
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Redmine on AlmaLinux 8. For those of you who didn’t know, Redmine is a cross-platform as well as cross-database flexible project management web application. Redmine includes support for multiple projects, wikis, issue tracking systems, forums, calendars, email notifications, and much more.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you through the step-by-step installation of Redmine open source project management software on an AlmaLinux 8. You can follow the same instructions for CentOS and Rocky Linux.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: AlmaLinux 8.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Redmine on AlmaLinux 8
Step 1. First, let’s start by ensuring your system is up-to-date.
sudo dnf update sudo dnf install epel-release sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled powertools
Step 2. Installing Required Dependencies.
Now run the following command below to install the dependencies to your system:
sudo dnf install ruby ruby-devel rpm-build wget libxml2-devel vim make openssl-devel automake libtool ImageMagick ImageMagick-devel MariaDB-devel gcc httpd-devel libcurl-devel gcc-c++
Step 3. Creating New System User.
Create a new user and group, with a home directory /opt/redmine that will run the Redmine:
useradd -r -m -d /opt/redmine redmine
Step 4. Installing Apache on AlmaLinux 8.
Run the following command to install the Apache webserver:
sudo dnf install httpd httpd-tools
Once installed Apache services on your system, start all required services:
sudo systemctl enable httpd sudo systemctl start httpd sudo systemctl status httpd
Next, since we will be using Apache as our HTTP server, add Apache to the Redmine group:
usermod -aG redmine apache
Step 5. Installing MariaDB on AlmaLinux 8.
MariaDB is a popular database server. The installation is simple and requires just a few steps as shown:
sudo dnf install mariadb-server mariadb
Once the installation is complete, start to enable it to start on system start-up using:
sudo systemctl restart mariadb sudo systemctl status mariadb sudo systemctl enable mariadb
By default, MariaDB is not hardened. You can secure MariaDB using the mysql_secure_installation script. you should read and below each step carefully which will set a root password, remove anonymous users, disallow remote root login, and remove the test database and access to secure MariaDB:
mysql_secure_installation
Configure it like this:
- Set root password? [Y/n] y - Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y - Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y - Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y - Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
To log into MariaDB, use the following command (note that it’s the same command you would use to log into a MariaDB database):
mysql -u root -p
Execute the following commands at MariaDB shell to create a database and user for Redmine software.
MariaDB [(none)]> create database redminedb; MariaDB [(none)]> grant all on redminedb.* to redmineadmin@localhost identified by 'your-strong-password'; MariaDB [(none)]> flush privileges; MariaDB [(none)]> quit
Step 6. Installing Redmine on AlmaLinux 8.
Now we download the latest version of Redmine from the official page:
wget https://www.redmine.org/releases/redmine-4.2.2.tar.gz -P /tmp
After that, extract the Redmine tarball to the Redmine user’s home directory:
sudo -u redmine tar xzf /tmp/redmine-4.2.2.tar.gz -C /opt/redmine/ --strip-components=1
Step 7. Configuring Redmine Database.
First switch to Redmine’s user account:
su - redmine
Rename the sample Redmine configuration:
cp config/configuration.yml{.example,}
Rename the sample dispatch CGI configuration file under the public folder:
cp public/dispatch.fcgi{.example,}
Rename the sample to the database configuration file:
cp config/database.yml{.example,}
Next, open the database configure file:
nano config/database.yml
Add the following file:
... production: adapter: mysql2 database: redminedb host: localhost username: redmineadmin password: "your-strong-password" # Use "utf8" instead of "utfmb4" for MySQL prior to 5.7.7 encoding: utf8mb4 ...
Step 7. Installing Ruby Dependencies.
Switch to Redmine user and install the Ruby dependencies:
su - redmine
Next, install Bundler for managing gem dependencies:
gem install bundler bundle config set --local without 'development test' bundle install
Step 8. Generate Keys and Migrate the Database.
To prevent tempering of the cookies that store session data, you need to generate a random secret key that Rails uses to encode them:
bundle exec rake generate_secret_token RAILS_ENV=production bundle exec rake db:migrate
Once the database migration is done, insert default configuration data into the database:
RAILS_ENV=production REDMINE_LANG=en bundle exec rake redmine:load_default_data
Then, configure FileSystem Permissions:
for i in tmp tmp/pdf public/plugin_assets; do [ -d $i ] || mkdir -p $i; done chown -R redmine:redmine files log tmp public/plugin_assets chmod -R 755 /opt/redmine/
Step 9. Configure Firewall.
Use the following commands to open the necessary port:
sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=3000/tcp --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Step 10. Configure Apache for Redmine.
Switch to Redmine user created above to install the Phusion Passenger Apache module:
su - redmine gem install passenger --no-rdoc --no-ri
Then, install the Passenger Apache module using the following command below:
passenger-install-apache2-module
Next, create an Apache module configuration file by using nano text editor:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/00-passenger.conf
Add the following file:
LoadModule passenger_module /opt/redmin/.gem/ruby/gems/passenger-6.0.10/buildout/apache2/mod_passenger.so
<IfModule mod_passenger.c>
PassengerRoot /opt/redmine/.gem/ruby/gems/passenger-6.0.10
PassengerDefaultRuby /usr/bin/ruby
</IfModule>
Then, create an Apache configuration file:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/redmine.conf
Add the following file:
Listen 3000
<IfModule mod_passenger.c>
PassengerRoot /opt/redmin/.gem/ruby/gems/passenger-6.0.10
PassengerDefaultRuby /usr/bin/ruby
</IfModule>
<VirtualHost *:3000>
ServerName redmine.idroot.us
DocumentRoot "/opt/redmine/public"
CustomLog logs/redmine_access.log combined
ErrorLog logs/redmine_error_log
LogLevel warn
<Directory "/opt/redmine/public">
Options Indexes ExecCGI FollowSymLinks
Require all granted
AllowOverride all
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
Verify the Apache configurations by executing the following command:
httpd -t sudo systemctl restart httpd
Finally, disable SELinux on your Linux server:
setenforce 0 sed -i 's/=enforcing/=disabled/' /etc/selinux/config
Step 11. Accessing Redmine Web Interface.
Once successfully installed, now access Redmine web interface via the browser using the address, http://redmine.idroot.us:3000.
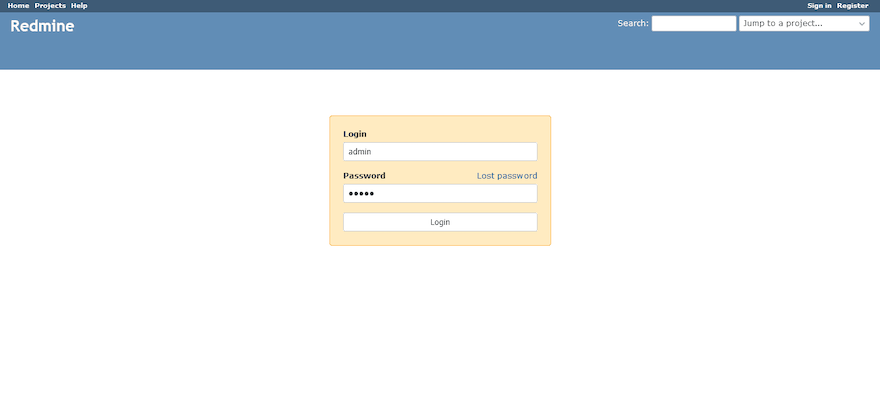
The default login credentials for Redmine are:
- Username: admin
- Password: admin
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Redmine. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Redmine open source project management app on your AlmaLinux 8 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Redmine website.