How To Install Rocket.Chat on Fedora 42

Rocket.Chat stands as one of the most powerful open-source communication platforms available today, offering enterprise-grade messaging, video conferencing, and collaboration tools. Installing this versatile platform on Fedora 42 provides organizations with complete control over their communication infrastructure while maintaining the security and performance benefits of a cutting-edge Linux distribution.
This comprehensive guide walks you through multiple installation methods for Rocket.Chat on Fedora 42, from quick Snap deployments to advanced Docker configurations and manual source installations. Whether you’re setting up a small team communication hub or deploying an enterprise-scale messaging solution, you’ll find the approach that best fits your requirements.
Prerequisites and System Requirements
Before beginning the Rocket.Chat installation process on Fedora 42, ensure your system meets the essential hardware and software requirements for optimal performance.
Hardware Requirements
Your Fedora 42 system should have a minimum of 2GB RAM for basic installations, though 4GB or more is recommended for production environments. The processor requirements are modest – any modern x86_64 CPU will suffice. Storage needs vary significantly based on usage patterns, but allocate at least 10GB of free disk space for the base installation and initial data. For high-traffic deployments, consider 20GB or more to accommodate message history, file uploads, and system logs.
Software Prerequisites
Fedora 42 systems require root or sudo access for installation procedures. Ensure your system maintains an active internet connection throughout the installation process. The package management system should be up to date, which you can verify by running sudo dnf update before proceeding.
Domain name configuration, while optional, significantly enhances the user experience and enables SSL certificate generation. If you plan to access Rocket.Chat from external networks, configure your DNS records to point to your server’s IP address.
Initial System Preparation
Update your Fedora 42 system packages to the latest versions to ensure compatibility and security. Run the following commands:
sudo dnf update -y
sudo dnf install wget curl git -yConfigure the firewall to allow necessary ports. Rocket.Chat typically uses port 3000 for HTTP access, though production deployments often use standard web ports (80/443) behind a reverse proxy:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=3000/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadUnderstanding Rocket.Chat Installation Methods
Fedora 42 users have several robust options for installing Rocket.Chat, each with distinct advantages depending on your specific use case and technical requirements.
Available Installation Options
The Snap package installation offers the quickest deployment path with automatic updates and dependency management. This method works exceptionally well for development environments and small team deployments where simplicity takes precedence over customization.
Docker deployment provides excellent isolation, scalability, and reproducibility. Container-based installations excel in production environments where you need precise control over the application stack and easy backup/restore capabilities.
Manual source installation delivers maximum flexibility and customization options. System administrators who require specific configurations, custom integrations, or performance optimizations often prefer this approach.
Pros and Cons of Each Method
Snap installations minimize setup complexity and provide automatic security updates. However, they offer limited customization options and may consume more system resources due to the containerized nature of Snap applications.
Docker deployments excel in scalability and environment consistency. The containerized approach simplifies backup procedures and enables easy migration between servers. The learning curve for Docker newcomers and additional resource overhead represent the primary drawbacks.
Manual installations provide complete control over every aspect of the deployment. You can optimize performance, integrate with existing systems, and customize configurations extensively. This flexibility comes with increased complexity and manual maintenance responsibilities.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Needs
Small team deployments (5-50 users) typically benefit most from Snap installations due to their simplicity and low maintenance requirements. The automatic update mechanism ensures security patches are applied promptly without administrator intervention.
Enterprise-level installations (100+ users) generally require Docker or manual installations to handle the increased load and customization requirements. These methods provide the scalability and configuration flexibility needed for large-scale deployments.
Development and testing environments work well with any method, though Docker offers advantages for creating consistent development environments across team members.
Method 1: Installing Rocket.Chat via Snap
Snap packages provide the most straightforward installation path for Rocket.Chat on Fedora 42, combining ease of use with automatic update management.
Setting Up Snap Support on Fedora 42
Fedora 42 includes native support for Snap packages, but you may need to enable the snapd service. Install and configure Snap support:
sudo dnf install snapd -y
sudo systemctl enable --now snapd.socket
sudo ln -s /var/lib/snapd/snap /snapVerify snap functionality by checking the service status:
systemctl status snapdEnable classic snap support, which some applications require:
sudo snap install coreInstalling Rocket.Chat Desktop Client
Install the Rocket.Chat desktop application using the snap package manager:
sudo snap install rocketchat-desktopThe installation process downloads and configures all necessary dependencies automatically. Launch the application from your desktop environment’s application menu or via command line:
rocketchat-desktopCOPR Alternative Installation
The Fedora COPR (Community Projects) repository provides an alternative installation method that integrates more closely with the native package management system. Add the Rocket.Chat COPR repository:
sudo dnf copr enable xenithorb/rocketchat-devInstall Rocket.Chat using DNF:
sudo dnf install rocketchat -yThis method provides better integration with Fedora’s package management system and may offer improved performance compared to Snap packages.
Troubleshooting Common Snap Issues
Permission problems often arise when Snap applications attempt to access system resources. Grant additional permissions using:
sudo snap connect rocketchat-desktop:home
sudo snap connect rocketchat-desktop:networkNetwork connectivity issues may prevent the application from accessing remote Rocket.Chat servers. Verify your firewall configuration allows outbound connections on ports 80 and 443.
Update and maintenance procedures happen automatically with Snap packages. However, you can manually trigger updates:
sudo snap refresh rocketchat-desktopMethod 2: Docker-Based Installation
Docker provides a robust, scalable deployment option for Rocket.Chat on Fedora 42, offering excellent isolation and management capabilities.
Installing Docker on Fedora 42
Remove any existing Docker installations to prevent conflicts:
sudo dnf remove docker docker-client docker-client-latest docker-common docker-latest docker-latest-logrotate docker-logrotate docker-selinux docker-engine-selinux docker-engineInstall Docker Community Edition:
sudo dnf install dnf-plugins-core -y
sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/fedora/docker-ce.repo
sudo dnf install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-plugin -yStart and enable Docker service:
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo systemctl enable dockerAdd your user to the docker group to run commands without sudo:
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
newgrp dockerRocket.Chat Docker Deployment
Create a dedicated directory for your Rocket.Chat deployment:
mkdir ~/rocketchat-docker
cd ~/rocketchat-dockerCreate a docker-compose.yml file with the following configuration:
version: '3.8'
services:
rocketchat:
image: rocket.chat:latest
command: >
bash -c
"for i in `seq 1 30`; do
node main.js &&
s=$$? && break || s=$$?;
echo \"Tried $$i times. Waiting 5 secs...\";
sleep 5;
done; (exit $$s)"
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
- ./uploads:/app/uploads
environment:
- PORT=3000
- ROOT_URL=http://localhost:3000
- MONGO_URL=mongodb://mongo:27017/rocketchat
- MONGO_OPLOG_URL=mongodb://mongo:27017/local
depends_on:
- mongo
ports:
- "3000:3000"
mongo:
image: mongo:5.0
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
- ./data/db:/data/db
command: mongod --oplogSize 128 --replSet rs0 --storageEngine=wiredTiger
labels:
- "traefik.enable=false"
mongo-init-replica:
image: mongo:5.0
command: >
bash -c
"for i in `seq 1 30`; do
mongo mongo/rocketchat --eval \"
rs.initiate({
_id: 'rs0',
members: [ { _id: 0, host: 'localhost:27017' } ]})\" &&
s=$$? && break || s=$$?;
echo \"Tried $$i times. Waiting 5 secs...\";
sleep 5;
done; (exit $$s)"
depends_on:
- mongoSSL/TLS Configuration with Let’s Encrypt
For production deployments, configure SSL/TLS encryption using Nginx as a reverse proxy. Create an nginx.conf file:
server {
listen 80;
server_name your-domain.com;
return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
server_name your-domain.com;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/your-domain.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/your-domain.com/privkey.pem;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3000;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto https;
proxy_set_header X-Nginx-Proxy true;
proxy_redirect off;
}
}Container Management and Monitoring
Start your Rocket.Chat deployment:
docker-compose up -dMonitor container status and logs:
docker-compose ps
docker-compose logs -f rocketchatBackup procedures involve backing up both the uploads directory and MongoDB data:
docker-compose exec mongo mongodump --out /backup
cp -r ./uploads ./uploads-backup
cp -r ./data ./data-backupMethod 3: Manual Source Installation
Manual installation provides maximum control and customization options for advanced users and production environments requiring specific configurations.
Installing System Dependencies
Install Node.js version 14.x, which Rocket.Chat requires:
curl -fsSL curl -fsSL https://rpm.nodesource.com/setup_22.x | sudo bash -
sudo dnf install nodejs npm -yVerify the installation:
node --version
npm --versionInstall additional build dependencies:
sudo dnf install gcc-c++ make python3 git -yDatabase Configuration
Install and configure MongoDB, Rocket.Chat’s database backend:
sudo dnf install mongodb-server -yConfigure MongoDB with replica set support, which Rocket.Chat requires:
sudo systemctl start mongod
sudo systemctl enable mongodConnect to MongoDB and initialize the replica set:
mongo --eval "rs.initiate()"Rocket.Chat Server Installation
Create a dedicated user for Rocket.Chat:
sudo useradd -r -s /bin/false -d /opt/Rocket.Chat rocketchatDownload and extract the latest Rocket.Chat release:
cd /tmp
curl -L https://releases.rocket.chat/latest/download -o rocket.chat.tgz
tar -xzf rocket.chat.tgz -C /opt
sudo mv /opt/bundle /opt/Rocket.Chat
sudo chown -R rocketchat:rocketchat /opt/Rocket.ChatInstall Node.js dependencies:
cd /opt/Rocket.Chat/programs/server
sudo npm installSystem Service Setup
Create a systemd service file for Rocket.Chat:
sudo tee /etc/systemd/system/rocketchat.service << EOF
[Unit]
Description=Rocket.Chat Server
After=network.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target nginx.service mongod.service
Wants=network.target
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/bin/node /opt/Rocket.Chat/main.js
StandardOutput=syslog
StandardError=syslog
SyslogIdentifier=rocketchat
User=rocketchat
Environment=MONGO_URL=mongodb://localhost:27017/rocketchat?replicaSet=rs0
Environment=MONGO_OPLOG_URL=mongodb://localhost:27017/local?replicaSet=rs0
Environment=ROOT_URL=http://localhost:3000/
Environment=PORT=3000
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOFEnable and start the Rocket.Chat service:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable rocketchat
sudo systemctl start rocketchatReverse Proxy Configuration
Install and configure Nginx as a reverse proxy:
sudo dnf install nginx -yCreate an Nginx configuration file for Rocket.Chat:
sudo tee /etc/nginx/conf.d/rocketchat.conf << EOF
upstream rocketchat_backend {
server 127.0.0.1:3000;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name your-domain.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://rocketchat_backend;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade \$http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
proxy_set_header Host \$http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP \$remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For \$proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto \$scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Nginx-Proxy true;
proxy_redirect off;
}
}
EOFEnable and start Nginx:
sudo systemctl enable nginx
sudo systemctl start nginxInitial Configuration and Setup
After successful installation using any method, complete the initial Rocket.Chat configuration through the web interface.
First-Time Setup Wizard
Access Rocket.Chat through your web browser at http://your-server-ip:3000 or your configured domain name. The setup wizard guides you through essential configuration steps.
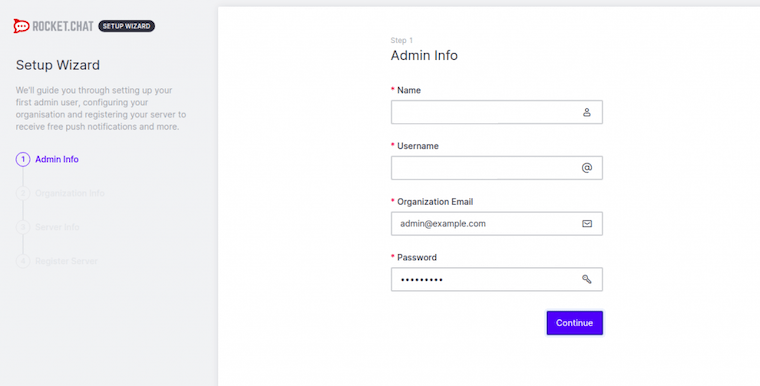
Create your administrator account by providing a username, email address, and secure password. This account has full administrative privileges over your Rocket.Chat instance.
Configure organization information including your organization name, country, and website. This information appears in various parts of the interface and helps personalize your Rocket.Chat deployment.
Basic Security Configuration
Navigate to Administration > Settings > Accounts to configure user authentication settings. Enable two-factor authentication for enhanced security:
Administration > Settings > Accounts > Two Factor Authentication > EnableConfigure channel permissions by accessing Administration > Permissions. Review and modify default permissions based on your organization’s security requirements.
Establish privacy and data retention policies through Administration > Settings > Message. Configure message retention periods and file upload restrictions to comply with your organization’s policies.
Integration and Plugin Setup
Rocket.Chat supports numerous integrations and plugins to extend functionality. Popular integrations include:
- Jitsi Meet for video conferencing
- Hubot for chatbot automation
- LDAP/Active Directory for user authentication
- Webhooks for external service integration
Install plugins through Administration > Apps, where you can browse the marketplace for additional functionality.
Security Hardening and Best Practices
Implementing comprehensive security measures protects your Rocket.Chat installation from potential threats and ensures data integrity.
System-Level Security
Configure SELinux (Security-Enhanced Linux) for additional security layers. Fedora 42 enables SELinux by default, but you may need to create custom policies for Rocket.Chat:
sudo setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect 1Implement regular security updates using automated update mechanisms:
sudo dnf install dnf-automatic -y
sudo systemctl enable --now dnf-automatic.timerConfigure fail2ban to protect against brute-force attacks:
sudo dnf install fail2ban -y
sudo systemctl enable --now fail2banApplication-Level Security
Enable strong authentication policies requiring complex passwords and regular password changes. Configure these settings through Administration > Settings > Accounts > Password Policy.
Implement data encryption for data at rest and in transit. Use TLS/SSL certificates for all communications and consider encrypting database storage.
Establish comprehensive backup procedures including regular automated backups of both application data and configuration files. Test restore procedures regularly to ensure backup integrity.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Deploy monitoring tools to track system performance and detect potential issues:
sudo dnf install htop iotop nethogs -yConfigure log rotation to prevent log files from consuming excessive disk space:
sudo tee /etc/logrotate.d/rocketchat << EOF
/var/log/rocketchat.log {
daily
missingok
rotate 52
compress
delaycompress
notifempty
copytruncate
}
EOFEstablish regular maintenance schedules including system updates, log analysis, and performance optimization reviews.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Understanding common problems and their solutions helps maintain a stable Rocket.Chat deployment.
Installation Problems
Dependency conflicts often occur when multiple Node.js versions exist on the system. Use Node Version Manager (nvm) to manage Node.js versions:
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.0/install.sh | bash
nvm install 14.21.3
nvm use 14.21.3Permission-related issues typically involve incorrect file ownership or SELinux policies. Verify file permissions:
sudo chown -R rocketchat:rocketchat /opt/Rocket.Chat
sudo chmod -R 750 /opt/Rocket.ChatNetwork connectivity problems may prevent database connections or external API access. Verify firewall rules and network configuration.
Runtime Issues
Database connection problems often result from MongoDB replica set configuration issues. Verify replica set status:
mongo --eval "rs.status()"Memory and performance issues may indicate insufficient system resources or suboptimal configuration. Monitor system resources and adjust accordingly:
free -h
top -p $(pgrep -f rocketchat)Service startup failures require log analysis to identify root causes:
sudo journalctl -u rocketchat -fCongratulations! You have successfully installed Rocket.Chat. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Rocket.Chat on Fedora 42 Linux system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Rocket.Chat website.