How To Install SeaMonkey on Linux Mint 22

SeaMonkey stands as a versatile all-in-one internet suite that brings together multiple essential tools under one integrated platform. Built on Mozilla’s trusted technology, this powerful application combines a web browser, email client, IRC chat, HTML editor, and developer tools into a single cohesive package. For Linux Mint 22 users seeking an efficient and comprehensive internet experience without juggling multiple applications, SeaMonkey presents an excellent solution. This guide provides detailed instructions for installing, configuring, and optimizing SeaMonkey on Linux Mint 22.
Introduction to SeaMonkey and Linux Mint 22
SeaMonkey represents the continuation of the original Mozilla Application Suite, offering users a complete internet solution in one package. Unlike using separate programs for different online activities, SeaMonkey integrates essential internet tools seamlessly. This integration not only saves system resources but also streamlines workflow for users who require multiple online functionalities.
Linux Mint 22, the latest release of this popular Ubuntu-based distribution, provides an excellent platform for running SeaMonkey. The operating system’s stability, user-friendly interface, and robust package management make it an ideal choice for users wanting to experience SeaMonkey’s full capabilities.
The primary components of SeaMonkey include:
- A full-featured web browser based on Mozilla’s rendering engine
- A comprehensive email and newsgroups client
- An integrated IRC chat application
- Composer, a WYSIWYG HTML editor for web development
- Advanced developer tools, including a JavaScript debugger and DOM inspector
Whether you’re a regular internet user seeking simplicity, a professional needing email and web browsing capabilities, or a web developer requiring specialized tools, SeaMonkey on Linux Mint 22 delivers a powerful and efficient solution.
Prerequisites and System Preparation
Before installing SeaMonkey on your Linux Mint 22 system, several preparatory steps ensure a smooth installation process. Proper preparation helps avoid common issues and ensures your system has the necessary components to support SeaMonkey effectively.
System Requirements
SeaMonkey runs efficiently on most modern computers but benefits from:
- At least 1GB of RAM (2GB or more recommended)
- 300MB of available hard drive space
- A processor with SSE2 support (virtually all CPUs manufactured after 2004)
Checking Your Linux Mint Version
To verify you’re running Linux Mint 22, open a terminal window and enter:
lsb_release -aThe output should display information about your Linux distribution, including the version number. Ensure it shows Linux Mint 22 before proceeding.
Updating Your System
A crucial preliminary step involves updating your existing system. Open your terminal and execute the following commands:
sudo apt updateThis command refreshes your package lists, ensuring your system knows about the latest available software versions. After completion, upgrade all installed packages:
sudo apt upgradeWhen prompted, confirm the upgrades by pressing ‘Y’ and Enter. This process may take several minutes depending on your internet connection and how many packages need updating.
Installing Essential Preparatory Tools
SeaMonkey installation requires specific tools for managing secure repositories and verification keys. Install these packages by running:
sudo apt install dirmngr software-properties-common apt-transport-https -yThis command installs:
dirmngr: A server for managing and downloading OpenPGP keyssoftware-properties-common: Tools for managing software repositoriesapt-transport-https: Support for downloading packages over HTTPS connections
The -y parameter automatically confirms installation of these packages without prompting for confirmation.
Creating a Backup (Optional but Recommended)
Before any significant software installation, creating a system backup provides protection against unexpected issues. For Linux Mint 22, you can use the built-in Timeshift application:
- Open Timeshift from the application menu
- Follow the on-screen instructions to create a system snapshot
- Ensure the backup completes successfully before proceeding
With these preparations complete, your system is ready for the SeaMonkey installation process.
Adding the SeaMonkey Repository
Installing SeaMonkey on Linux Mint 22 requires adding a dedicated repository to your system. This repository, maintained by the UbuntuZilla project, provides up-to-date SeaMonkey packages specifically designed for Ubuntu-based systems like Linux Mint.
Understanding Linux Repositories
Repositories are centralized storage locations containing software packages and their dependencies. By adding the SeaMonkey repository to your system, you gain access to the application and ensure you’ll receive updates when new versions are released.
Setting Up the GPG Key System
The repository uses GPG (GNU Privacy Guard) keys to verify package authenticity, protecting your system from potentially harmful software. First, initialize the GPG key system by running:
sudo gpg --list-keysThis command may display a message indicating that new directories have been created, which is normal if you haven’t used GPG before.
Importing the SeaMonkey Repository Key
Next, import the specific GPG key used to sign SeaMonkey packages:
sudo gpg --no-default-keyring --keyring /usr/share/keyrings/ubuntuzilla.gpg --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys 2667CA5CThis complex command:
- Creates a separate keyring file for the UbuntuZilla repository
- Connects to the Ubuntu key server
- Downloads the specific key (2667CA5C) for verifying SeaMonkey packages
When executed successfully, you’ll see output confirming the key has been imported, similar to:
gpg: keybox '/usr/share/keyrings/ubuntuzilla.gpg' created
gpg: key B7B9C16F2667CA5C: public key "Daniel Folkinshteyn (Ubuntuzilla signing key) <nanotube@users.sourceforge.net>" imported
gpg: Total number processed: 1
gpg: imported: 1Adding the Repository to Your System
With the verification key in place, add the actual repository to your system’s software sources:
printf 'deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/ubuntuzilla.gpg] https://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/ubuntuzilla/mozilla/apt all main\n' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ubuntuzilla.listThis command creates a new file in the /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ directory containing the repository information. The signed-by parameter ensures that only packages verified with the previously imported key will be installed.
Updating Package Lists
Finally, update your system’s package lists to include the newly added repository:
sudo apt updateYou should see the UbuntuZilla repository being checked during the update process. If you encounter any errors related to the repository, double-check the previous steps for typos or missing commands.
With the repository successfully added, your system can now access and install SeaMonkey directly through the package manager.
Installing SeaMonkey on Linux Mint 22
With the repository properly set up, installing SeaMonkey becomes a straightforward process. This section guides you through the actual installation and verification steps.
Installation Command
To install SeaMonkey, run the following command in your terminal:
sudo apt install seamonkey-mozilla-buildThe system will calculate dependencies and display a list of packages to be installed, including SeaMonkey and any required supporting libraries. When prompted, confirm the installation by typing ‘Y’ and pressing Enter.
Understanding the Installation Process
During installation, the package manager:
- Downloads the SeaMonkey package and any dependencies
- Unpacks the files into the appropriate system directories
- Sets up application launchers and file associations
- Configures the application for system-wide use
The installation may take several minutes depending on your internet connection speed and system performance. Terminal output provides real-time progress information.
Verifying the Installation
Once the installation completes, verify that SeaMonkey was installed correctly by checking its version:
apt list --installed seamonkey-mozilla-buildThis command should display the installed SeaMonkey package along with its version number, confirming successful installation.
Common Installation Issues and Solutions
If you encounter errors during installation, consider these common issues and solutions:
Package Not Found Error
- Error:
E: Unable to locate package seamonkey-mozilla-build - Solution: Ensure you’ve correctly added the repository and updated the package lists as described in the previous section.
Dependency Conflicts
- Error: Messages about conflicting packages or unmet dependencies
- Solution: Try running
sudo apt -f installto fix broken dependencies, then attempt the SeaMonkey installation again.
Repository Authentication Problems
- Error:
The following signatures couldn't be verified because the public key is not available - Solution: Double-check that you properly imported the GPG key as described earlier.
With SeaMonkey successfully installed, you’re ready to launch and configure the application for your specific needs.
Alternative Installation Methods
While installing SeaMonkey through the repository is the recommended approach, alternative methods exist for specific scenarios. This section covers manual installation from the official SeaMonkey archives.
When to Consider Manual Installation
Manual installation might be preferable in certain situations:
- When you need a specific version not available in the repository
- If you prefer not to add external repositories to your system
- When you want to run multiple versions side by side
- If you’re experiencing issues with the repository version
Downloading the Official Archive
Visit the official SeaMonkey website (www.seamonkey-project.org) and navigate to the download section. Choose the Linux version appropriate for your system architecture (typically x86_64 for modern systems).
The downloaded file will have a name similar to seamonkey-2.53.15.tar.bz2 (version number may vary).
Manual Installation Steps
- Create a dedicated directory for the installation:
mkdir ~/seamonkey2 cd ~/seamonkey2 - Move the downloaded archive to this directory:
mv ~/Downloads/seamonkey-*.tar.bz2 . - Extract the contents:
tar jxvf seamonkey-*.tar.bz2This creates a
seamonkeysubdirectory containing the application files. - Navigate to the extracted directory:
cd seamonkey - Launch SeaMonkey directly:
./seamonkey
Creating a Desktop Shortcut for Manual Installation
For easier access to manually installed SeaMonkey, create a desktop shortcut:
- Create a new file in
~/.local/share/applications/namedseamonkey-manual.desktop:nano ~/.local/share/applications/seamonkey-manual.desktop - Add the following content (adjust paths as needed):
[Desktop Entry] Name=SeaMonkey (Manual) Comment=SeaMonkey Internet Suite Exec=/home/yourusername/seamonkey2/seamonkey/seamonkey Icon=/home/yourusername/seamonkey2/seamonkey/chrome/icons/default/default128.png Type=Application Categories=Network;WebBrowser;Email; - Save the file and exit the editor (Ctrl+O, Enter, then Ctrl+X in nano)
Comparing Repository vs. Manual Installation
| Aspect | Repository Installation | Manual Installation |
|---|---|---|
| Updates | Automatic through package manager | Manual downloads required |
| System Integration | Complete with menu entries | Limited unless manually configured |
| Multiple Versions | Difficult to maintain | Easy to manage multiple versions |
| Dependencies | Automatically handled | May require manual installation |
| Security | Verified by repository maintainers | Relies on user verification |
Choose the installation method that best suits your specific requirements and technical comfort level.
Launching and Configuring SeaMonkey
After installing SeaMonkey on Linux Mint 22, you’ll want to launch the application and configure it to match your preferences. This section covers various launch methods and essential first-time configuration steps.
Terminal Launch Method
The simplest way to launch SeaMonkey is through the terminal. Open a terminal window and type:
seamonkeyThis command launches the complete SeaMonkey suite. To launch specific components directly, you can use additional parameters:
- For just the browser:
seamonkey -browser - For the mail client:
seamonkey -mail - For the HTML editor:
seamonkey -composer
GUI Launch Methods
Linux Mint 22 also provides graphical methods to launch SeaMonkey:
- Applications Menu: Click on the Menu button in the bottom-left corner of the screen, navigate to “Internet” or search for “SeaMonkey” and click the icon.
- Desktop Shortcut: Right-click on the desktop, select “Create Launcher,” and enter the details:
- Type: Application
- Name: SeaMonkey
- Command: seamonkey
- Icon: Click the icon button and search for “seamonkey”
- Panel/Favorites: Right-click on the SeaMonkey icon in the applications menu and select “Add to Panel” or “Add to Favorites” for quick access.
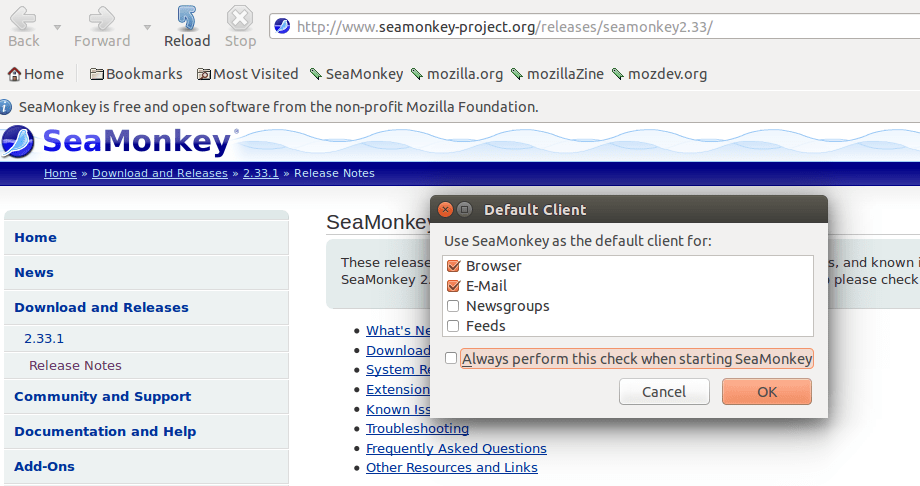
First-Time Setup and Configuration
When launching SeaMonkey for the first time, a setup wizard guides you through the initial configuration:
- Default Browser: Choose whether to set SeaMonkey as your default browser.
- Profile Creation: SeaMonkey will create a new profile to store your settings and data.
- Data Import: If you’ve used other browsers or email clients, SeaMonkey offers to import your bookmarks, saved passwords, and mail settings.
Essential Configuration Options
After the initial setup, consider configuring these important settings:
Browser Settings:
- Open SeaMonkey and click “Edit” > “Preferences”
- Set your homepage under the “Browser” category
- Configure privacy and security options under the “Privacy & Security” category
- Adjust download settings under the “Navigator” > “Downloads” section
Email Account Setup:
- In SeaMonkey, click “Window” > “Mail & Newsgroups”
- Select “Edit” > “Mail & Newsgroups Account Settings”
- Click “Add Account” and follow the wizard to set up your email account
- Configure message storage, composition settings, and junk mail controls
Profile Management:
- Close SeaMonkey completely
- Launch profile manager with:
seamonkey -ProfileManager - Create different profiles for different purposes (e.g., work, personal)
User Interface Customization:
- Modify the toolbar by right-clicking it and selecting “Customize”
- Drag and drop buttons to reorganize them
- Add or remove features based on your preferences
Language and Localization:
- Install additional language packs if needed
- Set your preferred language in “Edit” > “Preferences” > “Appearance” > “Languages”
With these configurations in place, SeaMonkey will be optimized for your specific needs and preferences on Linux Mint 22.
SeaMonkey Components and Features
SeaMonkey’s strength lies in its comprehensive integration of multiple internet tools into a cohesive suite. Understanding each component helps you leverage the full potential of this versatile application.
Web Browser: Navigator
At the core of SeaMonkey is its powerful web browser, based on the same Mozilla technology that powers Firefox:
- Tabbed Browsing: Manage multiple websites in a single window
- Bookmark Management: Organize your favorite sites with tags and folders
- Privacy Controls: Block trackers and manage cookies effectively
- Search Integration: Use the integrated search bar with multiple search engines
- Add-on Support: Extend functionality with compatible extensions
Compared to standalone browsers, SeaMonkey’s Navigator offers comparable performance with the advantage of direct integration with other components.
Mail and Newsgroups Client
SeaMonkey includes a full-featured email and newsgroups client similar to Mozilla Thunderbird:
- Multiple Account Support: Manage various email accounts in one interface
- Message Filtering: Automatically sort and organize incoming messages
- Spam Control: Built-in junk mail detection and filtering
- RSS Feed Reader: Subscribe to and read web feeds directly
- Address Book: Maintain contact information with customizable fields
The address book integrates seamlessly with the email client, making communication efficient and organized.
HTML Editor: Composer
Web developers appreciate SeaMonkey’s Composer, a WYSIWYG HTML editor:
- Visual Editing: Create web content without writing code
- HTML Source Mode: Switch to direct HTML editing when needed
- Table Creation: Insert and format tables visually
- Image Handling: Insert, align, and resize images easily
- Live Preview: See changes in real-time as you edit
This tool is particularly valuable for quick webpage edits or creating simple HTML documents without requiring a separate application.
IRC Chat Client: ChatZilla
For real-time communication, SeaMonkey includes ChatZilla:
- Multi-Server Support: Connect to multiple IRC networks simultaneously
- Channel Management: Join and organize various chat channels
- Custom Scripts: Extend functionality with JavaScript
- Notification System: Receive alerts for messages and mentions
- Logging: Save chat sessions for future reference
Developer Tools
Web developers benefit from SeaMonkey’s integrated development tools:
- DOM Inspector: Examine and modify the Document Object Model of web pages
- JavaScript Debugger: Find and fix errors in JavaScript code
- Error Console: View JavaScript, CSS, and XML errors
- Web Development Extensions: Add specialized tools as needed
Component Integration
What sets SeaMonkey apart is how these components work together:
- Click an email link in the browser to open the mail composer
- Use the address book contacts in email and chat
- Edit web pages directly from the browser
- Share bookmarks and preferences across components
This integration creates a seamless workflow that standalone applications cannot match, making SeaMonkey a powerful choice for users who regularly use multiple internet tools.
Updating and Maintaining SeaMonkey
Keeping SeaMonkey up to date ensures you have the latest features, security patches, and performance improvements. This section covers various update methods and maintenance practices for SeaMonkey on Linux Mint 22.
Checking for Updates Within SeaMonkey
SeaMonkey can check for updates to itself:
- Open SeaMonkey
- Click “Help” in the menu bar
- Select “About SeaMonkey”
- Click “Check for Updates”
If updates are available, SeaMonkey will prompt you to install them. However, this method typically works best for minor updates rather than major version changes.
Terminal Update Commands
For more reliable updates, use the terminal commands:
sudo apt updateThis refreshes your package lists, checking for available updates to all installed software, including SeaMonkey.
To upgrade only SeaMonkey without affecting other packages:
sudo apt install --only-upgrade seamonkey-mozilla-buildFor a complete system update, including SeaMonkey:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeUpdate Frequency Recommendations
For optimal security and performance:
- Check for updates weekly
- Apply security updates immediately
- Consider enabling automatic updates through Linux Mint’s Update Manager
- Subscribe to SeaMonkey’s announcement mailing list for update notifications
Verifying Update Success
After updating, verify the new version:
apt list --installed seamonkey-mozilla-buildAlternatively, within SeaMonkey, go to “Help” > “About SeaMonkey” to see the current version number.
Managing Automatic Updates
Configure Linux Mint’s Update Manager to handle SeaMonkey updates:
- Open Update Manager from the application menu
- Click “Edit” > “Preferences”
- Select the “Automation” tab
- Configure automatic update checks and installations according to your preferences
Handling Broken Updates
If an update causes issues:
- Try repairing packages:
sudo apt --fix-broken install - If problems persist, consider downgrading to the previous version:
sudo apt install seamonkey-mozilla-build=previous_version_number(Replace “previous_version_number” with the actual version)
- As a last resort, remove and reinstall SeaMonkey:
sudo apt remove --purge seamonkey-mozilla-build sudo apt install seamonkey-mozilla-build
Regular maintenance ensures your SeaMonkey installation remains secure and performs optimally on Linux Mint 22.
Extending SeaMonkey Functionality
One of SeaMonkey’s greatest strengths is its extensibility. Through add-ons, extensions, and themes, you can customize and enhance SeaMonkey to better suit your specific needs and preferences.
Finding and Installing Add-ons
SeaMonkey supports various types of extensions, though compatibility may vary by version:
- Open SeaMonkey and click “Tools” > “Add-ons”
- Select “Get Extensions” to browse the available add-ons
- When you find an extension you want, click “Install”
- Restart SeaMonkey when prompted to activate the new extension
Many Firefox extensions are compatible with SeaMonkey, expanding your options beyond the dedicated SeaMonkey add-ons.
Recommended Extensions
Enhance your SeaMonkey experience with these useful extensions:
Security Extensions:
- NoScript: Block potentially harmful scripts
- uBlock Origin: Efficient ad and tracker blocking
- HTTPS Everywhere: Enforce secure connections when available
Productivity Tools:
- Lightning Calendar: Integrate calendar functionality
- Quick Folder Move: Simplify email organization
- QuickNote: Take notes while browsing
UI Enhancements:
- Classic Theme Restorer: Customize the user interface
- Status-4-Evar: Restore status bar functionality
- ColorfulTabs: Differentiate tabs with colors
Installing and Managing Themes
Customize SeaMonkey’s appearance with themes:
- Go to “Tools” > “Add-ons”
- Select “Get Themes”
- Browse available themes and click “Install” on your preferred option
- Apply the theme by selecting it in the Themes section and clicking “Enable”
Managing Extensions
Properly manage your installed extensions:
- Open “Tools” > “Add-ons”
- Select the “Extensions” tab to see all installed extensions
- Use the “Disable” button to temporarily turn off an extension
- Click “Remove” to uninstall unwanted extensions
- Select “Preferences” or “Options” (if available) to configure individual extensions
Performance Considerations
Extensions can impact SeaMonkey’s performance and memory usage:
- Install only essential extensions
- Disable rarely used extensions
- Monitor system resource usage after installing new extensions
- Update extensions regularly for optimal compatibility
- Remove problematic extensions that cause crashes or slowdowns
Security Precautions
When installing third-party add-ons:
- Only download from trusted sources (preferably the official SeaMonkey/Mozilla repositories)
- Read user reviews and check the developer’s reputation
- Be wary of extensions requesting excessive permissions
- Keep extensions updated to patch security vulnerabilities
- Consider using a separate profile for testing new extensions
By carefully selecting and managing extensions, you can transform SeaMonkey into a highly personalized and powerful internet suite tailored to your specific requirements.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with careful installation and configuration, you might encounter occasional issues with SeaMonkey on Linux Mint 22. This section addresses common problems and provides practical solutions.
Startup and Launching Problems
Issue: SeaMonkey Won’t Start
- Check for running instances:
ps aux | grep seamonkey - Kill any hanging processes:
killall seamonkey - Launch from terminal to see error messages:
seamonkey - Check permissions:
ls -la ~/.mozilla/seamonkey - Try safe mode:
seamonkey -safe-mode
Issue: Profile Cannot Be Loaded
- Create a new profile:
seamonkey -ProfileManager - Check for profile lock files:
rm ~/.mozilla/seamonkey/*.default/*.lock - Restore profile from backup if available
Performance and Memory Issues
Issue: SeaMonkey Runs Slowly
- Disable resource-intensive extensions
- Clear cache: “Edit” > “Preferences” > “Advanced” > “Cache” > “Clear Cache”
- Reduce browser history retention period
- Check system resources:
toporhtop - Consider adding more RAM if consistently using over 80%
Issue: High Memory Usage
- Limit open tabs and windows
- Restart SeaMonkey periodically
- Add the following to
user.jsin your profile folder:user_pref("browser.cache.memory.capacity", 65536); user_pref("browser.sessionhistory.max_total_viewers", 3);
Repository and Update Errors
Issue: Repository Not Found
- Verify internet connection
- Check repository file:
cat /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ubuntuzilla.list - Re-add the repository if necessary
- Check for proxy settings if behind a firewall
Issue: GPG Key Errors
- Re-import the GPG key:
sudo gpg --no-default-keyring --keyring /usr/share/keyrings/ubuntuzilla.gpg --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys 2667CA5C - Try an alternative keyserver if the main one fails:
sudo gpg --no-default-keyring --keyring /usr/share/keyrings/ubuntuzilla.gpg --keyserver keys.gnupg.net --recv-keys 2667CA5C
Component-Specific Problems
Issue: Email Client Problems
- Check mail server settings
- Verify account credentials
- Compact folders: Right-click folder > “Properties” > “Compact”
- Rebuild index: Rename or delete
.msffiles in the mail directory
Issue: Browser Rendering Issues
- Clear cache and cookies
- Disable hardware acceleration: “Edit” > “Preferences” > “Advanced” > “General” > uncheck “Use hardware acceleration when available”
- Reset browser settings: Remove
prefs.jsfrom your profile (after backing up)
Issue: Add-on Compatibility Conflicts
- Start in safe mode:
seamonkey -safe-mode - Disable add-ons one by one to identify the problematic one
- Check for updated versions of incompatible add-ons
- Consider alternatives for incompatible add-ons
Diagnosing with Log Files
Examine log files for detailed error information:
- Browser console: Press Ctrl+Shift+J
- System logs:
journalctl -f | grep seamonkey - X server errors:
cat ~/.xsession-errors
Community Support Resources
When troubleshooting fails, seek help from:
- SeaMonkey’s official support forums
- Linux Mint forums and community channels
- IRC channel: #seamonkey on Mozilla IRC
- Stack Exchange communities related to Linux
Documenting the steps you’ve taken and any error messages received helps community members provide more effective assistance.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed SeaMonkey. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the SeaMonkey internet suite on Linux Mint 22 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official SeaMonkey website.