How To Install Thunderbird Mail on AlmaLinux 10

Mozilla Thunderbird stands as one of the most reliable and feature-rich email clients available for Linux distributions. This comprehensive guide walks through every method to successfully install Thunderbird Mail on AlmaLinux 10, ensuring optimal performance and seamless integration with your desktop environment.
AlmaLinux 10, being the latest enterprise-grade Linux distribution, provides excellent compatibility with Thunderbird’s robust email management capabilities. Whether you’re migrating from another email client or setting up a fresh email solution, Thunderbird offers enterprise-level features wrapped in an intuitive interface that scales from personal use to organizational deployment.
Prerequisites and System Requirements
AlmaLinux 10 System Requirements
Before installing Thunderbird on AlmaLinux 10, verify your system meets the minimum requirements. Thunderbird requires glibc 2.17 or higher, GTK+ 3.14 or later, and libstdc++ 4.8.1 or newer. Most AlmaLinux 10 installations exceed these specifications by default.
Your system needs at least 200 MB of available disk space for the basic installation. Additional space is required for email storage, which varies based on usage patterns. Memory requirements are modest, with 512 MB RAM being sufficient for basic operations, though 1 GB or more provides better performance for heavy email usage.
Administrative privileges are essential for system-wide installation methods. Ensure your user account has sudo access or root permissions before proceeding with the installation process.
Network and Repository Access
A stable internet connection is mandatory for downloading packages and dependencies. Verify that your AlmaLinux 10 system can access external repositories by running basic connectivity tests. The default AlmaLinux repositories should be enabled and functional for package manager installations.
Understanding DNF Package Manager
DNF (Dandified YUM) serves as AlmaLinux 10’s default package manager, offering superior dependency resolution and improved performance over its predecessor. This modern package manager automatically handles software dependencies, ensuring Thunderbird installs with all required libraries and components.
DNF maintains package integrity through cryptographic verification and provides rollback capabilities for failed installations. Understanding basic DNF commands enhances your ability to manage Thunderbird installations effectively, including updates, queries, and troubleshooting.
The package manager integrates seamlessly with AlmaLinux’s system update mechanisms, ensuring Thunderbird receives security updates and bug fixes automatically through regular system maintenance.
Method 1: Installing Thunderbird via DNF (Recommended)
System Preparation
Begin by updating your AlmaLinux 10 system to ensure all packages are current. Open a terminal and execute the following command:
sudo dnf update -yThis command refreshes the package cache and updates existing packages to their latest versions. The process may take several minutes depending on your system’s current state and available updates.
Thunderbird Installation Process
Install Thunderbird using DNF with this simple command:
sudo dnf install thunderbird -yDNF automatically resolves dependencies and downloads approximately 80-100 MB of packages. The installation process typically completes within 2-5 minutes on modern systems with adequate internet connectivity.
Verify the installation by checking Thunderbird’s version:
thunderbird --versionThis command displays the installed Thunderbird version, confirming successful installation. The output should show something like “Thunderbird 115.x.x” or similar, depending on the version available in AlmaLinux 10 repositories.
Advantages of DNF Installation
The DNF method provides several benefits over alternative installation approaches. System integration is seamless, with automatic desktop file creation, menu entries, and file associations. Updates arrive through regular system maintenance, ensuring consistent security patches.
Dependencies are automatically managed, preventing library conflicts and ensuring optimal performance. The installation follows AlmaLinux packaging standards, maintaining system stability and compatibility with other applications.
Method 2: Installing Thunderbird via Flatpak
Setting up Flatpak Environment
Flatpak offers access to the latest Thunderbird releases directly from Mozilla’s development team. Install Flatpak and configure Flathub repository access:
sudo dnf install flatpak -y
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepoRestart your system or log out and back in to complete the Flatpak integration with your desktop environment.
Flatpak Thunderbird Installation
Install Thunderbird using Flatpak with this command:
flatpak install flathub org.mozilla.ThunderbirdThe installation downloads approximately 150-200 MB of data, including Thunderbird and its runtime dependencies. This method often provides newer versions than distribution repositories.
Launch Thunderbird using Flatpak:
flatpak run org.mozilla.ThunderbirdBenefits and Considerations
Flatpak installations run in sandboxed environments, providing enhanced security isolation. This method delivers the latest stable Thunderbird versions directly from Mozilla, often weeks ahead of distribution repositories.
However, Flatpak applications consume more disk space due to bundled dependencies and may have slightly longer startup times. The sandboxing occasionally limits integration with system components, though this rarely affects email functionality.
Method 3: Manual Installation from Mozilla
Downloading Official Thunderbird
Visit Mozilla’s official Thunderbird download page and select the Linux version. Download the tar.bz2 archive, which typically ranges from 60-80 MB depending on the version.
Navigate to your download directory:
cd ~/DownloadsSystem-Wide Manual Installation
Extract the downloaded archive:
tar xjf thunderbird-*.tar.bz2
rm thunderbird-*.tar.bz2Move Thunderbird to the system directory:
sudo mv thunderbird /optCreate a symbolic link for system-wide access:
sudo ln -s /opt/thunderbird/thunderbird /usr/local/bin/thunderbirdDownload and install the desktop file:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mozilla/sumo-kb/main/installing-thunderbird-linux/thunderbird.desktop -P /usr/local/share/applicationsThis method provides complete control over the installation location and version management.
User-Specific Installation Alternative
For installations without administrative privileges, extract Thunderbird to your home directory:
mv thunderbird $HOME/thunderbirdLaunch Thunderbird directly:
$HOME/thunderbird/thunderbird &Create a desktop shortcut by downloading the desktop file to your user applications directory and modifying the paths accordingly.
Post-Installation Configuration
Initial Thunderbird Launch
Launch Thunderbird using any of these methods:
- Command line:
thunderbird - Desktop menu: Search for “Thunderbird” in activities
- Flatpak:
flatpak run org.mozilla.Thunderbird
The first launch presents a setup wizard guiding you through initial configuration. Thunderbird automatically detects common email providers and suggests optimal settings.
Desktop Integration Verification
Confirm that Thunderbird appears in your desktop environment’s application menu. The installation should create appropriate file associations for email-related files and protocols.
Check system notifications work correctly by sending yourself a test email after configuration. Thunderbird integrates with AlmaLinux 10’s notification system to alert you of new messages.
Email Account Configuration
Setting Up Your First Account
Thunderbird’s Account Setup Wizard simplifies email configuration for most providers. Enter your email address and password; Thunderbird automatically detects server settings for major providers like Gmail, Outlook, and Yahoo.
For manual configuration, gather these details from your email provider:
- IMAP/POP3 server addresses
- SMTP server settings
- Port numbers and security protocols
- Authentication methods
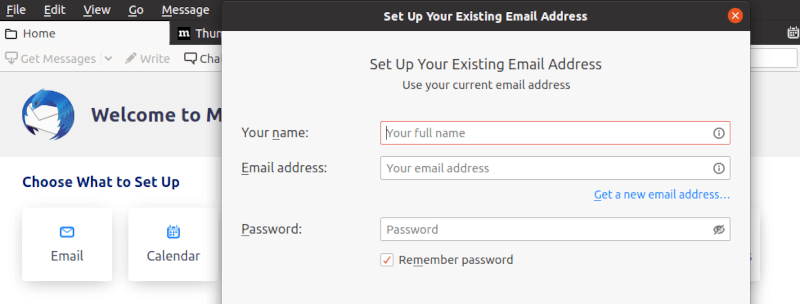
IMAP vs POP3 Configuration
Choose IMAP for multi-device email access, as it synchronizes messages across all devices. IMAP stores emails on the server, making them accessible from anywhere with an internet connection.
POP3 downloads emails to your local machine, removing them from the server by default. This protocol suits single-device usage and conserves server storage space.
Configure SSL/TLS encryption for all connections to ensure email security. Modern email providers require encrypted connections for both incoming and outgoing mail servers.
Managing Multiple Email Accounts
Add additional accounts through Account Settings > Account Actions > Add Mail Account. Thunderbird supports unlimited email accounts, organizing them in a unified interface.
Configure different notification settings for each account based on priority. Set up unified folders to view messages from all accounts in combined inbox views.
Organize accounts using folder structures and filters to maintain efficient email management across multiple addresses.
Security and Privacy Settings
Essential Security Configuration
Enable strong encryption for all email communications. Navigate to Preferences > Privacy & Security to configure encryption settings. Consider installing privacy-focused add-ons for enhanced security.
Configure automatic updates to receive security patches promptly. Set up master password protection for stored account credentials, adding an extra security layer to your email access.
Enable two-factor authentication where your email providers support it. This significantly enhances account security beyond password protection alone.
Privacy Protection Measures
Disable remote content loading by default to prevent tracking pixels from revealing when you read emails. Configure do-not-track preferences and limit data collection in Thunderbird’s privacy settings.
Review and customize cookie policies for web content displayed within Thunderbird. Enable safe browsing features to protect against malicious email content and phishing attempts.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Installation Problems
Repository connection issues may prevent DNF installations. Verify internet connectivity and check repository configuration:
sudo dnf repolistIf repositories are missing or disabled, re-enable them or check network settings.
Dependency conflicts occasionally occur during installation. Resolve these by updating the entire system first or using DNF’s conflict resolution options:
sudo dnf install thunderbird --best --allowerasingRuntime and Display Issues
Missing library errors typically indicate incomplete installations or corrupted packages. Reinstall Thunderbird completely:
sudo dnf remove thunderbird
sudo dnf install thunderbirdDisplay problems in Wayland environments may require specific environment variables. Launch Thunderbird with:
MOZ_ENABLE_WAYLAND=1 thunderbirdEmail Configuration Problems
Server connection failures often result from incorrect settings or firewall restrictions. Verify server addresses, ports, and authentication methods with your email provider.
Test connections using command-line tools like telnet or openssl to isolate network issues from Thunderbird-specific problems.
Firewall configurations may block email ports (993 for IMAPS, 465/587 for SMTP). Configure firewall rules to allow these connections for Thunderbird functionality.
Updating and Maintenance
Keeping Thunderbird Current
DNF installations receive updates through regular system maintenance:
sudo dnf update -yThis command updates Thunderbird along with other system packages. Configure automatic updates in AlmaLinux 10’s system settings for seamless maintenance.
Flatpak installations require separate update commands:
flatpak updateManual installations need periodic checks at Mozilla’s website for new releases, followed by manual update procedures.
System Maintenance Best Practices
Regular database maintenance improves Thunderbird’s performance. Compact folders periodically to reclaim disk space and optimize message access speeds.
Backup Thunderbird profiles before major updates or system changes. Profiles contain all email data, settings, and customizations, making backup essential for data preservation.
Monitor disk space usage, especially with IMAP accounts that cache large amounts of email data locally. Configure storage limits to prevent excessive disk consumption.
Advanced Features and Customization
Add-ons and Extensions
Thunderbird’s add-on ecosystem extends functionality significantly. Popular add-ons include:
- Lightning Calendar for scheduling
- ExQuilla for Exchange server support
- QuickText for email templates
- ImportExportTools for data migration
Install add-ons through Tools > Add-ons and Themes. Verify add-on compatibility with your Thunderbird version before installation.
Interface Customization
Thunderbird supports multiple themes, from light and dark modes to custom color schemes. Access themes through the Add-ons manager’s Themes section.
Customize toolbars by right-clicking and selecting “Customize.” Rearrange buttons, add new functions, or remove unused elements to optimize workflow.
Configure keyboard shortcuts through Preferences > General to accelerate common operations. Custom shortcuts significantly improve productivity for frequent email users.
Advanced Email Management
Create sophisticated filter rules to automatically sort incoming messages. Filters can move messages to folders, tag them, forward to other addresses, or delete unwanted content.
Set up message archiving strategies to manage long-term email storage. Configure automatic archiving based on age or folder rules to maintain organized mailboxes.
Optimize search indexing for faster email retrieval. Thunderbird builds searchable indexes of email content, making message location efficient even in large archives.
Performance Optimization
Resource Management
Thunderbird’s memory usage varies based on account configuration and usage patterns. Limit memory consumption by configuring cache sizes appropriately for your system’s available RAM.
Disk space management becomes critical with multiple IMAP accounts. Set offline storage limits to prevent excessive local caching while maintaining adequate performance.
Network bandwidth optimization involves configuring message download limits and offline synchronization settings. Balance performance with data usage constraints.
Thunderbird-Specific Optimizations
Database maintenance tools built into Thunderbird improve long-term performance. Use “Repair Folder” options for corrupted mailboxes and compact folders regularly.
Disable unnecessary features like automatic spell-checking for non-English users or chat integration if unused. Each disabled feature reduces resource consumption.
Configure startup optimization by limiting accounts that check mail automatically at launch. Stagger mail checking intervals to reduce simultaneous network activity.
Alternative Installation Methods
Snap Package Installation
AlmaLinux 10 supports Snap packages as an alternative installation method. Install snapd first:
sudo dnf install snapd
sudo systemctl enable --now snapd.socketInstall Thunderbird via Snap:
sudo snap install thunderbirdSnap packages update automatically and provide sandboxed execution similar to Flatpak installations.
AppImage Execution
While not officially supported, Thunderbird AppImage versions provide portable execution without installation. Download AppImage files from third-party sources and execute directly after making them executable.
Uninstallation Procedures
Complete DNF Removal
Remove Thunderbird installed via DNF:
sudo dnf remove thunderbirdThis command removes the application while preserving user data and configuration files.
Flatpak Uninstallation
Remove Flatpak installations completely:
flatpak uninstall --delete-data org.mozilla.ThunderbirdThe --delete-data flag removes user data along with the application.
Manual Installation Cleanup
For manual installations, remove files from their installation directories:
sudo rm -rf /opt/thunderbird
sudo rm /usr/local/bin/thunderbird
sudo rm /usr/local/share/applications/thunderbird.desktopData Migration and Backup
Profile Management
Thunderbird profiles contain all user data, including emails, settings, and add-ons. Locate profiles in ~/.thunderbird/ directory for backup purposes.
Copy entire profile folders to preserve complete email environments. Profile backups enable easy restoration after system changes or migrations to different machines.
Import and Export Options
Thunderbird supports various import formats for migrating from other email clients. The ImportExportTools add-on expands import capabilities significantly.
Export email data in standard formats like mbox or EML for compatibility with other email clients. Regular exports serve as additional backup measures beyond profile copying.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Thunderbird. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Thunderbird open-source e-mail client on your AlmaLinux OS 10 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Thunderbird website.