How To Install Timeshift on AlmaLinux 10

System backups represent one of the most critical aspects of Linux administration, particularly in enterprise environments where data integrity and system availability are paramount. Timeshift emerges as the premier system restoration tool for AlmaLinux 10, offering administrators and users alike a robust solution for creating incremental system snapshots that can restore their systems to previous stable states.
This comprehensive guide explores every aspect of installing and configuring Timeshift on AlmaLinux 10, from initial system preparation through advanced automation techniques. Whether you’re managing a single workstation or orchestrating multiple server deployments, this tutorial provides the detailed instructions needed to implement a reliable backup strategy.
Understanding Timeshift: Architecture and Core Features
Timeshift functions as a sophisticated system restore utility that creates filesystem snapshots similar to Windows System Restore or macOS Time Machine. The application focuses exclusively on system files rather than personal data, making it ideal for recovering from system updates, configuration errors, or software installation problems.
The tool supports two distinct snapshot methods: RSYNC and BTRFS approaches. RSYNC snapshots utilize hard-link technology to create space-efficient copies of system files, working with any filesystem type including ext4, which is standard on AlmaLinux 10. BTRFS snapshots leverage the advanced features of the BTRFS filesystem to create near-instantaneous snapshots with minimal storage overhead.
Timeshift’s architecture prioritizes system-level protection, excluding user home directories by default. This design philosophy ensures rapid restoration times while maintaining clear separation between system configuration and user data. The application integrates seamlessly with both graphical desktop environments and command-line server installations, providing flexibility for diverse deployment scenarios.
Enterprise-Grade Features for AlmaLinux Environments
The software offers automated scheduling capabilities supporting hourly, daily, weekly, and monthly backup intervals. Advanced users benefit from comprehensive command-line interface support, enabling integration with existing automation frameworks and monitoring systems. The tool’s compatibility with AlmaLinux’s enterprise-focused architecture makes it particularly suitable for production environments requiring reliable system recovery options.
Timeshift’s resource efficiency aligns perfectly with AlmaLinux 10’s stability-first approach. The application minimizes CPU and memory consumption during snapshot operations, ensuring minimal impact on system performance during backup processes. Integration capabilities with existing Red Hat ecosystem tools enhance its value proposition for organizations already invested in enterprise Linux infrastructure.
System Prerequisites and Requirements
Hardware and Storage Specifications
Successful Timeshift deployment requires minimum 20GB free disk space for initial snapshot storage. Storage requirements scale based on system size and snapshot retention policies, with enterprise installations typically requiring 50-100GB for comprehensive backup coverage. Memory requirements remain modest, with 1GB RAM sufficient for most installations, though larger systems benefit from additional memory allocation.
Storage location selection critically impacts backup effectiveness. External storage devices provide additional protection against hardware failures, while internal partitions offer faster backup and restoration operations. Network-attached storage (NAS) solutions enable centralized backup management for multiple systems, particularly valuable in enterprise deployments.
Software Dependencies and System State
AlmaLinux 10 installations require current system updates and functioning package management before Timeshift installation. Essential dependencies include rsync for file synchronization operations and git for source code compilation if building from source. Internet connectivity enables package downloads and repository access during installation procedures.
User privileges represent another critical prerequisite. Installation procedures require root access or sudo privileges for system-level modifications. Standard user accounts cannot install or configure Timeshift due to its system-wide scope and privilege requirements. Administrative access remains necessary for ongoing snapshot management and system restoration operations.
Preparing AlmaLinux 10 for Installation
System Updates and Package Management
Begin Timeshift installation by ensuring your AlmaLinux 10 system maintains current package versions. Execute comprehensive system updates using the following command sequence:
sudo dnf update -y
sudo dnf clean all
sudo dnf autoremoveThis process downloads and installs all available security patches and software updates. The cleaning operation removes cached package files, freeing storage space and ensuring clean package management operations. Autoremove eliminates unnecessary dependency packages, optimizing system resource utilization.
Verify successful update completion by checking for remaining updates:
sudo dnf list updatesEmpty output confirms your system maintains current software versions. Address any remaining updates before proceeding with Timeshift installation to prevent potential compatibility issues.
Essential Dependencies Installation
Install required dependencies using AlmaLinux’s native package manager:
sudo dnf install -y rsync git wget curlThese packages provide core functionality for Timeshift operations. Rsync handles file synchronization during snapshot creation, while git enables source code compilation if required. Wget and curl facilitate package downloads and repository configuration during installation procedures.
Verify successful dependency installation:
rsync --version
git --versionBoth commands should display version information, confirming proper installation. Missing dependencies will generate error messages requiring resolution before continuing with Timeshift installation.
Repository Configuration and EPEL Setup
Enable the EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) repository to access Timeshift packages:
sudo dnf install -y epel-release
sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled powertools
sudo dnf update -yEPEL provides additional software packages not included in standard AlmaLinux repositories. PowerTools repository access enables development libraries and tools necessary for some Timeshift dependencies. The final update command refreshes package lists with newly available EPEL packages.
Confirm EPEL repository activation:
sudo dnf repolist enabled | grep -i epelSuccessful configuration displays EPEL repository information in the output. Repository activation enables Timeshift package installation through standard package management procedures.
Installation Methods for Timeshift
Method 1: EPEL Repository Installation
The recommended installation approach utilizes EPEL repository packages for maximum compatibility and ease of maintenance. Search for available Timeshift packages:
sudo dnf search timeshiftInstall Timeshift using the discovered package name:
sudo dnf install -y timeshiftThis method automatically resolves dependencies and integrates with AlmaLinux’s package management system. Regular system updates will include Timeshift updates, ensuring security patches and feature improvements remain current.
Verify successful installation:
timeshift --version
sudo which timeshiftBoth commands should produce output confirming Timeshift installation and location. Version information indicates the installed release, while the which command displays the executable location in the system path.
Method 2: Source Code Compilation
Advanced users may prefer compiling Timeshift from source code for custom configuration options or latest development features. Install development dependencies first:
sudo dnf groupinstall -y "Development Tools"
sudo dnf install -y cmake make gcc gcc-c++ autoconf automake libtoolDownload and compile Timeshift source code:
git clone https://github.com/linuxmint/timeshift.git
cd timeshift
make clean
make all
sudo make installSource compilation enables custom feature selection and optimization for specific hardware configurations. However, this method requires manual updates and lacks integration with AlmaLinux package management systems.
Method 3: RPM Package Installation
Alternative RPM packages may be available from third-party repositories or direct downloads. Download RPM packages manually:
wget [RPM_PACKAGE_URL]
sudo dnf localinstall timeshift*.rpmThis approach provides installation flexibility when repository packages are unavailable or outdated. Manual dependency resolution may be required if package dependencies are not automatically satisfied. Verify package authenticity through GPG signature verification before installation.
Initial Timeshift Configuration
First-Time Setup and Configuration Wizard
Launch Timeshift’s graphical configuration interface:
sudo timeshift-gtkThe setup wizard guides users through initial configuration decisions. Select your preferred snapshot type based on filesystem and requirements. RSYNC snapshots work with all filesystem types and provide browsable backup contents, while BTRFS snapshots offer superior speed and efficiency on compatible filesystems.
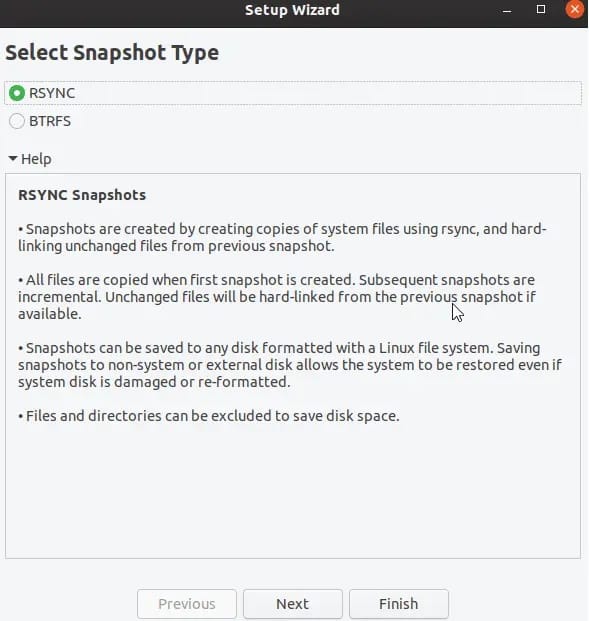
Choose your backup storage location carefully. External drives provide additional hardware failure protection, while internal partitions offer faster backup operations. Consider network storage for centralized backup management in multi-system environments.
Configure initial backup schedule during setup. Daily backups provide optimal protection for most users, with weekly and monthly snapshots for longer-term system state preservation. Adjust retention policies based on available storage space and recovery requirements.
Advanced Configuration Options
Access advanced settings through the graphical interface or configuration files. Include and exclude specific directories to customize backup scope. Standard exclusions prevent backup of temporary files, cache directories, and user data locations that should be backed up separately.
Configure custom snapshot naming conventions to improve backup organization:
sudo timeshift --create --comments "Pre-system-update"
sudo timeshift --create --tags D --comments "Daily-backup-$(date +%Y%m%d)"These commands create tagged snapshots with descriptive comments. Tags facilitate automated retention policies, while comments provide human-readable backup descriptions for easier identification during restoration procedures.
Performance Optimization Settings
Optimize Timeshift performance for your specific hardware configuration. Adjust I/O priority and CPU usage to minimize impact on system operations:
sudo timeshift --create --scripted --btrfs-modeEnable scripted mode for automated operations without user interaction. BTRFS mode selection improves performance on compatible filesystems through native snapshot capabilities rather than file copying operations.
Configure logging levels and notification preferences to maintain awareness of backup operations without overwhelming system administrators with excessive information. Balance detail levels with practical monitoring requirements for effective backup management.
Creating and Managing Snapshots
Manual Snapshot Creation
Create immediate system snapshots before making significant system changes:
sudo timeshift --create --comments "Before-kernel-update"
sudo timeshift --create --tags O --comments "Pre-application-install"Manual snapshots provide precise control over backup timing. The comments parameter enables descriptive labeling for easier identification during restoration procedures. Tags (D=Daily, W=Weekly, M=Monthly, O=On-demand) integrate with automated retention policies.
Monitor snapshot creation progress:
sudo timeshift --list
tail -f /var/log/timeshift.logThe list command displays all available snapshots with creation dates, sizes, and descriptions. Log monitoring provides real-time feedback during lengthy snapshot operations, particularly useful for large system backups.
Automated Backup Scheduling
Configure automated snapshot schedules through the graphical interface or command-line options:
sudo timeshift --snapshot-device /dev/sda1 --backup-device /dev/sdb1
sudo crontab -eAdd cron entries for automated backup execution:
0 2 * * * /usr/bin/timeshift --create --comments "Automated-daily-$(date +\%Y\%m\%d)"
0 3 * * 0 /usr/bin/timeshift --delete --tags W --older-than 4These entries create daily backups at 2 AM and remove weekly snapshots older than four weeks every Sunday at 3 AM. Adjust timing and retention policies based on system usage patterns and storage capacity.
Snapshot Management and Maintenance
Monitor and maintain snapshot collections to prevent storage exhaustion:
sudo timeshift --list --scripted
sudo timeshift --delete --snapshot "2024-01-01_12-00-00"Regular maintenance removes outdated snapshots and monitors storage utilization. Scripted output enables parsing by monitoring scripts and automation frameworks for integrated backup management systems.
Implement storage threshold monitoring:
df -h /timeshift-backup
sudo timeshift --delete --tags D --older-than 7These commands check backup storage utilization and remove daily snapshots older than seven days when storage space becomes limited. Automated cleanup prevents backup failures due to insufficient disk space.
System Restoration Procedures
Complete System Restoration
Restore your system to a previous snapshot when system problems occur:
sudo timeshift --restore --snapshot "2024-01-15_14-30-00"
sudo timeshift --restore --scripted --snapshot "latest"Restoration procedures require careful consideration of data loss implications. Recent changes made after snapshot creation will be lost during restoration. Verify snapshot selection before proceeding with restoration operations.
Monitor restoration progress and prepare for system reboot:
sudo timeshift --restore --check --snapshot "2024-01-15_14-30-00"The check option validates snapshot integrity before restoration. Successful validation confirms snapshot completeness and reduces restoration failure risk. System reboot completes the restoration process and loads the restored system state.
Emergency Recovery Procedures
Boot from live USB environments when normal system access is impossible:
- Boot AlmaLinux 10 live USB/DVD
- Install Timeshift in live environment:
sudo dnf install -y timeshift - Mount backup storage device
- Restore snapshot:
sudo timeshift --restore --snapshot [SNAPSHOT_NAME] - Reinstall bootloader:
sudo grub2-install /dev/sda
Emergency recovery requires external media and backup storage access. Live environment limitations may require additional dependency installation before Timeshift operation. Complete restoration procedures with bootloader reinstallation to ensure proper system startup.
Command-Line Interface and Automation
Essential CLI Commands Reference
Master Timeshift command-line operations for advanced automation and scripting:
# Create snapshots with different tags
sudo timeshift --create --tags D --comments "Daily backup"
sudo timeshift --create --tags W --comments "Weekly system state"
sudo timeshift --create --tags M --comments "Monthly checkpoint"
# List and manage snapshots
sudo timeshift --list --scripted
sudo timeshift --delete --snapshot "2024-01-01_00-00-00"
sudo timeshift --delete --tags D --older-than 30These commands provide comprehensive snapshot management capabilities. Scripted output enables parsing by monitoring tools and automation frameworks. Retention management prevents storage exhaustion through automated cleanup procedures.
Advanced Automation Scripting
Integrate Timeshift with system maintenance scripts:
#!/bin/bash
# Pre-update backup script
echo "Creating pre-update backup..."
sudo timeshift --create --comments "Pre-update-$(date +%Y%m%d-%H%M%S)"
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
echo "Backup successful, proceeding with updates..."
sudo dnf update -y
else
echo "Backup failed, aborting updates..."
exit 1
fiAutomation scripts ensure consistent backup procedures before system modifications. Error checking prevents system updates without successful backup creation, reducing recovery complexity when problems occur.
Implement monitoring and alerting:
#!/bin/bash
# Backup monitoring script
BACKUP_COUNT=$(sudo timeshift --list --scripted | wc -l)
STORAGE_USAGE=$(df -h /timeshift-backup | tail -1 | awk '{print $5}' | sed 's/%//')
if [ $BACKUP_COUNT -lt 3 ]; then
echo "Warning: Only $BACKUP_COUNT backups available"
fi
if [ $STORAGE_USAGE -gt 90 ]; then
echo "Critical: Backup storage $STORAGE_USAGE% full"
sudo timeshift --delete --tags D --older-than 7
fiMonitoring scripts provide proactive backup management and storage utilization alerts. Automated cleanup responds to storage pressure while maintaining minimum backup counts for system protection.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Installation and Configuration Problems
Resolve dependency conflicts and installation failures:
# Check for conflicting packages
sudo dnf list installed | grep timeshift
sudo dnf remove timeshift
sudo dnf autoremove
# Clean installation
sudo dnf clean all
sudo dnf install -y timeshiftDependency conflicts may prevent successful Timeshift installation. Complete removal followed by clean installation resolves most package-related issues. Repository configuration problems require EPEL repository verification and re-enabling.
Address permission and privilege issues:
# Verify user permissions
sudo -l
groups $USER
# Fix timeshift permissions
sudo chown -R root:root /usr/bin/timeshift
sudo chmod +s /usr/bin/timeshiftPermission problems prevent Timeshift operation even with proper installation. Setuid bit configuration enables normal users to create snapshots while maintaining security boundaries. Group membership may be required for certain Timeshift operations.
Runtime and Performance Issues
Diagnose snapshot creation failures:
# Check available disk space
df -h
sudo timeshift --check
# Monitor system resources during backup
top -p $(pgrep timeshift)
iotop -p $(pgrep timeshift)Storage space exhaustion represents the most common snapshot failure cause. Resource monitoring identifies performance bottlenecks during backup operations. I/O throttling may be necessary on heavily loaded systems to prevent backup impact on normal operations.
Resolve filesystem and storage problems:
# Check filesystem integrity
sudo fsck /dev/sdb1
sudo mount -o remount,rw /timeshift-backup
# Verify backup device accessibility
sudo blkid
lsblk -fFilesystem corruption prevents successful backup operations. Regular filesystem checks maintain backup storage integrity. Mount options and device accessibility verification resolves storage-related backup failures.
Security Considerations and Best Practices
Backup Security Implementation
Secure backup storage locations against unauthorized access:
# Set restrictive permissions
sudo chmod 700 /timeshift-backup
sudo chown root:root /timeshift-backup
# Implement access controls
sudo setfacl -m u:backup:rwx /timeshift-backup
sudo setfacl -d -m u:backup:rwx /timeshift-backupBackup security requires careful permission management and access control implementation. Restrictive permissions prevent unauthorized snapshot access while maintaining necessary functionality for backup operations. Access Control Lists (ACLs) provide granular permission management for complex organizational requirements.
Consider encryption for sensitive environments:
# Create encrypted backup storage
sudo cryptsetup luksFormat /dev/sdb1
sudo cryptsetup luksOpen /dev/sdb1 timeshift-backup
sudo mkfs.ext4 /dev/mapper/timeshift-backupEncryption protects backup contents against physical media theft or unauthorized access. LUKS encryption integrates seamlessly with Linux systems while providing robust protection for sensitive system configurations and data.
Enterprise Compliance Requirements
Implement audit trails and documentation:
# Enable detailed logging
echo "TIMESHIFT_LOG_LEVEL=DEBUG" | sudo tee -a /etc/environment
sudo systemctl restart rsyslog
# Create backup documentation
sudo timeshift --list --scripted > /var/log/backup-inventory.logCompliance requirements may mandate detailed backup logging and inventory maintenance. Audit trails document backup operations for regulatory review and security assessment procedures. Regular inventory reports demonstrate backup coverage and retention policy compliance.
Performance Optimization Strategies
Resource Management and Tuning
Optimize system resource utilization during backup operations:
# Set I/O priority for backup operations
sudo ionice -c 3 -p $(pgrep timeshift)
sudo renice +10 $(pgrep timeshift)I/O priority and CPU nice values minimize backup impact on system performance. Lower priority settings ensure normal system operations maintain responsiveness during backup procedures. Resource throttling prevents backup operations from overwhelming system capacity.
Configure storage optimization:
# Enable filesystem compression
sudo mount -o compress=zstd /dev/sdb1 /timeshift-backup
# Implement storage deduplication
sudo btrfs filesystem defragment -r -v /timeshift-backupStorage optimization reduces backup space requirements and improves performance. Compression algorithms like zstd provide excellent compression ratios with minimal CPU overhead. Deduplication eliminates redundant data across multiple snapshots, maximizing storage efficiency.
Scaling for Enterprise Environments
Implement centralized backup management:
# Network backup storage configuration
sudo mount -t nfs backup-server:/timeshift /timeshift-backup
echo "backup-server:/timeshift /timeshift-backup nfs defaults 0 0" | sudo tee -a /etc/fstabCentralized storage enables consistent backup management across multiple systems. Network File System (NFS) or other network storage protocols provide shared backup repositories for organizational backup strategies. Automated mounting ensures backup availability across system restarts.
Deploy automated monitoring systems:
#!/bin/bash
# Centralized backup monitoring
for server in server1 server2 server3; do
ssh $server "sudo timeshift --list --scripted" > /tmp/${server}-backups.log
BACKUP_COUNT=$(wc -l < /tmp/${server}-backups.log)
echo "Server $server: $BACKUP_COUNT backups available"
doneMonitoring automation provides comprehensive backup status across multiple systems. Centralized reporting enables proactive backup management and issue identification before system failures occur. Integration with existing monitoring infrastructure enhances operational visibility.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Timeshift. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Timeshift on the AlmaLinux OS 10 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Timeshift website.