
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install OwnCloud on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS. For those of you who didn’t know, OwnCloud is free and open-source software that enables you to create a private “file-hosting” cloud. OwnCloud is similar to DropBox service with the difference of being free to download and install on your private server. Owncloud is made by PHP and backend database MySQL (MariaDB), SQLLite, or PostgreSQL. OwnCloud also enables you to easily view and sync address books, calendar events, tasks, and bookmarks. You can access it via the good-looking and easy-to-use web interface or install the OwnCloud client on your Desktop or Laptop machine (which supports Linux, Windows, and macOS).
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation OwnCloud on a Ubuntu 18.04 (Bionic Beaver) server.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Ubuntu 18.04 (Bionic Beaver).
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install OwnCloud on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS Bionic Beaver
Step 1. First, make sure that all your system packages are up-to-date by running the following apt-get commands in the terminal.
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade
Step 2. Install LAMP (Linux, Apache, MariaDB, and PHP) server.
A Ubuntu 18.04 LAMP server is required. If you do not have LAMP installed, you can follow our guide here. Also, install all required PHP modules:
apt-get install php7.1-cli php7.1-gd php7.1-opcache php7.1-mysql php7.1-json php7.1-mcrypt php7.1-xml php7.1-curl
Step 3. Installing OwnCloud 10 on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS.
The first thing to do is to go to OwnCloud’s download page and download the latest stable version of OwnCloud, At the moment of writing this article it is version 10:
wget https://download.owncloud.org/community/owncloud-10.0.9.zip unzip owncloud-10.0.9.zip sudo mv owncloud /var/www/html/owncloud/
We will need to change some folders permissions:
chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/owncloud/ chmod -R 755 /var/www/html/owncloud/
Step 4. Configuring MariaDB for OwnCloud.
By default, MariaDB is not hardened. You can secure MariaDB using the mysql_secure_installation script. you should read and below each step carefully which will set a root password, remove anonymous users, disallow remote root login, and remove the test database and access to secure MariaDB:
mysql_secure_installation
Configure it like this:
- Set root password? [Y/n] y - Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y - Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y - Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y - Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
Next, we will need to log in to the MariaDB console and create a database for the OwnCloud. Run the following command:
mysql -u root -p
This will prompt you for a password, so enter your MariaDB root password and hit Enter. Once you are logged in to your database server you need to create a database for OwnCloud installation:
CREATE DATABASE ownclouddb; CREATE USER 'ownclouduser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'YOURPASSWORD'; GRANT ALL ON ownclouddb.* TO 'ownclouduser'@'localhost'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES; exit
Step 5. Configuring Apache web server for OwnCloud.
Create a new virtual host directive in Apache. For example, create a new Apache configuration file named ‘owncloud.conf’ on your virtual server:
touch /etc/apache2/sites-available/owncloud.conf ln -s /etc/apache2/sites-available/owncloud.conf /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/owncloud.conf nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/owncloud.conf
Add the following lines:
<VirtualHost *:80> ServerAdmin admin@yourdomain.com DocumentRoot /var/www/html/owncloud/ ServerName your-domain.com ServerAlias www.your-domain.com <Directory /var/www/html/owncloud/> Options FollowSymLinks AllowOverride All Order allow,deny allow from all </Directory> ErrorLog /var/log/apache2/your-domain.com-error_log CustomLog /var/log/apache2/your-domain.com-access_log common </VirtualHost>
Now, we can restart the Apache webserver so that the changes take place:
a2ensite owncloud.conf a2enmod rewrite a2enmod headers a2enmod env a2enmod dir a2enmod mime systemctl restart apache2.service
Step 6. Accessing the OwnCloud Configuration.
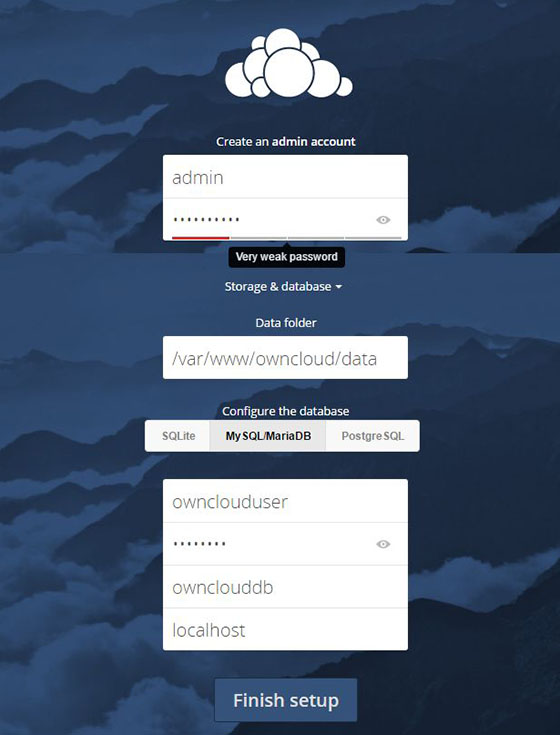
To configure our ownCloud, we will use the web interface. So, go ahead and open up a web browser and point it to http://your-domain.com. You should see a web page like this. Enter username and password for the administrator user account, click on the ‘Advanced options’ hyperlink and enter the data directory (or leave the default setting), then enter database username, database password, database name, host (localhost), and click ‘Finish setup’.
Alternately you can also download the ownCloud clients to sync the documents across your devices.
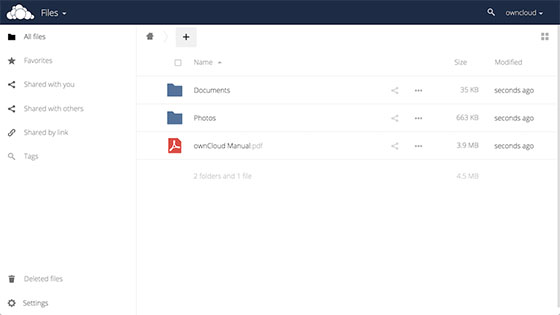
The home page will look like the below; you can start uploading the contents using “+ sign” button.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed OwnCloud. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing OwnCloud on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS (Bionic Beaver) system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official OwnCloud website.