DB=postgres
- POSTGRES_USER=odoo
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=myodoo
- PGDATA=/var/lib/postgresql/data/pgdata
volumes:
- odoo-db-data:/var/lib/postgresql/data/pgdata
restart: always
volumes:
odoo-web-data:
odoo-db-data:Container Management
Start the containers using docker-compose:
docker-compose up -dMonitor container logs:
docker-compose logs -f webStop the containers when needed:
docker-compose downPost-Installation Configuration
After successful installation, several configuration steps ensure optimal Odoo operation.
Service Management
For source installations, create a systemd service file:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/odoo.serviceAdd the service configuration:
[Unit]
Description=Odoo
Requires=postgresql.service
After=network.target postgresql.service
[Service]
Type=simple
SyslogIdentifier=odoo
PermissionsStartOnly=true
User=odoo
Group=odoo
ExecStart=/opt/odoo/odoo-venv/bin/python3 /opt/odoo/odoo-bin -c /etc/odoo/odoo.conf
StandardOutput=journal+console
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetEnable and start the service:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable odoo
sudo systemctl start odooWeb Interface Access
Access Odoo through your web browser at http://your-server-ip:8069. The initial setup wizard will guide you through database creation and administrator account configuration.
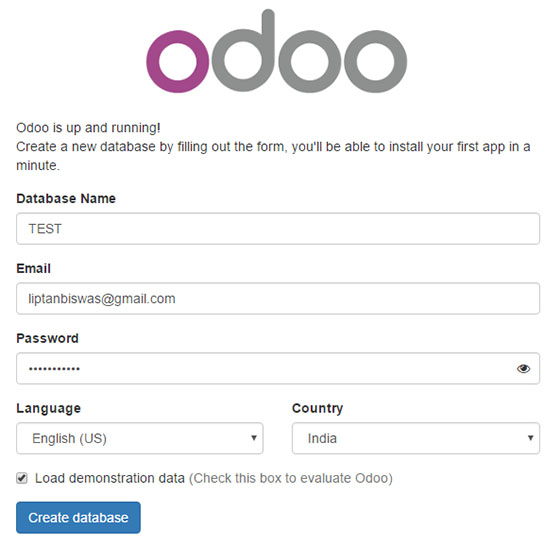
Configure your firewall to allow external access if needed:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadDatabase Configuration
Set a strong master password during the initial setup wizard. This password protects database management operations. Create your first database with appropriate settings for your locale and business requirements.
Configure automatic backups using PostgreSQL’s built-in tools:
sudo -u postgres pg_dump odoo_database > /backup/odoo_backup_$(date +%Y%m%d).sqlSecurity Hardening
Implement SSL/TLS encryption for production environments by configuring a reverse proxy with Apache or Nginx. Update the Odoo configuration to bind only to localhost when using a reverse proxy:
xmlrpc_interface = 127.0.0.1
netrpc_interface = 127.0.0.1Set appropriate file permissions:
sudo chmod 640 /etc/odoo/odoo.conf
sudo chown root:odoo /etc/odoo/odoo.confAddon and Module Management
Odoo’s modular architecture allows extensive customization through additional modules and custom addons.
Addon Path Configuration
Configure custom addon directories in the Odoo configuration file:
addons_path = /opt/odoo/addons,/opt/odoo/custom-addonsCreate the custom addons directory:
sudo mkdir /opt/odoo/custom-addons
sudo chown odoo:odoo /opt/odoo/custom-addonsModule Installation and Updates
Install modules through the web interface by navigating to Apps and clicking “Install” on desired modules. For command-line installation, use:
/opt/odoo/odoo-bin -c /etc/odoo/odoo.conf -i module_name -d database_name --stop-after-initUpdate existing modules:
/opt/odoo/odoo-bin -c /etc/odoo/odoo.conf -u module_name -d database_name --stop-after-initDevelopment Environment Setup
Enable developer mode for module development:
dev_mode = reload,qweb,werkzeug,xmlConfigure logging for development:
log_level = debug
log_handler = :DEBUGTroubleshooting Common Issues
Understanding common installation and runtime issues helps maintain a stable Odoo deployment.
Installation Problems
Dependency resolution failures often occur due to missing packages in openSUSE repositories. Install missing dependencies manually using pip or alternative package sources. Package conflicts may require removing conflicting packages before proceeding with installation.
Permission issues can prevent proper installation or operation. Ensure the odoo user has appropriate permissions:
sudo chown -R odoo:odoo /opt/odoo
sudo chmod -R 755 /opt/odooRuntime Issues
Service startup failures commonly result from configuration errors or dependency issues. Check service logs for detailed error messages:
sudo journalctl -u odoo -fDatabase connection problems may indicate PostgreSQL configuration issues or incorrect credentials. Verify database connectivity:
sudo -u odoo psql -h localhost -U odoo -d postgresPort binding conflicts occur when multiple services attempt to use port 8069. Check for conflicting processes:
sudo netstat -tlnp | grep 8069Performance Optimization
Configure appropriate worker processes based on your server’s CPU cores:
workers = 4
max_cron_threads = 2Optimize PostgreSQL for Odoo workloads by adjusting memory settings in /var/lib/pgsql/data/postgresql.conf:
shared_buffers = 256MB
effective_cache_size = 1GB
work_mem = 4MBMaintenance and Updates
Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance and security for your Odoo installation.
Regular Maintenance Tasks
Update system packages regularly:
sudo zypper refresh && sudo zypper updateFor source installations, update Odoo by pulling the latest changes:
cd /opt/odoo
git pull origin 16.0
pip3 install -r requirements.txt --upgradePerform database maintenance operations:
sudo -u postgres vacuumdb --all --analyze --verboseBackup and Recovery
Implement automated backup procedures for both database and file system components:
#!/bin/bash
BACKUP_DIR="/backup/odoo"
DATE=$(date +%Y%m%d_%H%M%S)
# Database backup
sudo -u postgres pg_dump odoo_production > $BACKUP_DIR/db_backup_$DATE.sql
# File system backup
tar -czf $BACKUP_DIR/filestore_backup_$DATE.tar.gz /opt/odoo/data/filestoreSchedule backups using cron:
0 2 * * * /usr/local/bin/odoo_backup.shDisaster Recovery Planning
Document your installation configuration and maintain copies of configuration files. Test backup restoration procedures regularly to ensure data integrity. Consider implementing high-availability configurations for critical business operations.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Odoo. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Odoo open-source ERP and CRM on Manjaro Linux system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Odoo website.