How To Install TeamViewer on Fedora 42

Remote access technology has become fundamental to modern computing workflows. TeamViewer stands as one of the most trusted remote desktop solutions, offering comprehensive features for remote control, file sharing, and collaborative work. For Fedora 42 users, installing TeamViewer provides seamless connectivity across different platforms and operating systems.
This comprehensive guide covers multiple installation methods, troubleshooting techniques, and optimization strategies specifically tailored for Fedora 42. Whether you’re a system administrator managing multiple servers or a developer requiring remote access capabilities, this tutorial ensures successful TeamViewer deployment on your Fedora system.
Understanding TeamViewer and Fedora 42 Compatibility
What is TeamViewer?
TeamViewer is a proprietary remote access software that enables users to connect to computers and mobile devices anywhere in the world. The software provides essential functions including remote desktop control, file transfer capabilities, desktop sharing, and web conferencing features. Unlike open-source alternatives, TeamViewer offers enterprise-grade security and cross-platform compatibility.
The application supports various use cases from technical support to business presentations. Remote server management, troubleshooting assistance, and collaborative development work represent common scenarios where TeamViewer excels. Its intuitive interface makes it accessible for both technical and non-technical users.
Fedora 42 System Requirements
Before proceeding with installation, verify your Fedora 42 system meets TeamViewer’s requirements. The software requires a Linux kernel version 2.6.27 or higher, which Fedora 42 easily satisfies. Both x86_64 and x86_32 bit architectures are supported, though x86_64 is recommended for optimal performance.
TeamViewer depends on GLIBC 2.17 for core functionality. Fedora 42’s modern package management ensures these dependencies are automatically resolved during installation. Additionally, sufficient RAM (minimum 2GB) and storage space (approximately 200MB) are necessary for smooth operation.
The software integrates with both GNOME and KDE desktop environments commonly used on Fedora systems. Network connectivity requirements include stable internet access and appropriate firewall configuration for remote connections.
Pre-Installation Preparation
System Updates and Prerequisites
Maintaining an updated Fedora 42 system ensures compatibility and security. Execute the following command to update your system packages:
sudo dnf update -yInstall essential utilities required for TeamViewer installation:
sudo dnf install wget curl -yVerify your system architecture using the uname -m command. This information helps select the correct TeamViewer package version. Most modern Fedora installations use x86_64 architecture.
Check available disk space in your home directory and /opt folder where TeamViewer files will be stored. Insufficient space can cause installation failures or runtime issues.
Display Server Considerations
Fedora 42 typically uses Wayland as the default display server, but TeamViewer lacks native Wayland support. This compatibility limitation requires switching to GNOME on Xorg for proper functionality.
To switch from Wayland to Xorg, log out of your current session and select “GNOME on Xorg” from the login screen gear menu. This change ensures TeamViewer can properly access display resources and input devices.
The Xorg switch may impact trackpad gesture functionality and some modern display features. However, remote desktop performance typically improves with Xorg’s mature graphics handling. Consider this trade-off when planning your TeamViewer deployment.
Method 1: Direct RPM Package Installation
Downloading TeamViewer RPM Package
The most straightforward installation method involves downloading TeamViewer’s official RPM package. Navigate to TeamViewer’s Linux download page or use wget for direct download:
wget https://download.teamviewer.com/download/linux/teamviewer.x86_64.rpm
This command downloads the latest x86_64 RPM package to your current directory. The package size typically ranges from 30-50MB depending on the version. Verify the download completed successfully by checking file size and integrity.
Alternative download methods include using curl or downloading through a web browser. Ensure you download from TeamViewer’s official sources to avoid security risks from unofficial packages.
Installing via DNF Package Manager
DNF (Dandified YUM) serves as Fedora’s primary package manager, providing automatic dependency resolution. Install the downloaded RPM package using:
sudo dnf install ./teamviewer.x86_64.rpm -yThis command automatically handles dependency installation, including required libraries and framework components. DNF resolves conflicts and ensures system compatibility during the process.
If you encounter “dnf command not found” errors, verify DNF installation or use the legacy YUM package manager as an alternative. Modern Fedora systems should include DNF by default.
Monitor the installation output for any error messages or warnings. Successful installation displays a “Complete!” message along with installed package details.
Verifying Installation Success
Confirm TeamViewer installation using the RPM query command:
rpm -qi teamviewerThis command displays comprehensive package information including version number, installation date, and package description. Verify the version matches your expected TeamViewer release.
Check installation directories and file permissions:
ls -la /opt/teamviewer/Proper installation creates the TeamViewer directory structure with appropriate executable permissions. Missing files or incorrect permissions indicate installation problems requiring troubleshooting.
Method 2: Repository-Based Installation
Adding TeamViewer Official Repository
Repository-based installation provides automatic updates and simplified package management. Create a repository configuration file using your preferred text editor:
sudo nano /etc/yum.repos.d/teamviewer.repoAdd the following repository configuration:
[teamviewer]
name=TeamViewer
baseurl=https://linux.teamviewer.com/yum/stable/main/binary-$basearch/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://linux.teamviewer.com/pubkey/currentkey.ascThis configuration enables the official TeamViewer repository with GPG verification for enhanced security. The $basearch variable automatically selects the appropriate architecture package.
Import the GPG key to verify package authenticity:
sudo rpm --import https://linux.teamviewer.com/pubkey/currentkey.ascInstalling from Repository
With the repository configured, install TeamViewer using standard DNF commands:
sudo dnf install teamviewer -yRepository installation offers several advantages over direct RPM installation. Automatic dependency resolution ensures all required packages are installed. Future updates arrive through normal system update procedures.
The installation process downloads the latest TeamViewer version from the official repository. This method typically provides more recent versions than standalone RPM packages.
Repository Troubleshooting
Common repository issues include 403 errors and $basearch variable problems. If encountering access errors, verify internet connectivity and DNS resolution to TeamViewer’s servers.
GPG key import failures may occur due to network restrictions or proxy configurations. Manually download and import the key file if automatic import fails:
wget https://linux.teamviewer.com/pubkey/currentkey.asc
sudo rpm --import currentkey.ascRepository metadata cache problems can cause update failures. Clear DNF cache and regenerate metadata:
sudo dnf clean all
sudo dnf makecachePost-Installation Configuration
Initial Launch and Setup
Launch TeamViewer from the command line to initiate first-time setup:
teamviewerThe initial launch performs system compatibility checks and license agreement acceptance. TeamViewer verifies CPU architecture, graphics capabilities, and network connectivity during initialization.
Accept the license terms to proceed with configuration. The software creates user configuration directories and establishes system integration settings. This process typically completes within 30-60 seconds.
First launch may display security warnings related to Wayland compatibility. These warnings are expected when using Xorg and don’t indicate installation problems.
GUI Configuration
Access TeamViewer through Fedora’s Activities menu in GNOME. Click “Show Applications” to display the application grid and locate the TeamViewer icon.
Create desktop shortcuts for convenient access:
cp /opt/teamviewer/tv_bin/desktop/com.teamviewer.TeamViewer.desktop ~/Desktop/Pin TeamViewer to your dock or favorites for quick launching. The application integrates seamlessly with GNOME’s notification system and desktop environment features.
Account Setup and Authentication
Create a TeamViewer account for enhanced features including unattended access and contact management. Account creation enables cloud-based connection history and cross-device synchronization.
Configure unattended access credentials for remote server management. Set strong passwords and enable two-factor authentication for security. Document your TeamViewer ID and password for future reference.
Security settings include connection logging, session recording, and access restrictions. Customize these features based on your security requirements and organizational policies.
Testing and Verification
Basic Functionality Testing
Verify TeamViewer functionality by testing core features. Initiate a connection to another device using the partner ID system. Test both incoming and outgoing connections to ensure bidirectional compatibility.
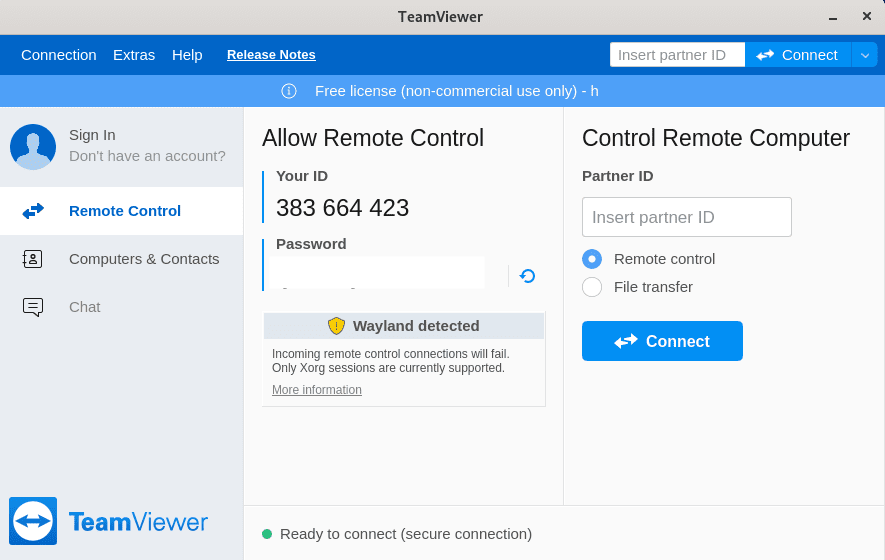
Evaluate file transfer capabilities by exchanging small test files between connected devices. Check file integrity and transfer speeds to assess network performance. Audio and video quality testing ensures multimedia features function correctly.
Performance benchmarking helps establish baseline expectations for your Fedora 42 system. Monitor CPU usage, memory consumption, and network utilization during active sessions.
Network Configuration Validation
Configure firewall rules to allow TeamViewer traffic. The software uses dynamic port allocation but typically requires outbound HTTPS (port 443) and HTTP (port 80) access.
Test connections through different network configurations including NAT, firewall, and proxy environments. NAT traversal capabilities handle most network scenarios automatically without manual configuration.
Verify connection quality indicators within TeamViewer’s interface. Green indicators suggest optimal connectivity while yellow or red warnings indicate potential performance issues requiring network optimization.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Installation Problems
Dependency conflicts represent common installation challenges. Resolve conflicts by updating system packages or manually installing missing dependencies. Use dnf deplist teamviewer to identify specific requirements.
Package signature verification errors occur when GPG keys are missing or corrupted. Re-import TeamViewer’s public key and verify its authenticity through official channels.
Insufficient permissions during installation require sudo access or root privileges. Ensure your user account has appropriate administrative rights for system-wide software installation.
Disk space limitations prevent successful installation. Clear temporary files and ensure adequate space in /opt, /tmp, and user directories before attempting installation.
Runtime Issues
Wayland compatibility problems manifest as display errors or input device malfunctions. Switch to GNOME on Xorg session to resolve these issues. Restart your desktop session after making display server changes.
Audio and video synchronization problems may occur with certain hardware configurations. Adjust audio settings within TeamViewer’s preferences and verify ALSA/PulseAudio configuration.
Performance optimization on older hardware involves reducing visual effects and limiting concurrent sessions. Monitor system resources and adjust quality settings based on available capacity.
Network and Connectivity Issues
Firewall configuration significantly impacts TeamViewer performance. Configure iptables or firewalld to allow necessary ports and protocols. Consider creating specific rules for TeamViewer traffic.
Corporate networks and proxy servers may block or restrict remote desktop connections. Configure proxy settings within TeamViewer or request network administrator assistance for proper access.
VPN compatibility varies depending on the VPN protocol and configuration. Some VPN configurations may conflict with TeamViewer’s connection establishment requiring protocol adjustments or exclusions.
Security Considerations and Best Practices
Security Configuration
Enable two-factor authentication for all TeamViewer accounts to prevent unauthorized access. Use authenticator applications rather than SMS-based verification for enhanced security.
Configure strong passwords with complexity requirements including uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and special characters. Avoid dictionary words and personal information in password creation.
Implement session recording for audit trails and compliance requirements. Configure automatic recording for unattended sessions while allowing manual control for interactive sessions.
Understanding TeamViewer’s encryption protocols ensures data protection during transmission. The software uses RSA public/private key exchange and AES session encryption for secure communications.
Best Practices for Safe Usage
Maintain regular software updates through DNF’s automatic update system or manual update procedures. Security patches and feature improvements require current software versions.
Monitor active sessions through TeamViewer’s management console. Unauthorized access detection helps identify potential security breaches or compromised credentials.
Implement corporate policy compliance measures for business environments. Document acceptable use policies and provide user training for secure remote access practices.
Privacy considerations include data retention policies and geographic restrictions. Configure settings to meet organizational privacy requirements and regulatory compliance needs.
Alternatives and Comparisons
Open Source Alternatives
VNC-based solutions provide open-source remote access capabilities for Fedora systems. TigerVNC and RealVNC offer similar functionality without proprietary licensing restrictions.
SSH with X11 forwarding enables secure remote application execution over encrypted connections. This method suits command-line intensive workflows and provides excellent security.
RDP clients such as Remmina facilitate connections to Windows systems using Microsoft’s Remote Desktop Protocol. These tools complement TeamViewer for mixed-environment deployments.
Performance comparisons reveal different strengths among remote access solutions. Open-source alternatives often provide better customization while proprietary solutions offer superior ease-of-use.
Commercial Alternatives
AnyDesk represents a direct TeamViewer competitor with similar features and cross-platform support. Installation procedures and system requirements closely match TeamViewer’s specifications.
Chrome Remote Desktop offers browser-based remote access without dedicated client software. This solution works well for occasional remote access needs with minimal setup requirements.
Enterprise solutions including Citrix and VMware provide comprehensive virtual desktop infrastructure. These platforms suit large-scale deployments with advanced management requirements.
Cost-benefit analysis should consider licensing costs, feature requirements, and support needs when selecting remote access solutions for different use cases.
Maintenance and Updates
Keeping TeamViewer Updated
Repository-based installations receive automatic updates through standard DNF update procedures. Enable automatic updates or perform manual updates regularly to maintain security and functionality.
Manual update procedures for RPM installations require downloading and installing new package versions. Monitor TeamViewer’s website for security advisories and feature releases.
Version compatibility checking ensures updated software maintains compatibility with existing configurations and connected devices. Test updates in non-production environments when possible.
Rollback procedures help recover from problematic updates. Maintain backup configurations and document rollback steps for critical system deployments.
System Maintenance
Regular Fedora system updates may affect TeamViewer compatibility or performance. Test TeamViewer functionality after major system updates to identify potential issues.
Log file management prevents disk space consumption from growing log files. Configure log rotation and cleanup procedures for /opt/teamviewer/logfiles/ directory.
Performance monitoring helps identify degradation over time. Monitor CPU usage, memory consumption, and network performance during typical usage patterns.
Backup and restore procedures should include TeamViewer configurations, contact lists, and access credentials. Document recovery procedures for disaster recovery planning.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed TeamViewer. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the TeamViewer remote desktop software on your Fedora 42 Linux system. For additional or useful information, we recommend you check the official TeamViewer website.