
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Prometheus on Debian 11. For those of you who didn’t know, Prometheus is an open-source monitoring system with a dimensional data model, flexible query language, efficient time-series database, and a modern alerting approach.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you through the step-by-step installation of the Prometheus monitoring system on a Debian 11 (Bullseye).
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Debian 11 (Bullseye).
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Prometheus on Debian 11 Bullseye
Step 1. Before we install any software, it’s important to make sure your system is up to date by running the following apt commands in the terminal:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
Step 2. Create Prometheus Users.
We’ll create a dedicated Prometheus system user and group:
sudo groupadd --system prometheus sudo useradd -s /sbin/nologin --system -g prometheus prometheus
Step 3. Installing Prometheus on Debian 11.
Now we download Prometheus packages installer from the official page:
mkdir -p /tmp/prometheus && cd /tmp/prometheus curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/prometheus/prometheus/releases/latest|grep browser_download_url|grep linux-amd64|cut -d '"' -f 4|wget -qi -
Then, extract the Prometheus packages file:
tar xvf prometheus*.tar.gz
After file extraction, then we will move the files to the right directory:
sudo mv prometheus.yml /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml sudo mv consoles/ console_libraries/ /etc/prometheus/
Step 4. Configuration Prometheus.
By default, the Prometheus configuration file will be located on /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml. The default configuration file looks similar to below:
cat /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
Output:
# my global config
global:
scrape_interval: 15s # Set the scrape interval to every 15 seconds. Default is every 1 minute.
evaluation_interval: 15s # Evaluate rules every 15 seconds. The default is every 1 minute.
# scrape_timeout is set to the global default (10s).
# Alertmanager configuration
alerting:
alertmanagers:
- static_configs:
- targets:
# - alertmanager:9093
# Load rules once and periodically evaluate them according to the global 'evaluation_interval'.
rule_files:
# - "first_rules.yml"
# - "second_rules.yml"
# A scrape configuration containing exactly one endpoint to scrape:
# Here it's Prometheus itself.
scrape_configs:
# The job name is added as a label `job=` to any timeseries scraped from this config.
- job_name: "prometheus"
# metrics_path defaults to '/metrics'
# scheme defaults to 'http'.
static_configs:
- targets: ["localhost:9090"]
Step 5. Creating Prometheus Systemd Service
Now we create a Prometheus systemd service file using the following command below:
nano /etc/systemd/system/prometheus.service
Add the following file:
[Unit] Description=Prometheus Documentation=https://prometheus.io/docs/introduction/overview/ Wants=network-online.target After=network-online.target [Service] Type=simple User=prometheus Group=prometheus ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/prometheus \ --config.file=/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml \ --storage.tsdb.path=/var/lib/prometheus \ --web.console.templates=/etc/prometheus/consoles \ --web.console.libraries=/etc/prometheus/console_libraries \ --web.listen-address=0.0.0.0:9090 \ --web.external-url= SyslogIdentifier=prometheus Restart=always [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save and close the file, then we will change its permission:
for i in rules rules.d files_sd; do sudo chown -R prometheus:prometheus /etc/prometheus/${i}; done
for i in rules rules.d files_sd; do sudo chmod -R 775 /etc/prometheus/${i}; done
sudo chown -R prometheus:prometheus /var/lib/prometheus/
Next, reload systemd daemon and start the service:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl start prometheus sudo systemctl enable prometheus
Step 6. Accessing Prometheus Web Interface.
Once successfully installed, open your favorite browser and navigate to http://your-domain.com:9090 or http://your-ip-address:9090 and complete the required steps to finish the installation.
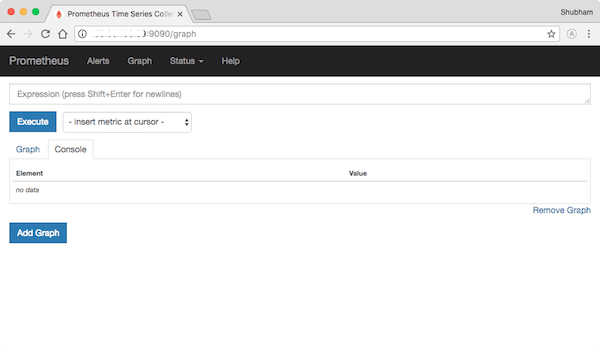
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Prometheus. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the latest version of Prometheus on Debian 11 Bullseye. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Prometheus website.