
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install OpenFire on Debian 11. For those of you who didn’t know, OpenFire is a cross-platform, real-time chat server that is based on the XMPP protocol. It uses the only widely adopted open protocol for instant messaging, XMPP Openfire is incredibly easy to set up and administer but offers rock-solid security and performance.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the OpenFire on a Debian 11 (Bullseye).
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Debian 10 or Debian 11.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install OpenFire on Debian 11 Bullseye
Step 1. Before we install any software, it’s important to make sure your system is up to date by running the following apt commands in the terminal:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
Step 2. Installing OpenFire on Debian 11.
By default, OpenFire is not available on Debian 11 base repository. So, now run the following command below to download the OpenFire installer from the official page:
wget https://www.igniterealtime.org/downloadServlet?filename=openfire/openfire_4.7.1_all.deb
Then, run the following command below to install it:
sudo apt -f install ./openfire.deb
Once the installation is complete, now enable OpenFire (to start automatically upon system boot), and verify the status using the commands below:
sudo systemctl start openfire sudo systemctl enable openfire sudo systemctl status openfire
Step 3. Configure Firewall.
Debian comes with UFW enabled by default, and it will block other connections from other computers that are trying to access our OpenFire service. We must open the appropriate ports so that the OpenFire resources can be accessed from other machines:
sudo ufw allow 9090 sudo ufw allow 9091 sudo ufw allow 5222 sudo ufw allow 7777
Step 5. Accessing OpenFire Web Panel.
Once successfully installed, now open your web browser and access the Openfire web interface using the URL http://your-ip-addres:9090. You should see the following screen:
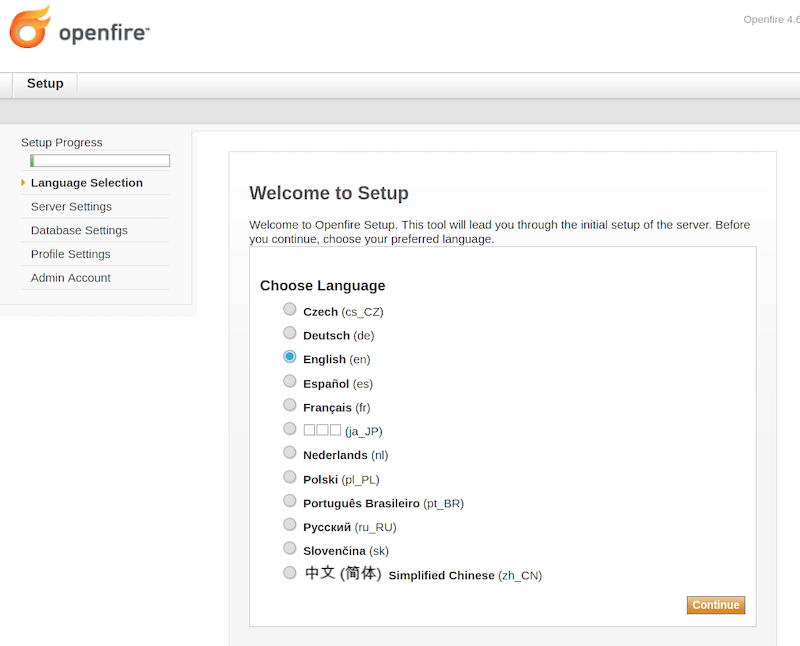
Congratulations! You have successfully installed OpenFire. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the latest version of the OpenFire on Debian 11 Bullseye. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official OpenFire website.