How To Install Shotcut Video Editor on Linux Mint 22

Linux Mint 22 users seeking a powerful video editing solution need look no further than Shotcut. This comprehensive guide walks you through every method to install this robust open-source video editor on your system. Whether you’re a video editing novice or a seasoned content creator, Shotcut offers a feature-rich environment without the premium price tag. Follow along as we explore multiple installation approaches, optimize performance, and get you ready to start your video editing journey.
What is Shotcut Video Editor?
Shotcut stands as one of the most versatile open-source video editing platforms available today. Developed as a free alternative to premium editing software, Shotcut has evolved significantly since its inception to become a staple in the Linux video editing ecosystem.
Key Features That Make Shotcut Stand Out
Shotcut comes packed with impressive capabilities that rival commercial alternatives:
- Support for hundreds of audio and video formats through FFmpeg
- Non-destructive editing with a native timeline
- Multi-track editing with advanced features
- 4K resolution support for modern video projects
- Rich filter library for visual effects and corrections
- Cross-platform availability across Linux, Windows, and macOS
When compared to other Linux video editors like Kdenlive or OpenShot, Shotcut strikes an excellent balance between feature depth and usability. The software provides enough advanced tools to satisfy experienced editors while maintaining an interface approachable for beginners. For Linux Mint users specifically, Shotcut integrates well with the system’s aesthetics and resource management.
System Requirements for Linux Mint 22
Before proceeding with installation, ensure your system meets these requirements for optimal Shotcut performance:
Hardware Requirements:
- Processor: Multi-core 64-bit CPU (Intel i5 or AMD equivalent recommended)
- RAM: Minimum 4GB, 8GB or more recommended for HD/4K editing
- Graphics: OpenGL 2.0 compatible GPU
- Storage: 300MB for the application plus additional space for projects and media
Software Dependencies:
- Updated Linux Mint 22 system with the latest updates
- Various libraries depending on installation method (detailed in each section)
- JACK audio system for specific features (optional but recommended)
Before installation, it’s prudent to update your system completely:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
Checking your system specifications helps ensure compatibility:
# Check available disk space df -h # Check RAM free -h # Check CPU information lscpu
Installation Methods Overview
Shotcut can be installed on Linux Mint 22 through several methods, each with distinct advantages. The table below provides a quick comparison:
| Method | Ease of Installation | Update Process | System Integration | Portability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Snap | Simple | Automatic | Good | Low |
| AppImage | Moderate | Manual | Manual setup required | High |
| Portable tar | Advanced | Manual | Manual setup required | Very High |
| Flatpak | Simple | Semi-automatic | Good | Low |
Your choice depends on your specific needs. Beginners may prefer Snap or Flatpak for their simplicity, while advanced users might opt for AppImage or Portable tar packages for greater control and portability. Let’s examine each method in detail.
Method 1: Installing Shotcut via Snap
Snap packages provide a convenient way to install applications on Linux Mint with automatic updates and sandboxed security. Although Linux Mint doesn’t include Snap support by default, adding it is straightforward.
Enabling Snap Support in Linux Mint 22
First, you need to install the Snap daemon:
sudo apt update sudo apt install snapd
After installation, it’s crucial to reboot your system to ensure proper integration:
sudo reboot
This restart ensures that Snap applications will properly appear in your Linux Mint menu system.
Installing Shotcut Using Snap
Once Snap is configured, installing Shotcut becomes remarkably simple:
sudo snap install shotcut --classic
The --classic flag is essential as it gives Shotcut the necessary system access for full functionality.
Verifying Installation and First Launch
After installation completes, you can verify it worked correctly:
snap list
You should see Shotcut in the list of installed Snap applications. Launch it either from your application menu or by typing:
shotcut
Managing Snap Updates
One advantage of using Snap is automatic updates. However, you can manually check for updates with:
sudo snap refresh
If you ever need to remove Shotcut:
sudo snap remove shotcut
Benefits and Limitations
Snap installation offers easy updates and good system integration. However, Snap packages can be larger than other formats and might have slightly slower startup times. For most users, these tradeoffs are worthwhile for the convenience provided.
Method 2: Installing Shotcut via AppImage
AppImage offers a portable installation method that doesn’t require system-wide installation or administrative privileges.
What is AppImage?
AppImage is a universal package format that bundles applications with their dependencies. This self-contained approach allows software to run on any Linux distribution without traditional installation.
Downloading the Shotcut AppImage
Visit the official Shotcut website (shotcut.org) and navigate to the download section. Look for the Linux AppImage option and download the file to your computer.
Making the AppImage Executable
After downloading, you need to make the file executable:
cd ~/Downloads chmod +x shotcut-linux-*.AppImage
Running Shotcut from AppImage
Execute the AppImage file directly:
./shotcut-linux-*.AppImage
The application will launch immediately without installation.
Creating a Desktop Shortcut
For convenient access, create a desktop shortcut:
cat > ~/.local/share/applications/shotcut.desktop << EOF [Desktop Entry] Name=Shotcut Comment=Video Editor Exec=/path/to/your/shotcut-linux-*.AppImage Icon=shotcut Terminal=false Type=Application Categories=AudioVideo;Video;AudioVideoEditing; EOF
Replace /path/to/your/ with the actual path to your AppImage file.
AppImage Advantages and Disadvantages
AppImage provides excellent portability and version control. You can keep multiple versions simultaneously and run directly from external drives. However, AppImages require manual updates and might need additional configuration for full desktop integration.
Method 3: Using the Portable tar Package
The portable tar package offers the most flexible installation option for advanced users.
Understanding the Portable tar Package
This distribution method provides a compressed archive containing all necessary files to run Shotcut without formal installation.
Downloading and Extracting
Download the Linux portable tar file from the Shotcut website. Extract it to your preferred location:
tar -xzf shotcut-linux-x86_64-*.tar.gz -C ~/Applications/
The example above extracts to a directory called “Applications” in your home folder.
Launching Shotcut
Navigate to the extracted directory and launch the application:
cd ~/Applications/Shotcut ./Shotcut.app
Do not try to run bin/shotcut directly as noted in the documentation.
Setting Up Desktop Integration
Similar to AppImage, you can create a desktop entry:
cat > ~/.local/share/applications/shotcut-portable.desktop << EOF [Desktop Entry] Name=Shotcut (Portable) Comment=Video Editor Exec=/home/username/Applications/Shotcut/Shotcut.app Icon=/home/username/Applications/Shotcut/icon.png Terminal=false Type=Application Categories=AudioVideo;Video;AudioVideoEditing; EOF
Replace the paths with your actual installation location.
Additional Requirements
You may need to install JACK audio system from your distribution repositories for full functionality:
sudo apt install jackd2
Benefits for Advanced Users
The portable package offers complete control over installation location and easy version management. It’s ideal for users who need to customize their setup or maintain specific versions for compatibility with projects.
Method 4: Installing via Flatpak
Flatpak provides another excellent option for installing Shotcut, with good isolation and dependency management.
Setting Up Flatpak on Linux Mint 22
First, install Flatpak and the required plugin:
sudo apt install flatpak sudo apt install gnome-software-plugin-flatpak
Add the Flathub repository:
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo
Installing Shotcut Through Flatpak
With Flatpak configured, install Shotcut:
sudo flatpak install flathub org.shotcut.Shotcut
After installation, restart your system to ensure proper registration:
sudo reboot
Managing Flatpak Installations
Useful commands for managing your Flatpak applications:
# List all installed Flatpak applications flatpak list # Update all Flatpak applications flatpak update # Remove Shotcut if needed flatpak uninstall org.shotcut.Shotcut
Flatpak Advantages and Limitations
Flatpak offers excellent security through sandboxing and consistent behavior across distributions. However, Flatpak installations are typically larger due to bundled dependencies and may have slightly higher resource usage than native installations.
Troubleshooting Common Installation Issues
Even with straightforward installation procedures, issues can arise. Here are solutions to common problems:
Dependency Problems
If you encounter missing dependency errors:
sudo apt install libgl1-mesa-glx libpulse0 libxcb-xinerama0
This installs the most commonly required libraries for Shotcut across all installation methods.
Permission Issues
If you receive “permission denied” errors when launching:
# For AppImage chmod +x shotcut-linux-*.AppImage # For Portable tar chmod +x ~/Applications/Shotcut/Shotcut.app
Application Not Starting
For interface-related errors, try reinstalling with alternative graphics drivers:
# For Intel GPUs sudo apt install mesa-utils # For NVIDIA GPUs sudo apt install nvidia-driver-latest
If Shotcut crashes on startup, try launching from terminal to see error messages:
# For Snap snap run shotcut # For Flatpak flatpak run org.shotcut.Shotcut
Audio Configuration Issues
For audio problems, ensure JACK is installed and properly configured:
sudo apt install jackd2 qjackctl
Use QjackCtl to configure audio settings before launching Shotcut.
Post-Installation Configuration
After successful installation, optimize your Shotcut experience with these configurations:
First-Time Setup Recommendations
When first launching Shotcut, take time to:
- Configure default project settings via Settings > Video Mode
- Set your preferred default save locations in Settings > General
- Explore and customize the interface layout that works best for your workflow
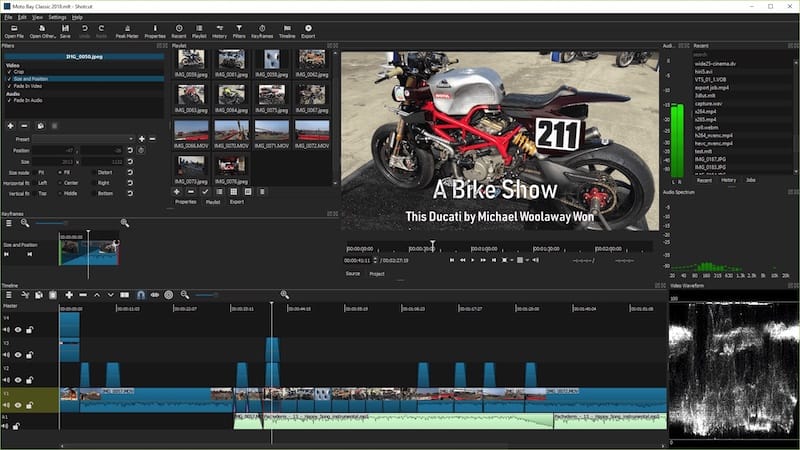
Setting Up Hardware Acceleration
Hardware acceleration significantly improves performance:
- Go to Settings > Display
- Enable GPU Processing if available
- Select the appropriate Graphics Processing option for your hardware
Customizing Interface and Shortcuts
Personalize your editing experience:
- Go to Settings > Keyboard to customize shortcuts
- Use View menu to show/hide panels based on your needs
- Save your layout via View > Layout > Save Layout
Optimizing Shotcut Performance on Linux Mint 22
Get the most out of Shotcut with these performance tips:
Memory Management
Adjust memory usage in Settings > General > Performance:
- Increase “GPU processing threads” on systems with powerful GPUs
- Adjust “Image processing threads” based on your CPU cores
- Limit timeline thumbnails on systems with limited RAM
Project Settings Optimization
For smoother editing:
- Match project resolution to output needs (don’t edit in 4K if outputting to 1080p)
- Use proxy editing for high-resolution footage
- Disable real-time effects preview when working with complex projects
Cache Management
Manage Shotcut’s cache to prevent performance degradation:
- Set a dedicated cache location on a fast drive
- Periodically clear the cache via Settings > Cache
- Allocate sufficient cache size based on available storage
Updating Shotcut
Keeping Shotcut updated ensures access to the latest features and bug fixes.
Update Methods by Installation Type
Each installation method has its update procedure:
- Snap: Updates occur automatically, or manually with
sudo snap refresh shotcut - AppImage: Download the latest AppImage file and replace the old one
- Portable tar: Download the newest package and extract to a new location
- Flatpak: Update with
flatpak update org.shotcut.Shotcut
Checking Current Version
Verify your current version via Help > About Shotcut. Compare with the latest version on the official website.
When to Update
Consider these factors before updating:
- Mid-project updates may introduce compatibility issues
- Major version updates might change interface elements or workflows
- Read release notes to understand changes before updating
Basic Usage Tutorial
Start your editing journey with these fundamental steps:
Creating Your First Project
- Launch Shotcut and select File > New
- Choose your project settings based on intended output
- Save your project immediately via File > Save As
Importing Media
Add content to your project:
- Use the Open File button or File > Open File
- Alternatively, drag and drop files from your file manager
- Use the Playlist panel to organize imported media
Basic Editing Operations
Get familiar with essential editing tasks:
- Drag clips from the playlist to the timeline
- Use the trim handles to adjust clip length
- Apply transitions between clips via the Transitions panel
- Add text and titles from the Filters panel
Exporting Your Video
Complete your project:
- Select Export from the main menu
- Choose your output format and quality settings
- Use the Video tab to adjust resolution and framerate
- Use the Audio tab to configure sound quality
- Click Export File to render your project
Congratulation’s! You have successfully installed Shotcut. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Shotcut video editor on your Linux Mint 22 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Shotcut website.