How To Install Subsonic Media Server on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS

Setting up your own personal music streaming server has never been more accessible. Subsonic Media Server transforms your Ubuntu 24.04 LTS system into a powerful, self-hosted music streaming platform that rivals commercial services like Spotify or Apple Music. This comprehensive guide walks you through every step of installing and configuring Subsonic on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS, ensuring you have complete control over your music library while enjoying seamless streaming across all your devices.
The beauty of self-hosting lies in data ownership and privacy. Unlike subscription-based streaming services, Subsonic gives you unlimited access to your personal music collection without monthly fees or content restrictions. You’ll stream your media from anywhere in the world, share access with family members, and maintain complete control over your digital music library.
Ubuntu 24.04 LTS provides the perfect foundation for hosting Subsonic. Its long-term support ensures stability and security updates for years to come. The robust package management system simplifies installation, while the mature Linux ecosystem offers excellent performance for media streaming applications.
What is Subsonic Media Server?
Definition and Core Features
Subsonic represents a revolutionary approach to personal music streaming. This Java-based application creates a web-accessible music server that transforms any computer into a streaming powerhouse. The software supports virtually every audio format, including MP3, FLAC, OGG, and AAC, ensuring compatibility with your entire music collection.
The cross-platform nature of Subsonic means seamless operation across Linux, macOS, and Windows environments. Its web-based interface eliminates the need for complex client software installation. Users access their music libraries through any modern web browser, making it incredibly convenient for both local and remote streaming scenarios.
Remote access capabilities set Subsonic apart from simple media players. The server streams music over the internet, allowing you to enjoy your personal collection from anywhere with an internet connection. This functionality proves invaluable for travelers, commuters, or anyone who wants access to their music library beyond their home network.
Key Benefits and Use Cases
Personal cloud music streaming eliminates dependency on commercial streaming services. You maintain complete ownership of your music library while enjoying modern streaming conveniences. No monthly subscriptions or content licensing issues affect your listening experience.
Multi-user support transforms Subsonic into a family-friendly solution. Create separate user accounts with customized access permissions and personalized playlists. Each family member enjoys their own streaming experience while sharing the same media server infrastructure.
Mobile app compatibility extends Subsonic’s reach to smartphones and tablets. Official and third-party applications provide native mobile experiences, complete with offline download capabilities for situations with limited internet connectivity. Popular mobile clients include DSub for Android and play:Sub for iOS.
Transcoding capabilities ensure optimal playback across different devices and network conditions. Subsonic automatically converts high-quality audio files to lower bitrates when streaming over slower connections, maintaining smooth playback while conserving bandwidth.
System Requirements and Prerequisites
Hardware Requirements
Subsonic’s hardware demands remain modest for most home installations. A minimum of 1GB RAM suffices for small music libraries, though 2GB or more provides better performance with larger collections. CPU requirements depend heavily on transcoding usage; systems performing real-time audio conversion benefit from multi-core processors.
Storage considerations extend beyond the operating system requirements. Your music library size directly impacts storage needs, with additional space required for temporary transcoding files and system logs. A typical installation requires 500MB for Subsonic itself, plus adequate space for your media collection.
Network bandwidth affects streaming quality and concurrent user capacity. Higher bitrate audio files consume more bandwidth, particularly when multiple users stream simultaneously. Gigabit ethernet connections provide optimal performance for local network streaming, while internet upload speeds determine remote access quality.
Software Prerequisites
Ubuntu 24.04 LTS serves as our foundation, requiring a fully updated system with administrative access. The distribution’s stability and long-term support make it ideal for server applications requiring consistent uptime and security updates.
Java Runtime Environment represents Subsonic’s most critical dependency. The application requires Java 8 or newer, with OpenJDK providing an excellent open-source alternative to Oracle’s proprietary implementation. Proper Java installation ensures optimal Subsonic performance and compatibility.
Administrative privileges prove essential throughout the installation process. Root access or sudo capabilities enable package installation, service configuration, and system modifications necessary for proper Subsonic deployment.
Pre-installation Checklist
System update verification ensures compatibility and security. Fresh Ubuntu installations often require package updates before installing additional software. This process eliminates potential conflicts and provides the latest security patches.
User account planning affects long-term security and maintenance. Consider whether to run Subsonic under a dedicated system account or your primary user account. Dedicated accounts enhance security by limiting potential damage from application vulnerabilities.
Firewall preparation involves understanding network access requirements. Subsonic typically operates on port 4040, requiring firewall rules for remote access scenarios. Planning network configuration early prevents connectivity issues after installation.
Step 1: System Preparation and Updates
Updating Ubuntu 24.04 LTS
Begin by ensuring your Ubuntu system contains the latest packages and security updates. Open a terminal and execute the following commands to refresh package lists and upgrade existing software:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade -yThe update process may take several minutes depending on your system’s current state and internet connection speed. Allow the process to complete fully before proceeding. System updates provide critical security patches and ensure compatibility with newly installed software.
Reboot your system if kernel updates were installed during the upgrade process. While not always necessary, rebooting ensures all system components load with the latest updates. Check for required reboots by examining the /var/run/reboot-required file:
ls /var/run/reboot-requiredIf this file exists, reboot your system before continuing with the Subsonic installation.
Installing Java Runtime Environment
Subsonic requires Java Runtime Environment for proper operation. Ubuntu 24.04 LTS includes OpenJDK in its default repositories, providing a reliable and open-source Java implementation. Install OpenJDK 11, which offers excellent compatibility with Subsonic:
sudo apt install openjdk-11-jre-headless -yThe headless version excludes graphical components unnecessary for server applications, reducing system resource consumption and potential security exposure. Verify successful Java installation by checking the version:
java -versionExpected output should display OpenJDK version information, confirming proper installation. If multiple Java versions exist on your system, configure the default version using the alternatives system:
sudo update-alternatives --config javaSelect the appropriate Java version from the presented list if multiple options appear.
Step 2: Downloading and Installing Subsonic
Obtaining Subsonic Package
Navigate to the Subsonic download directory and obtain the latest Ubuntu/Debian package. Create a temporary directory for the download to maintain system organization:
mkdir ~/subsonic-install
cd ~/subsonic-installDownload the Subsonic .deb package using wget. The official Subsonic website provides direct links to the latest stable releases:
wget https://s3-eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/subsonic-public/download/subsonic-6.1.6.debVerify the downloaded package integrity by checking its size and ensuring the download completed successfully. The package should be approximately 100MB in size. If the download appears incomplete or corrupted, repeat the download process.
Alternative download methods include using a web browser to manually download the package from the official website, then transferring it to your Ubuntu server using SCP or other file transfer methods.
Installation Process
Install the downloaded Subsonic package using Ubuntu’s package manager. The dpkg command handles .deb package installation directly:
sudo dpkg -i subsonic-6.1.6.debDuring installation, you may encounter dependency warnings or errors. These typically involve missing Java dependencies that weren’t properly detected. Resolve dependency issues using apt:
sudo apt-get install -fThis command instructs apt to fix broken dependencies automatically, downloading and installing any required packages. After dependency resolution, verify Subsonic installation success by checking the service status:
sudo systemctl status subsonicThe output should indicate that Subsonic is loaded and active. If the service shows as failed or inactive, examine system logs for error messages that might indicate installation problems.
Enable Subsonic to start automatically at boot time, ensuring your media server remains available after system restarts:
sudo systemctl enable subsonicStep 3: Security Configuration and User Management
Creating Dedicated Subsonic User
Running applications as root poses significant security risks. Create a dedicated system user for Subsonic operations, limiting potential damage from security vulnerabilities. This user should have minimal privileges beyond those required for Subsonic functionality.
Create the subsonic user account with restricted shell access and no home directory:
sudo useradd -r -s /bin/false subsonicAdd the subsonic user to the audio group, enabling access to audio devices and files. This membership proves essential for proper media file handling and transcoding operations:
sudo usermod -a -G audio subsonicThe dedicated user approach follows security best practices by implementing the principle of least privilege. Should Subsonic experience security vulnerabilities, the impact remains limited to the subsonic user’s capabilities rather than full system access.
Modifying Configuration File
Subsonic’s primary configuration file resides at /etc/default/subsonic. This file controls service startup parameters, including user account, memory allocation, and network settings. Edit the configuration file using your preferred text editor:
sudo nano /etc/default/subsonicModify the SUBSONIC_USER parameter to use your newly created dedicated user:
SUBSONIC_USER=subsonicAdjust memory allocation based on your system’s available RAM and expected usage patterns. Larger music libraries benefit from increased memory allocation:
SUBSONIC_ARGS="--max-memory=512"For systems with 4GB or more RAM, consider allocating 1GB to Subsonic:
SUBSONIC_ARGS="--max-memory=1024"Configure the listening port if the default port 4040 conflicts with other services or security policies require alternative ports:
SUBSONIC_PORT=4040Save configuration changes and restart the Subsonic service to apply new settings:
sudo systemctl restart subsonicStep 4: Media Folder Setup and Permissions
Creating Media Directories
Subsonic requires properly configured directories for music storage and organization. Create a dedicated directory structure that facilitates media management and supports future expansion:
sudo mkdir -p /var/music
sudo mkdir -p /var/music/Music
sudo mkdir -p /var/music/Podcasts
sudo mkdir -p /var/music/VideosThis directory structure separates different media types while maintaining organizational clarity. The /var/music path serves as the primary media root, with subdirectories for specific content types.
Alternative directory locations include /home/subsonic/media or custom paths based on your storage configuration. Choose locations that provide adequate space for your media collection and allow for future growth.
Consider creating symbolic links if your media resides on different drives or network-attached storage devices. This approach maintains centralized directory structure while accessing distributed storage:
sudo ln -s /mnt/external-drive/music /var/music/ExternalMusicPermission Configuration
Proper file permissions ensure Subsonic can access media files while maintaining system security. Change ownership of the media directories to the subsonic user:
sudo chown -R subsonic:subsonic /var/musicSet appropriate permissions that allow reading by the subsonic user while preventing unauthorized access:
sudo chmod -R 755 /var/musicThese permissions grant full access to the subsonic user while allowing other users to read directory contents but not modify files. This configuration balances functionality with security considerations.
For existing media collections, copy or move files to the Subsonic directories while preserving proper ownership:
sudo cp -R /home/user/Music/* /var/music/Music/
sudo chown -R subsonic:subsonic /var/music/Music/Verify permissions are correctly applied by listing directory contents with detailed information:
ls -la /var/music/The output should show subsonic ownership for all directories and files within the media structure.
Step 5: Initial Web Interface Configuration
Accessing Subsonic Web Interface
With Subsonic installed and configured, access the web interface through your browser. Navigate to the server’s IP address followed by the configured port number. For local access, use:
http://localhost:4040For remote access from other devices on your network, replace localhost with your server’s IP address:
http://192.168.1.100:4040Determine your server’s IP address using the ip addr command if uncertain:
ip addr showLook for your primary network interface (usually eth0 or wlan0) and note the inet address listed.
Modern web browsers should display the Subsonic login page without issues. If the page fails to load, verify that the Subsonic service is running and check firewall settings that might block port 4040.
First-Time Setup
Subsonic ships with default administrator credentials for initial setup. Log in using the following credentials:
- Username:
admin - Password:
admin
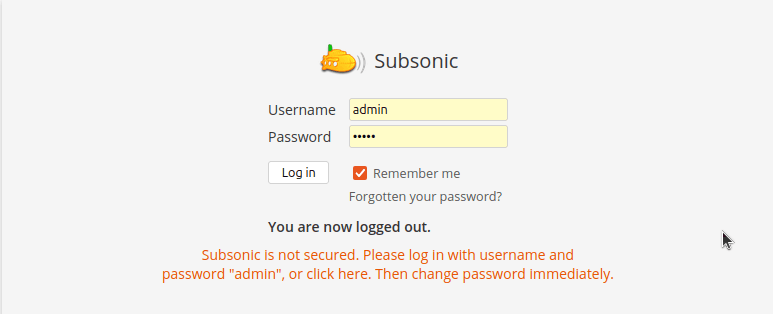
Immediately change the administrator password after first login to enhance security. Navigate to Settings > Users and select the admin user to modify the password. Choose a strong password containing uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
Create additional user accounts for family members or friends who will access your media server. Each user can have customized permissions controlling folder access, streaming quality, and administrative capabilities.
Configure basic server settings through the Settings > General tab. Set your server’s external URL if you plan to access Subsonic from outside your home network. This setting enables proper link generation and mobile app connectivity.
Add your media folders through Settings > Media folders. Click “Add folder” and browse to /var/music/Music or your chosen media directory. Subsonic will scan the folder and index all contained audio files, making them available for streaming.
Step 6: Advanced Configuration Options
Media Folder Configuration
Subsonic’s media folder management system provides granular control over content organization and access. Navigate to Settings > Media folders to configure multiple media sources and customize scanning behavior.
Add separate folders for different music genres, artists, or quality levels. This organization method enables creating user-specific access controls and simplifies library management:
/var/music/Music/Classical/var/music/Music/Rock/var/music/Music/Jazz
Configure folder scanning intervals to balance library freshness with system performance. Frequent scans ensure new additions appear quickly but consume system resources. For stable libraries, daily or weekly scans prove sufficient.
Enable folder watching for real-time updates when adding new media files. This feature automatically triggers rescans when file system changes occur within monitored directories, maintaining current library status without manual intervention.
Transcoding settings optimize streaming for different devices and network conditions. Configure multiple transcoding profiles targeting various scenarios:
- High quality for local network streaming
- Medium quality for mobile devices
- Low quality for limited bandwidth connections
Network and Remote Access
External access configuration enables streaming from anywhere with internet connectivity. This setup requires careful security considerations and network configuration to maintain both functionality and protection.
Configure your router to forward port 4040 to your Ubuntu server’s internal IP address. This port forwarding rule allows external internet traffic to reach your Subsonic server while maintaining local network security.
Set up Dynamic DNS if your internet service provider assigns changing IP addresses. Services like DuckDNS or No-IP provide stable domain names that automatically update when your IP address changes, ensuring consistent external access.
Consider implementing SSL/TLS encryption for external access scenarios. While Subsonic includes basic SSL support, a reverse proxy configuration with Nginx or Apache provides more robust security and certificate management capabilities.
Configure the external server URL in Subsonic settings to match your domain name or external IP address. This setting ensures mobile applications and external links function correctly when accessing your server remotely.
Step 7: Setting Up Reverse Proxy with Nginx (Optional)
Benefits of Reverse Proxy
Implementing a reverse proxy adds security layers and enables advanced features like SSL encryption and custom domain names. Nginx excels as a reverse proxy due to its performance characteristics and extensive configuration options.
SSL certificate management becomes streamlined through Nginx, supporting Let’s Encrypt for free automated certificates. This encryption protects authentication credentials and media streams from interception during transmission.
Custom domain names replace IP addresses and port numbers with memorable URLs like music.yourdomain.com. This improvement enhances user experience and simplifies mobile app configuration for family members and guests.
Basic Nginx Configuration
Install Nginx on your Ubuntu 24.04 LTS system using the default repository packages:
sudo apt install nginx -yCreate a new Nginx configuration file for your Subsonic proxy:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/subsonicAdd the following basic configuration, replacing yourdomain.com with your actual domain:
server {
listen 80;
server_name music.yourdomain.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:4040;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
}Enable the configuration by creating a symbolic link:
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/subsonic /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/Test the Nginx configuration for syntax errors:
sudo nginx -tRestart Nginx to apply the new configuration:
sudo systemctl restart nginxTroubleshooting Common Issues
Service and Startup Problems
Subsonic service failures often relate to Java configuration or permission issues. Check service status for detailed error information:
sudo systemctl status subsonic -lExamine Subsonic logs for specific error messages that indicate the root cause:
sudo tail -f /var/subsonic/subsonic.logCommon Java-related issues include incorrect JAVA_HOME environment variables or incompatible Java versions. Verify Java installation and set JAVA_HOME explicitly if necessary:
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64Memory allocation problems manifest as OutOfMemoryError exceptions in log files. Increase memory allocation in /etc/default/subsonic configuration file to resolve these issues.
Permission and Access Issues
File permission problems prevent Subsonic from accessing media files or writing to necessary directories. Verify subsonic user ownership of all media directories:
sudo find /var/music -not -user subsonic -lsThis command identifies files not owned by the subsonic user, allowing targeted permission corrections. Fix ownership issues using chown:
sudo chown -R subsonic:subsonic /var/musicNetwork connectivity problems often involve firewall rules blocking port access. Check UFW status and add rules if necessary:
sudo ufw status
sudo ufw allow 4040SELinux configurations on some systems may prevent Java applications from binding to network ports. Check SELinux status and create appropriate policies if enabled.
Performance Optimization
Memory allocation tuning improves performance for large music libraries and multiple concurrent users. Monitor memory usage during peak usage periods:
free -h
ps aux | grep subsonicAdjust memory allocation based on actual usage patterns rather than theoretical requirements. Start with conservative allocations and increase gradually while monitoring system performance.
Transcoding optimization reduces CPU usage during format conversion operations. Configure transcoding to use hardware acceleration when available, or limit concurrent transcoding sessions to prevent system overload.
Best Practices and Security Recommendations
Security Hardening
Regular system updates maintain security patches for both Ubuntu and Subsonic. Implement automatic security updates to ensure timely patch installation:
sudo apt install unattended-upgrades
sudo dpkg-reconfigure unattended-upgradesUser access control prevents unauthorized access to your media library. Implement strong password policies and consider two-factor authentication for administrative accounts when available through plugins or external authentication systems.
Network security involves limiting access to necessary ports and IP ranges. Configure firewall rules that restrict Subsonic access to trusted networks:
sudo ufw allow from 192.168.1.0/24 to any port 4040Regular security audits identify potential vulnerabilities in your configuration. Monitor access logs for unusual activity patterns that might indicate security breaches or unauthorized access attempts.
Backup and Maintenance
Configuration backup procedures protect against data loss during system failures or configuration errors. Create regular backups of critical Subsonic configuration files:
sudo tar -czf subsonic-backup-$(date +%Y%m%d).tar.gz /var/subsonic /etc/default/subsonicMedia library organization affects both performance and usability. Implement consistent naming conventions and directory structures that facilitate automated management and user navigation.
Database maintenance ensures optimal performance as your library grows. Subsonic automatically maintains its internal database, but periodic optimization during low-usage periods can improve responsiveness.
Monitor disk space usage regularly, particularly on systems with active transcoding that creates temporary files. Implement automated cleanup procedures for transcoding cache and log rotation to prevent disk space exhaustion.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Subsonic. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Subsonic Media Server on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Subsonic Media Server website.