How To Install Thunderbird Mail on Debian 13

Email management remains crucial for personal and professional communication in today’s digital landscape. Mozilla Thunderbird stands as one of the most reliable and feature-rich email clients available for Linux systems. This comprehensive guide demonstrates how to install Thunderbird Mail on Debian 13, providing multiple installation methods to suit different user preferences and technical requirements.
Debian 13 users benefit significantly from Thunderbird’s robust email management capabilities, cross-platform compatibility, and open-source foundation. Whether you’re migrating from another email client or setting up your first desktop email solution, this tutorial covers everything from basic installation to advanced configuration options.
This article explores three primary installation methods: using the APT package manager, manual installation from Mozilla’s official source, and Snap package installation. Each approach offers distinct advantages depending on your specific needs and system configuration preferences.
Understanding Thunderbird Mail Client
What is Thunderbird?
Mozilla Thunderbird represents a free, open-source email client developed by the Mozilla Foundation, the same organization behind Firefox browser. This cross-platform application supports Windows, macOS, and Linux distributions, making it an excellent choice for users seeking consistent email management across multiple operating systems.
The Thunderbird project maintains active community-driven development, ensuring regular updates, security patches, and feature enhancements. Its commitment to open-source principles means users enjoy complete transparency regarding functionality and data handling practices.
Key Features and Benefits
Thunderbird excels in supporting multiple email accounts simultaneously, accommodating both IMAP and POP3 protocols seamlessly. Users can manage personal, professional, and organizational email accounts within a unified interface, streamlining communication workflows.
Advanced spam filtering capabilities protect users from unwanted messages while intelligent security features safeguard against phishing attempts and malicious content. The integrated calendar system supports event scheduling, task management, and appointment reminders, transforming Thunderbird into a comprehensive productivity suite.
The extensive add-ons ecosystem allows users to customize functionality according to specific requirements. Popular extensions include advanced encryption tools, productivity enhancers, and interface modifications. Built-in OpenPGP support enables end-to-end email encryption for sensitive communications.
RSS feed reader functionality consolidates news consumption within the same application used for email management. This integration simplifies information gathering from multiple sources without requiring separate feed reader applications.
Prerequisites and System Requirements
System Requirements
Successful Thunderbird installation on Debian 13 requires several fundamental prerequisites. Your system must run a stable Debian 13 release with administrative privileges available through sudo access. An active internet connection facilitates package downloads and updates during the installation process.
Hardware requirements remain modest for typical email usage. Modern systems with 2GB RAM and 1GB available storage space comfortably support Thunderbird operations. However, users managing extensive email archives or utilizing multiple accounts simultaneously benefit from additional memory allocation.
Pre-installation Checklist
System preparation significantly improves installation success rates and reduces potential complications. Begin by updating existing package repositories and installed software to ensure compatibility with new installations.
Verify internet connectivity stability before proceeding with downloads. Unstable connections may corrupt package downloads, necessitating restart procedures. Gather email account credentials if you plan immediate configuration following installation.
Basic terminal familiarity proves helpful for troubleshooting potential issues, though graphical installation methods minimize command-line requirements for most users.
Method 1: Installing Thunderbird via APT Package Manager
Step 1: System Update
The APT package manager provides the most straightforward Thunderbird installation method for Debian users. Begin by opening a terminal window and updating your package repository information using the following command:
sudo apt updateThis command refreshes local package databases with the latest available software versions from configured repositories. The process typically completes within 30-60 seconds, depending on internet connection speed and repository response times.
Follow the repository update with a system upgrade to ensure all existing packages reflect current versions:
sudo apt upgradeSystem upgrades may require several minutes depending on the number of outdated packages. Keeping systems current prevents compatibility conflicts during new software installation and maintains optimal security postures.
Step 2: Install Thunderbird
Execute the Thunderbird installation command after completing system updates:
sudo apt install thunderbirdThe APT package manager automatically resolves dependencies and downloads required components. Thunderbird installation typically requires 150-300MB of disk space, including associated libraries and language packs. Installation duration varies from 2-10 minutes based on internet connection speeds and system performance.
During installation, APT displays progress indicators showing download progress and installation status. The system may prompt for confirmation before proceeding with package installation. Type ‘Y’ and press Enter to confirm installation when prompted.
Step 3: Launch Thunderbird
Access Thunderbird through multiple methods following successful installation. The desktop environment’s application launcher typically includes Thunderbird in the “Internet” or “Office” category. Navigate through the application menu to locate and click the Thunderbird icon.
Terminal users can launch Thunderbird directly using the command:
thunderbirdFirst-time launches trigger Thunderbird’s initial setup wizard, guiding users through basic configuration options and account setup procedures.
Advantages and Limitations
APT installation integrates seamlessly with Debian’s package management system, enabling automatic security updates through standard system maintenance routines. This approach ensures Thunderbird receives security patches and bug fixes without manual intervention.
However, repository versions may lag behind Mozilla’s latest releases. Users requiring cutting-edge features or recent security enhancements might prefer alternative installation methods that provide immediate access to current versions.
Method 2: Manual Installation from Mozilla
When to Use Manual Installation
Manual installation becomes necessary when requiring the absolute latest Thunderbird version or customizing installation locations. Advanced users often prefer this approach for greater control over software placement and configuration options.
Organizations with specific compliance requirements or custom deployment needs benefit from manual installation flexibility. This method accommodates non-standard directory structures and specialized security configurations.
Step 1: Download Latest Thunderbird
Navigate to Mozilla’s official Thunderbird download page using your preferred web browser. Locate the Linux download section and select the appropriate 64-bit version for your system architecture.
Download verification ensures package integrity and authenticity. Mozilla provides SHA256 checksums for downloaded files, enabling verification against corruption or tampering. Save the downloaded tar.bz2 file to a convenient location such as your Downloads directory.
Typical download sizes range from 60-80MB depending on the included language packs and optional components. Modern internet connections complete downloads within 2-5 minutes.
Step 2: Extract and Install
Navigate to your download directory using the terminal and extract the Thunderbird archive:
cd ~/Downloads
tar xjf thunderbird-*.tar.bz2The extraction process creates a “thunderbird” directory containing all necessary application files. Move this directory to a system-wide location for broader accessibility:
sudo mv thunderbird /opt/Create a symbolic link enabling system-wide executable access:
sudo ln -s /opt/thunderbird/thunderbird /usr/local/bin/thunderbirdEstablish proper ownership and permissions for the installation directory:
sudo chown -R root:root /opt/thunderbird
sudo chmod -R 755 /opt/thunderbirdStep 3: System Integration
Create a desktop entry file for graphical launcher integration:
sudo nano /usr/share/applications/thunderbird.desktopAdd the following content to the desktop file:
[Desktop Entry]
Name=Thunderbird
Comment=Email Client
Exec=/opt/thunderbird/thunderbird
Icon=/opt/thunderbird/chrome/icons/default/default48.png
Type=Application
Categories=Network;Email;This configuration enables Thunderbird appearance in application menus and desktop environments. The desktop file follows XDG Desktop Entry Specification standards for consistent behavior across different desktop environments.
Method 3: Installation via Snap Package
Snap Package Benefits
Snap packages deliver always-current software versions directly from developers, circumventing traditional repository update delays. The sandboxed security model isolates applications from system components, reducing potential security vulnerabilities and system conflicts.
Cross-distribution compatibility ensures identical functionality across different Linux distributions. Snap packages include all necessary dependencies, eliminating complex dependency resolution procedures.
Automatic update mechanisms maintain current software versions without user intervention. Updates apply in the background, ensuring users benefit from latest features and security improvements seamlessly.
Installation Steps
Install the snapd package manager if not already present on your system:
sudo apt install snapdInstall Thunderbird using the snap command:
sudo snap install thunderbirdSnap installation typically completes faster than traditional package installations due to optimized packaging and delivery systems. The process downloads and installs Thunderbird along with all required dependencies automatically.
Verify successful installation by launching Thunderbird:
thunderbirdSnap applications integrate with desktop environments similarly to traditional packages, appearing in application menus and supporting standard desktop interactions.
Initial Setup and Configuration
First Launch Experience
Thunderbird’s initial launch presents a welcome screen with configuration options. The setup wizard guides new users through essential configuration steps while offering advanced options for experienced users.
Choose between immediate account setup or delayed configuration based on current requirements. Users can skip initial setup to explore Thunderbird’s interface before committing to specific configuration choices.
The welcome screen provides access to account creation, import utilities, and help resources. New users benefit from exploring available options before proceeding with detailed configuration.
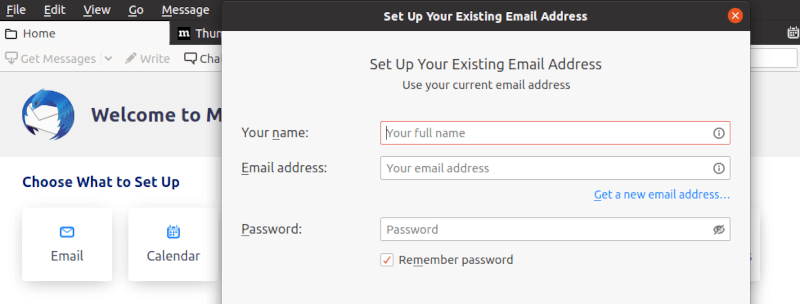
Email Account Configuration
Account setup begins with entering basic email credentials including email address and password. Thunderbird attempts automatic server configuration detection for popular email providers, streamlining setup procedures for common services.
The automatic configuration process queries Mozilla’s provider database and attempts standard server settings. Successful automatic detection displays detected server settings for user verification before proceeding.
Manual configuration becomes necessary for custom email providers or specialized server setups. Access manual configuration options through the “Manual config” button during account setup.
Essential manual configuration parameters include:
Incoming Mail Server (IMAP/POP3):
- Server hostname (e.g., mail.example.com)
- Port number (typically 993 for IMAP-SSL, 995 for POP3-SSL)
- Security settings (SSL/TLS recommended)
- Authentication method (usually “Normal password”)
Outgoing Mail Server (SMTP):
- Server hostname (often smtp.example.com)
- Port number (commonly 587 for SMTP-STARTTLS, 465 for SMTP-SSL)
- Security protocol selection
- Authentication requirements
Advanced Settings
SMTP server configuration requires careful attention to security protocols and authentication methods. Modern email providers mandate encrypted connections using SSL/TLS protocols for security compliance.
Standard port configurations include 993 for IMAP over SSL, 587 for SMTP with STARTTLS, and 465 for SMTP over SSL. These ports provide encrypted communication channels protecting credential transmission and email content.
Authentication methods vary among providers, with “Normal password” serving as the most common option. Some providers require OAuth2 authentication for enhanced security, particularly Google Workspace and Microsoft 365 accounts.
Troubleshooting Common Installation Issues
Package Manager Problems
Repository update failures often result from network connectivity issues or server maintenance periods. Resolve these problems by waiting 15-30 minutes before retrying update commands. Alternative repository mirrors may provide better connectivity during peak usage periods.
Dependency conflicts arise when existing packages conflict with Thunderbird requirements. Use APT’s conflict resolution tools:
sudo apt install -f
sudo apt autoremoveThese commands resolve broken dependencies and remove unnecessary packages that might interfere with new installations.
Package corruption manifests as checksum verification failures or incomplete installations. Clear the APT cache and retry downloads:
sudo apt clean
sudo apt update
sudo apt install thunderbirdManual Installation Issues
Permission denied errors typically occur when attempting operations without sufficient privileges. Ensure all file operations use sudo for system directory modifications. Verify user membership in necessary groups for file access permissions.
Extraction failures suggest corrupted downloads or insufficient disk space. Re-download installation packages and verify available storage before attempting extraction. Use disk usage commands to monitor space availability:
df -hSymbolic link creation problems result from existing files or permission restrictions. Remove conflicting files and ensure target directories exist before creating symbolic links.
Desktop integration issues stem from incorrect desktop file syntax or missing icon references. Validate desktop file contents against XDG specifications and verify icon file paths.
Configuration Problems
Email server detection failures occur with lesser-known providers or custom server configurations. Gather accurate server settings from your email provider’s documentation or support resources before attempting manual configuration.
Authentication errors suggest incorrect credentials or server configuration parameters. Verify username formats (often full email addresses vs. username-only requirements) and password accuracy. Some providers require application-specific passwords for desktop clients.
SSL certificate issues arise with self-signed certificates or expired security certificates. Contact your email provider regarding certificate problems, or temporarily disable SSL verification for testing purposes (not recommended for production use).
OAuth setup complications affect modern email providers implementing enhanced security measures. Follow provider-specific documentation for application registration and OAuth token generation procedures.
Post-Installation Optimization
Performance Tuning
Memory usage optimization improves Thunderbird performance on systems with limited resources. Access performance settings through Edit > Preferences > General > Config Editor. Modify memory allocation parameters for optimal performance based on available system resources.
Database maintenance prevents performance degradation over time. Thunderbird automatically optimizes databases, but manual maintenance helps systems managing extensive email archives. Access maintenance tools through Help > Troubleshooting Information > Repair.
Startup time improvements result from disabling unnecessary add-ons and optimizing account synchronization settings. Review installed extensions regularly and remove unused components that consume system resources during startup.
Disk space management becomes crucial for users with extensive email archives. Configure automatic message cleanup policies and archive older messages to separate storage locations. These practices maintain responsive performance while preserving important communications.
Add-on management significantly impacts overall performance. Install only necessary extensions and regularly review installed add-ons for continued relevance. High-quality add-ons enhance functionality without substantially affecting performance.
Security Enhancements
Master password implementation protects stored account credentials from unauthorized access. Configure master passwords through Edit > Preferences > Privacy & Security > Passwords. Choose strong passwords combining letters, numbers, and symbols for maximum security.
OpenPGP encryption configuration enables end-to-end email encryption for sensitive communications. Access OpenPGP settings through Account Settings > End-to-End Encryption. Generate or import existing PGP keys for secure email exchange.
Spam filter optimization reduces unwanted messages while maintaining legitimate communication flow. Train spam filters by marking suspicious messages as junk and legitimate messages as not junk. Adaptive filtering improves accuracy over time through user feedback.
Two-factor authentication strengthens account security where supported by email providers. Enable 2FA through provider account settings and generate application-specific passwords for Thunderbird authentication.
Regular security updates maintain protection against emerging threats. Enable automatic updates through Edit > Preferences > General > Updates for timely security patch installation.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Thunderbird. Thanks for using this tutorial to install the latest version of Thunderbird Mail on Debian 13 “Trixie”. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Thunderbird website.