How To Install PowerShell on Linux Mint 22

PowerShell, once exclusive to Windows environments, has evolved into a powerful cross-platform tool that Linux users can leverage for automation, system administration, and scripting tasks. Linux Mint 22, codenamed “Wilma,” offers a stable foundation for running PowerShell. This comprehensive guide walks you through various methods to install PowerShell on Linux Mint 22, troubleshoot common issues, and get started with basic PowerShell commands.
Understanding PowerShell on Linux
PowerShell has transformed from a Windows-only scripting language to an open-source, cross-platform automation tool. This evolution began when Microsoft released PowerShell Core (now simply called PowerShell) as an open-source project in 2016, making it available for Linux distributions including Linux Mint.
What is PowerShell?
PowerShell is a task automation and configuration management framework that consists of a command-line shell and scripting language. It’s built on the .NET framework and designed to help system administrators automate repetitive tasks. Unlike traditional Unix shells that work with text streams, PowerShell processes objects, giving it unique capabilities for complex data manipulation.
PowerShell Core vs Windows PowerShell
Windows PowerShell (5.1) remains Windows-exclusive and tied to the full .NET Framework. In contrast, PowerShell (version 7.x) runs on .NET Core, enabling cross-platform compatibility across Windows, macOS, and Linux distributions including Linux Mint 22. While core cmdlets remain similar, some Windows-specific modules aren’t available on Linux versions.
Benefits for Linux Mint Users
Installing PowerShell on Linux Mint 22 offers several advantages:
- Unified scripting environment across mixed Windows/Linux environments
- Powerful object-oriented approach to system administration
- Access to .NET libraries and frameworks
- Simplified management for Microsoft cloud services
- Consistent automation tools regardless of platform
Use Cases for PowerShell on Linux
Common scenarios where PowerShell excels on Linux Mint include:
- Managing multi-platform infrastructure
- Working with Azure and Microsoft 365 services
- Automating complex system tasks
- Creating cross-platform scripts for heterogeneous environments
- Processing structured data from various sources
Prerequisites for Installing PowerShell
Before installing PowerShell on Linux Mint 22, ensure your system meets the necessary requirements and prepare your environment for a smooth installation process.
System Requirements
Linux Mint 22 “Wilma” is based on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS and comes with long-term support until 2029. For optimal PowerShell performance, your system should have:
- At least 2GB RAM (4GB recommended)
- 1GHz processor or faster
- 100MB available disk space
- Internet connection for downloading packages
Required Dependencies
PowerShell on Linux depends on specific libraries. Most dependencies will be automatically installed, but you may need to manually install:
libssl(SSL support)libicu(Unicode and globalization support)libc6(C library)
Updating Linux Mint
Always start with an updated system. Open Terminal and run:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade -yThis ensures all system packages are current before installing PowerShell.
Checking for Conflicts
If you’ve previously installed older versions of PowerShell or have conflicting packages, clean them up:
# Check for existing PowerShell installations
which pwsh
# If found, consider removing old versions before proceedingMethod 1: Installing PowerShell Using Snap Packages
Snap is a package management system that provides a streamlined way to install applications across Linux distributions. This method offers the simplest installation process for PowerShell on Linux Mint 22.
Enabling Snap Support
Linux Mint doesn’t come with Snap pre-installed, so you’ll need to set it up first:
# Install Snap package manager
sudo apt install snapd -y
# Install core snap packages
sudo snap install core
# Ensure snap is properly initialized
sudo ln -s /var/lib/snapd/snap /snapAfter installing Snap, restart your system to ensure all snap services are properly initialized.
Installation Process
Once Snap is configured, installing PowerShell is straightforward:
# Install PowerShell from the stable channel
sudo snap install powershell --classicThe --classic flag is necessary because PowerShell requires system permissions that aren’t available in strict confinement mode.
Verification Steps
After installation completes, verify PowerShell works correctly:
# Launch PowerShell
pwsh
# Check the version
$PSVersionTableYou should see version information displayed, confirming successful installation.
PowerShell Channels
Snap offers different PowerShell channels:
- Stable:
sudo snap install powershell --classic - Preview:
sudo snap install powershell-preview --classic - Daily:
sudo snap install powershell-preview --edge --classic
Choose the stable channel for production use and preview/daily for testing new features.
Method 2: Installing PowerShell via Microsoft Repository
Installing PowerShell using Microsoft’s official repository gives you more control over the installation and ensures you receive official updates.
Adding Microsoft GPG Key
First, import Microsoft’s GPG key to verify package authenticity:
# Download the Microsoft GPG key
curl -sSL https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/microsoft-archive-keyring.gpg
# Create a new repository configuration file
echo "deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/microsoft-archive-keyring.gpg] https://packages.microsoft.com/repos/microsoft-debian-bookworm-prod bookworm main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/microsoft.listLinux Mint 22 is based on Ubuntu 24.04, which aligns with Debian’s package management system. The configuration above uses the Debian Bookworm repository, which is compatible with Linux Mint 22.
Configuring Repository
Update your package lists to include the new repository:
sudo apt updateIf you encounter errors, you may need to adjust the repository configuration to match the exact packages available for your system.
Handling Dependencies
PowerShell requires specific versions of libicu. Linux Mint 22 comes with libicu72, but PowerShell packages might require different versions. Resolve dependency issues with:
# Check installed libicu version
dpkg -l | grep libicu
# Install compatible libicu if needed
sudo apt install libicu72 -yInstallation Commands
Install PowerShell using apt:
# Install PowerShell
sudo apt install -y powershellIf you face dependency issues, try:
sudo apt --fix-broken installVerification Process
Verify the installation by launching PowerShell and checking its version:
# Launch PowerShell
pwsh
# Check version information
$PSVersionTableThe output should show PowerShell version 7.x running on .NET Core.
Troubleshooting Common Repository Issues
Repository signing key issues:
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv-keys 3FA7E0328081BFF6A14DA29AA6A19B38D3D831EFPackage conflicts:
sudo apt --fix-broken installRepository not found:
Verify your /etc/apt/sources.list.d/microsoft.list file contains the correct repository URL.
Method 3: Manual Installation from Binary Archives
For systems with restricted internet access or when you need a specific PowerShell version, manual installation provides the most control.
Downloading Appropriate Package
Download the latest PowerShell package from Microsoft’s GitHub repository:
# Create a directory for the download
mkdir -p ~/powershell-temp
cd ~/powershell-temp
# Download the latest stable release (adjust URL for the latest version)
wget https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShell/releases/download/v7.4.1/powershell-7.4.1-linux-x64.tar.gzExtraction Process
Extract the downloaded archive to your preferred location:
# Create directory for PowerShell
sudo mkdir -p /opt/microsoft/powershell/7
# Extract package
sudo tar -xzf powershell-7.4.1-linux-x64.tar.gz -C /opt/microsoft/powershell/7Setting Up Environment
Create a symbolic link to make PowerShell accessible system-wide:
# Create symbolic link
sudo ln -s /opt/microsoft/powershell/7/pwsh /usr/bin/pwsh
# Set appropriate permissions
sudo chmod +x /opt/microsoft/powershell/7/pwshVerification Steps
Ensure the installation was successful:
# Launch PowerShell
pwsh
# Check version
$PSVersionTableUse Cases
Manual installation is preferable when:
- Working in environments without internet access
- Needing multiple PowerShell versions side-by-side
- Testing specific versions without affecting system packages
- Deploying in custom environments where package managers are unavailable
Troubleshooting PowerShell Installation on Linux Mint 22
Even with careful installation, you might encounter issues specific to Linux Mint 22. Here are solutions for common problems.
Missing Dependencies
The most frequent installation error relates to libicu dependency issues:
# Check libicu versions
apt list --installed | grep libicu
# Install the required version
sudo apt install libicu72 -y
# If needed, create symbolic links for compatibility
sudo ln -s /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libicu72.so.72 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libicu70.so.70Repository Conflicts
When multiple repositories cause conflicts:
# Clean apt cache
sudo apt clean
# Update package lists
sudo apt update --fix-missingPermission Problems
If encountering permission errors:
# Check PowerShell executable permissions
ls -la /usr/bin/pwsh
# Set appropriate permissions if needed
sudo chmod +x /usr/bin/pwshPost-Installation Errors
If PowerShell launches but produces errors:
# Launch with verbose logging
pwsh -v
# Check for module path issues
echo $env:PSModulePathVersion Compatibility
PowerShell modules may have version compatibility issues. Check version requirements with:
Get-Module -ListAvailable | Select-Object Name, Version, PathBasic PowerShell Usage on Linux Mint
After successful installation, familiarize yourself with PowerShell basics on Linux Mint 22.
Starting PowerShell
Launch PowerShell using any of these methods:
- Terminal command:
pwsh - Application menu: Search for “PowerShell”
- Direct path execution:
/usr/bin/pwsh
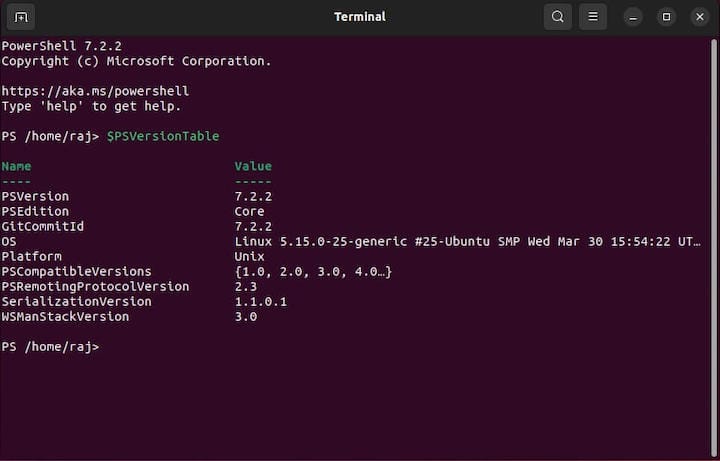
Essential Commands
PowerShell cmdlets follow a verb-noun naming convention. Essential commands include:
# Get system information
Get-ComputerInfo
# List files and directories (PowerShell equivalent of ls)
Get-ChildItem
# Find processes
Get-Process
# View environment variables
Get-ChildItem Env:
# Get help for commands
Get-Help Get-ProcessCross-Platform Scripting
Write scripts that work across platforms by avoiding OS-specific commands:
# Check operating system
if ($IsLinux) {
Write-Output "Running on Linux"
} elseif ($IsWindows) {
Write-Output "Running on Windows"
}
# Use path operations that work cross-platform
Join-Path -Path $HOME -ChildPath "Documents"Profile Configuration
Customize your PowerShell environment by creating a profile:
# Check if profile exists
Test-Path $PROFILE
# Create profile if it doesn't exist
if (!(Test-Path $PROFILE)) {
New-Item -Path $PROFILE -Type File -Force
}
# Edit profile
nano $PROFILEAdd your preferred settings to the profile file, such as:
# Set alias
Set-Alias -Name ll -Value Get-ChildItem
# Custom prompt
function prompt {
"PS $($executionContext.SessionState.Path.CurrentLocation) > "
}Updating and Managing PowerShell
Keep your PowerShell installation current with these methods.
Update Methods
For Snap installations:
sudo snap refresh powershellFor APT installations:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade powershellFor manual installations:
Download the new package and repeat the manual installation process.
Version Management
Run multiple PowerShell versions by installing to different directories:
# Install a specific version to a custom location
sudo mkdir -p /opt/microsoft/powershell/7.3.0
sudo tar -xzf powershell-7.3.0-linux-x64.tar.gz -C /opt/microsoft/powershell/7.3.0
# Create symbolic link with version suffix
sudo ln -s /opt/microsoft/powershell/7.3.0/pwsh /usr/bin/pwsh-7.3.0Configuration Management
PowerShell stores configuration in these locations:
- User modules:
~/.local/share/powershell/Modules - System modules:
/usr/local/share/powershell/Modules - User profiles:
~/.config/powershell/
Back up these directories before major updates to preserve your settings.
Uninstalling PowerShell
If you need to remove PowerShell, follow the appropriate method based on your installation.
Snap Removal Method
Uninstall PowerShell installed via Snap with:
sudo snap remove powershellAPT Removal Process
Remove PowerShell installed through the Microsoft repository:
sudo apt remove powershell -yTo completely remove the repository:
sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/microsoft.list
sudo apt updateManual Uninstallation
If you installed manually:
# Remove symbolic link
sudo rm /usr/bin/pwsh
# Remove installation directory
sudo rm -rf /opt/microsoft/powershellVerification
Confirm PowerShell is completely removed:
which pwsh
pwsh --versionBoth commands should return nothing or “command not found” if removal was successful.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed PowerShell. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the latest version of PowerShell on the Linux Mint 22 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official PowerShell website.