How To Install Rancher on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS

In the realm of modern IT infrastructure, containerization has become a cornerstone for deploying and managing applications. Rancher, a leading open-source container management platform, simplifies the complexities of Kubernetes, making it accessible to organizations of all sizes. Ubuntu 24.04 LTS, with its stability, security, and long-term support, provides an excellent foundation for hosting Rancher. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of installing Rancher on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS, ensuring a smooth and efficient setup.
This tutorial is designed for system administrators, DevOps engineers, and anyone looking to streamline their container management using Rancher on Ubuntu. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or new to container orchestration, this guide offers detailed, step-by-step instructions to get Rancher up and running. By the end of this article, you’ll have a fully functional Rancher instance, ready to manage your containerized applications. This process involves several key steps, including preparing your system, installing necessary components like Docker, and configuring Rancher for optimal performance and security. Let’s dive in!
Prerequisites and System Requirements
Before we begin, it’s crucial to ensure that your system meets the necessary prerequisites. Proper planning and adherence to these requirements will prevent potential issues during the installation process.
- Hardware Requirements: The following are the minimum hardware specifications recommended for running Rancher:
- Minimum RAM: 2GB. While 2GB is the absolute minimum, 4GB or more is highly recommended for better performance, especially when managing multiple clusters.
- Storage Space: 25GB. This provides enough space for the Rancher installation, container images, and logs. Consider allocating more space if you plan to manage a large number of containers.
- Processor Recommendations: A dual-core processor is sufficient for basic setups. However, for production environments, a quad-core or higher processor will provide better performance and stability.
- Software Prerequisites: Ensure that your system has the following software components installed and configured:
- Clean Ubuntu 24.04 LTS Installation: Start with a fresh installation of Ubuntu 24.04 LTS to avoid conflicts with existing software.
- Internet Connectivity: Rancher requires internet access to download necessary packages and updates.
- Administrative Privileges: You need sudo or root access to install software and configure system settings.
System Preparation
Preparing your Ubuntu system is a critical step in ensuring a successful Rancher installation. This involves updating system packages, configuring network settings, and setting up a proper hostname. By performing these tasks, you’ll create a stable and secure environment for Rancher to operate.
- Updating the System Packages:Start by updating the package list and upgrading existing packages to their latest versions. This ensures that you have the latest security patches and bug fixes.
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade -y - Configuring Network Settings:Ensure that your server has a static IP address. This prevents the IP address from changing, which can cause connectivity issues. Edit the network configuration file to set a static IP.
sudo nano /etc/netplan/01-network-config.yamlAdd the following configuration, adjusting the IP address, gateway, and DNS servers to match your network settings:
network: version: 2 renderer: networkd ethernets: ens33: dhcp4: no addresses: [192.168.1.100/24] gateway4: 192.168.1.1 nameservers: addresses: [8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4]Apply the network configuration:
sudo netplan apply - Setting up Proper Hostname:Set a fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for your server. This is important for Rancher to function correctly.
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname rancher.example.comEdit the
/etc/hostsfile to include the FQDN:sudo nano /etc/hostsAdd the following line, replacing
192.168.1.100with your server’s IP address:192.168.1.100 rancher.example.com rancher - Firewall Configuration:Ubuntu uses UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) by default. Enable the firewall and allow traffic on ports 80 and 443, which are used by Rancher.
sudo ufw enable sudo ufw allow 80 sudo ufw allow 443 sudo ufw status
Installing Essential Components
Rancher relies on several key components to function correctly. These include Docker, Helm, and Kubectl. Docker provides the container runtime, Helm simplifies the deployment of applications, and Kubectl allows you to interact with Kubernetes clusters. Installing and configuring these components is a crucial step in setting up Rancher.
- Docker Installation and Configuration:Docker is a containerization platform that Rancher uses to manage containers. Install Docker using the following steps:Remove old versions of Docker:
sudo apt-get remove docker docker-engine docker.io containerd runcInstall required packages:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install \ ca-certificates \ curl \ gnupgAdd Docker’s official GPG key:
sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpgAdd the Docker repository:
echo \ "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \ $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/nullInstall Docker Engine:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-pluginVerify Docker installation:
sudo docker run hello-worldEnable Docker to start on boot:
sudo systemctl enable docker - Helm Package Manager Setup:Helm is a package manager for Kubernetes, which simplifies the deployment and management of applications. Install Helm using the following steps:Download Helm:
curl -fsSL -o get_helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3 chmod +x get_helm.sh sudo ./get_helm.shVerify Helm installation:
helm version - Kubectl Installation and Setup:Kubectl is a command-line tool that allows you to interact with Kubernetes clusters. Install Kubectl using the following steps:Download Kubectl:
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(kubectl version --client --output='json' | jq -r '.clientVersion.gitVersion')/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl" sudo install -o root -g root -m 0755 kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectlVerify Kubectl installation:
kubectl version --client - Creating Necessary Directories and Permissions:Create directories for Rancher data and set appropriate permissions.
sudo mkdir /opt/rancher sudo chown -R $USER:$USER /opt/rancher
Rancher Installation Process
With the essential components installed, you can now proceed with the Rancher installation. This involves installing Cert-Manager, configuring SSL certificates, setting up the Rancher repository, and deploying Rancher using Helm.
- Installing Cert-Manager:Cert-Manager is a Kubernetes add-on that automates the management and issuance of TLS certificates. Install Cert-Manager using Helm:
helm repo add jetstack https://charts.jetstack.io helm repo update helm install cert-manager jetstack/cert-manager \ --namespace cert-manager \ --create-namespace \ --version v1.14.2 \ --set installCRDs=trueVerify Cert-Manager installation:
kubectl get pods --namespace cert-manager - Configuring SSL Certificates:Rancher requires SSL certificates to secure communication. You can use Let’s Encrypt to obtain free SSL certificates or use your own certificates. For this guide, we’ll use Let’s Encrypt.Install the Let’s Encrypt certificate issuer:
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/cert-manager/cert-manager/releases/download/v1.14.2/cert-manager.yaml - Setting up Rancher Repository:Add the Rancher Helm repository to your system:
helm repo add rancher-latest https://releases.rancher.com/server-charts/latest helm repo update - Deploying Rancher Using Helm:Deploy Rancher using Helm with SSL configured. Replace
rancher.example.comwith your FQDN.helm install rancher rancher-latest/rancher \ --namespace cattle-system \ --create-namespace \ --set hostname=rancher.example.com \ --set ingress.tls.source=letsEncrypt - Namespace Configuration:Ensure that Rancher is deployed in the
cattle-systemnamespace. This is where Rancher components reside.kubectl get pods --namespace cattle-system - Initial Container Deployment:Verify that the Rancher containers are running. This may take a few minutes.
kubectl rollout status deploy/rancher --namespace cattle-system
Post-Installation Configuration
Once Rancher is installed, you need to perform post-installation configuration tasks. These include accessing the Rancher web interface, retrieving the initial password, configuring security settings, and setting up the admin account. These steps are essential to ensure that your Rancher instance is secure and properly configured.
- Accessing the Rancher Web Interface:
Open your web browser and navigate to
https://rancher.example.com. If you are using a self-signed certificate, you may need to accept a security exception.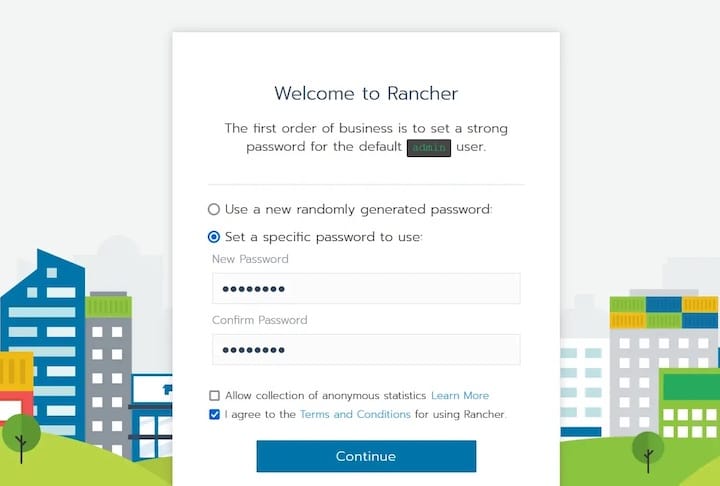
- Initial Password Retrieval:Retrieve the initial password from the Rancher container logs.
kubectl -n cattle-system get secret rancher-admin-secret -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 --decode - Security Configurations:Configure security settings to protect your Rancher instance. This includes setting up authentication and access control policies.
- Setting up Authentication:Configure an authentication method for Rancher. Rancher supports various authentication providers, including local authentication, Active Directory, and OpenID Connect.To set up local authentication:
- Log in to the Rancher web interface using the initial password.
- Navigate to Users & Authentication.
- Create a new user account with a strong password.
- Configuring the Admin Account:Set up an admin account to manage your Rancher instance. This account should have full administrative privileges.
- Log in to the Rancher web interface using the newly created user account.
- Assign the
administratorrole to the user.
Cluster Management Setup
With Rancher installed and configured, you can now start managing your Kubernetes clusters. This involves creating your first cluster, managing nodes, allocating resources, and configuring network settings.
- Creating Your First Cluster:Create a new Kubernetes cluster using the Rancher web interface.
- Log in to the Rancher web interface.
- Click on Clusters.
- Click on Create.
- Select a cluster provider (e.g., Amazon EKS, Google GKE, Azure AKS, or custom).
- Follow the instructions to configure and create the cluster.
- Node Management:Manage the nodes in your cluster. This includes adding, removing, and scaling nodes.
- In the Rancher web interface, navigate to the cluster you created.
- Click on Nodes.
- Add new nodes by following the instructions provided by your cluster provider.
- Resource Allocation:Allocate resources to your cluster. This includes setting CPU and memory limits for containers.
- In the Rancher web interface, navigate to the cluster you created.
- Click on Workloads.
- Configure resource limits for your deployments and pods.
- Network Configuration:Configure network settings for your cluster. This includes setting up network policies and ingress controllers.
- In the Rancher web interface, navigate to the cluster you created.
- Click on Networking.
- Configure network policies and ingress controllers as needed.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with careful planning and execution, issues may arise during or after the Rancher installation. This section provides troubleshooting tips for common problems, such as connection issues, certificate problems, and permission errors.
- Connection Issues:If you encounter connection issues, check the following:
- Verify that your server has internet connectivity.
- Check the firewall settings to ensure that ports 80 and 443 are open.
- Ensure that the DNS settings are correctly configured.
- Confirm that the Rancher containers are running.
- Certificate Problems:If you encounter certificate problems, check the following:
- Verify that the SSL certificates are correctly configured.
- Ensure that the FQDN is correctly set up.
- Check the Cert-Manager logs for any errors.
- Permission Errors:If you encounter permission errors, check the following:
- Verify that the user has the necessary administrative privileges.
- Ensure that the file and directory permissions are correctly set.
- Check the Rancher logs for any permission-related errors.
- Container Startup Issues:If you encounter container startup issues, check the following:
- Verify that Docker is running correctly.
- Check the container logs for any errors.
- Ensure that the container images are available.
Performance Optimization
Optimizing Rancher’s performance is crucial for ensuring a smooth and efficient container management experience. This involves resource management tips, cache configuration, network optimization, and storage management.
- Resource Management Tips:Optimize resource usage to improve Rancher’s performance.
- Set appropriate CPU and memory limits for containers.
- Monitor resource usage and adjust limits as needed.
- Use resource quotas to limit resource consumption by namespaces.
- Cache Configuration:Configure caching to improve Rancher’s response times.
- Enable caching for frequently accessed data.
- Use a caching proxy to cache static assets.
- Network Optimization:Optimize network settings to reduce latency and improve throughput.
- Use a content delivery network (CDN) to distribute content.
- Configure network policies to isolate network traffic.
- Storage Management:Optimize storage settings to improve Rancher’s performance.
- Use fast storage devices (e.g., SSDs) for Rancher data.
- Configure storage classes to dynamically provision storage.
Security Best Practices
Securing your Rancher instance is paramount to protect your containerized applications and data. This involves access control configuration, network security measures, certificate management, and regular updates and maintenance.
- Access Control Configuration:Configure access control policies to restrict access to Rancher resources.
- Use role-based access control (RBAC) to define roles and permissions.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for added security.
- Network Security:Implement network security measures to protect Rancher from network-based attacks.
- Use network policies to isolate network traffic.
- Implement a firewall to restrict access to Rancher.
- Certificate Management:Properly manage SSL certificates to ensure secure communication.
- Use Let’s Encrypt to obtain free SSL certificates.
- Rotate SSL certificates regularly.
- Regular Updates and Maintenance:Keep Rancher up-to-date with the latest security patches and bug fixes.
- Regularly update Rancher to the latest version.
- Monitor Rancher logs for any security-related events.
Advanced Configuration
For advanced users, Rancher offers several advanced configuration options, including load balancer setup, high availability configuration, backup and recovery options, and integration with existing systems.
- Load Balancer Setup:Set up a load balancer to distribute traffic across multiple Rancher instances.
- Use a load balancer such as Nginx or HAProxy.
- Configure the load balancer to forward traffic to Rancher instances.
- High Availability Configuration:Configure Rancher for high availability to ensure continuous operation.
- Deploy multiple Rancher instances behind a load balancer.
- Use a distributed database (e.g., etcd) to store Rancher data.
- Backup and Recovery Options:Implement backup and recovery procedures to protect against data loss.
- Regularly back up Rancher data.
- Test the recovery process to ensure that it works correctly.
- Integration with Existing Systems:Integrate Rancher with existing systems to streamline operations.
- Integrate with CI/CD pipelines to automate deployments.
- Integrate with monitoring systems to monitor Rancher’s performance.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Rancher. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Rancher container management on the Ubuntu 24.04 LTS system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Rancher website.