
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install phpMyAdmin with Nginx on Debian 11. For those of you who didn’t know, phpMyAdmin is a free, open-source, and web-based application used for managing MySQL databases, user accounts, and privileges, executing SQL statements, importing and exporting data in a variety of data formats, and much more from the web interface.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of phpMyAdmin on a Debian 11 (Bullseye).
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Debian 11 (Bullseye).
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install phpMyAdmin with Nginx on Debian 11 Bullseye
Step 1. Before we install any software, it’s important to make sure your system is up to date by running the following apt commands in the terminal:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
Step 2. Installing LEMP Stack.
If you don’t have a LEMP (Linux + Nginx+ MySQL/MariDB+ PHP) already installed on your server, you can follow our guide here.
Step 3. Configure MySQL.
Now we create a new superuser account just for phpMyAdmin:
sudo mysql -u root -p
This will prompt you for a password, so enter your MariaDB root password and hit Enter. Once you are logged in to your database server you need to create a database for phpMyAdmin installation:
MariaDB> CREATE DATABASE app_db; MariaDB> CREATE USER 'app_user'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'your-strong-password'; MariaDB> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON app_db.* TO 'app_user'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION; MariaDB> FLUSH PRIVILEGES; MariaDB> EXIT;
Step 4. Installing phpMyAdmin on Debian 11.
By default, phpMyAdmin is not available on Debian 11 Bullseye repository, so you’ll need to manually download the phpMyAdmin from the official page:
wget https://files.phpmyadmin.net/phpMyAdmin/5.1.1/phpMyAdmin-5.1.1-all-languages.tar.gz
Next, extract the phpMyAdmin archive to your web server root directory:
tar xvf phpMyAdmin-5.1.1-all-languages.tar.gz sudo mv phpMyAdmin-5.1.1-all-languages /usr/share/phpMyAdmin
Step 5. Configure phpMyAdmin.
Now we copy the sample phpMyAdmin configuration file and rename it as follows:
sudo cp -pr /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/config.sample.inc.php /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/config.inc.php
Next, edit the configuration file:
sudo nano /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/config.inc.php
Generate a blowfish secret and update the secret in the configuration file:
$cfg['blowfish_secret'] = 'eDjtEzAk8N3Rk}AFY.vBW}UtYL7VPbGo'; /* YOU MUST FILL IN THIS FOR COOKIE AUTH! */
Also, uncomment the phpMyAdmin storage settings:
/** * phpMyAdmin configuration storage settings. */ /* User used to manipulate with storage */ $cfg['Servers'][$i]['controlhost'] = 'localhost'; // $cfg['Servers'][$i]['controlport'] = ''; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['controluser'] = 'pma'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['controlpass'] = 'pmapass'; /* Storage database and tables */ $cfg['Servers'][$i]['pmadb'] = 'phpmyadmin'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['bookmarktable'] = 'pma__bookmark'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['relation'] = 'pma__relation'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['table_info'] = 'pma__table_info'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['table_coords'] = 'pma__table_coords'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['pdf_pages'] = 'pma__pdf_pages'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['column_info'] = 'pma__column_info'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['history'] = 'pma__history'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['table_uiprefs'] = 'pma__table_uiprefs'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['tracking'] = 'pma__tracking'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['userconfig'] = 'pma__userconfig'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['recent'] = 'pma__recent'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['favorite'] = 'pma__favorite'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['users'] = 'pma__users'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['usergroups'] = 'pma__usergroups'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['navigationhiding'] = 'pma__navigationhiding'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['savedsearches'] = 'pma__savedsearches'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['central_columns'] = 'pma__central_columns'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['designer_settings'] = 'pma__designer_settings'; $cfg['Servers'][$i]['export_templates'] = 'pma__export_templates';
Step 6. Configure Database and User for phpMyAdmin.
Now we create the configuration storage database and tables by running the following command below:
sudo mysql < /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/sql/create_tables.sql -u root -p
Next, connect to the MariaDB shell with the following command:
sudo mysql -u root -p
Once you are connected, grant all necessary privileges to the phpMyAdmin database:
CREATE USER 'pma'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'pmapass'; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON phpmyadmin.* TO 'pma'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION; FLUSH PRIVILEGES; EXIT;
Step 7. Configure Nginx for phpMyAdmin.
Now we create an Nginx virtual host configuration file for phpMyAdmin:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/phpMyAdmin.conf
Add the following file:
server {
listen 80;
server_name pma.your-domain.com;
root /usr/share/phpMyAdmin;
location / {
index index.php;
}
## Images and static content is treated different
location ~* ^.+.(jpg|jpeg|gif|css|png|js|ico|xml)$ {
access_log off;
expires 30d;
}
location ~ /\.ht {
deny all;
}
location ~ /(libraries|setup/frames|setup/libs) {
deny all;
return 404;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
include /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /usr/share/phpMyAdmin$fastcgi_script_name;
}
}
Save and close, then create a tmp directory for phpMyAdmin and then change the permission:
sudo mkdir /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/tmp sudo chmod 777 /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/tmp
Next, set proper ownership to the phpMyAdmin directory:
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /usr/share/phpMyAdmin
Finally, restart Nginx and PHP-fpm services:
sudo systemctl restart nginx sudo systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
Step 8. Accessing phpMyAdmin Web Interface.
Once successfully installed, open your browser and surf to http://your-domain.com/ and your phpMyAdmin will ask you for the user and password of your MySQL installation, you can use root as the user and the root MySQL password.
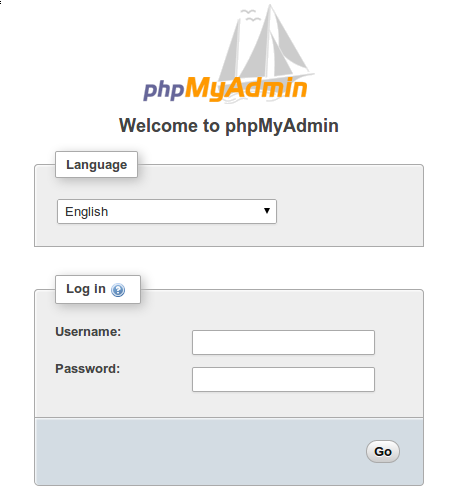
Congratulations! You have successfully installed phpMyAdmin. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the latest version of phpMyAdmin with Nginx on Debian 11 Bullseye. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official phpMyAdmin website.