How To Install Timeshift on Rocky Linux 10

System backups are the cornerstone of reliable IT infrastructure. Timeshift, a powerful snapshot-based backup solution, provides enterprise-grade system protection for Rocky Linux environments. This comprehensive guide walks you through installing and configuring Timeshift on Rocky Linux 10, ensuring your critical systems remain protected against failures, configuration errors, and unexpected issues.
What is Timeshift? Understanding the Backup Solution
Core Functionality and Purpose
Timeshift serves as a system restore utility that creates point-in-time snapshots of your Linux installation. Similar to Windows System Restore or macOS Time Machine, Timeshift captures the complete system state, enabling administrators to roll back problematic changes instantly. The tool focuses on system files rather than personal data, making it ideal for maintaining stable server environments and desktop systems.
Unlike traditional backup solutions, Timeshift creates incremental snapshots that consume minimal storage space while providing comprehensive system protection. The utility excels at protecting against system updates gone wrong, configuration mishaps, and software installation issues that could compromise system stability.
Key Features and Benefits
Timeshift offers dual snapshot modes: RSYNC and BTRFS, catering to different filesystem requirements and performance preferences. The RSYNC mode works with any Linux filesystem, creating hardlink-based snapshots that are space-efficient and reliable. BTRFS mode leverages built-in filesystem snapshot capabilities for near-instantaneous backup creation.
Automated scheduling ensures consistent system protection without manual intervention. Users can configure hourly, daily, weekly, or monthly snapshots based on their specific needs. The intelligent retention system automatically removes old snapshots while maintaining the desired backup history, preventing storage space exhaustion.
The tool provides both command-line and graphical interfaces, making it accessible for server administrators and desktop users alike. Cross-distribution restore capabilities mean snapshots created on one Linux system can potentially restore another compatible system, enhancing disaster recovery options.
System Requirements for Rocky Linux 10
Rocky Linux 10 systems require minimum 20GB free storage space for effective Timeshift operation. This allocation accommodates multiple snapshots while maintaining system performance. Modern multi-core processors and at least 2GB RAM ensure smooth snapshot creation and restoration processes.
Timeshift works optimally with EXT4 filesystems, though BTRFS support provides additional functionality for systems using that filesystem. Network connectivity enables automatic updates and dependency resolution during installation.
Prerequisites and System Preparation
System Requirements Verification
Before installing Timeshift, verify your Rocky Linux 10 system meets all prerequisites. Check available storage space using the df -h command to ensure sufficient room for snapshots. Confirm you have root privileges or sudo access, as Timeshift requires elevated permissions for system-level operations.
Validate your Rocky Linux 10 installation status by reviewing the /etc/redhat-release file. Ensure your system has an active internet connection for downloading packages and dependencies during the installation process.
Pre-Installation System Updates
Maintaining current system packages prevents installation conflicts and ensures compatibility. Update your Rocky Linux 10 system using the DNF package manager:
sudo dnf update -yThis command downloads and installs all available package updates, bringing your system to the latest stable state. System updates address security vulnerabilities and compatibility issues that could interfere with Timeshift installation. Allow the update process to complete fully before proceeding with Timeshift installation.
Installing Essential Dependencies
Timeshift requires specific system utilities for proper operation. Install essential dependencies using DNF:
sudo dnf install -y rsync gitRSYNC handles the core snapshot functionality, while git may be needed for certain installation methods. These utilities form the foundation for Timeshift’s backup operations. Verify successful installation by checking each utility’s version:
rsync --version
git --versionRepository Configuration and Setup
Understanding Rocky Linux 10 Repositories
Rocky Linux 10’s default repositories don’t include Timeshift packages, necessitating external repository configuration. The modular nature of Enterprise Linux distributions prioritizes stability over bleeding-edge software availability. Understanding repository hierarchy helps administrators make informed decisions about software sources.
Official Rocky Linux repositories provide core system components and security updates. Third-party repositories like EPEL extend functionality with additional packages while maintaining security standards. Repository configuration affects system security and update policies, making careful selection crucial.
Installing and Configuring EPEL Repository
The Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux (EPEL) repository provides Timeshift packages for Rocky Linux systems. EPEL maintains high standards for package quality while extending the software catalog beyond base repositories.
Install the EPEL repository with this command:
sudo dnf install epel-releaseAfter EPEL installation, enable additional repositories that provide dependencies:
sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled powertoolsThe PowerTools repository contains development libraries and tools required by various EPEL packages. Update the package database to reflect new repository additions:
sudo dnf updateVerify repository configuration by listing available packages:
sudo dnf repolistAlternative Installation Methods
While EPEL provides the recommended installation path, source compilation offers alternative installation options for specific requirements. Building from source enables customization but requires additional development tools and compilation time.
Third-party repositories may offer newer Timeshift versions, though they introduce additional security considerations. Evaluate repository maintainer reputation and package signatures before adding unofficial sources. Consider containerized deployment options for isolated Timeshift installations.
Installing Timeshift on Rocky Linux 10
Installation via DNF Package Manager
With EPEL configured, install Timeshift using the DNF package manager:
sudo dnf install timeshiftDNF automatically resolves dependencies and displays the installation plan. Review the package list and confirm installation by typing ‘y’ when prompted. The installation process downloads Timeshift and required dependencies from configured repositories.
Monitor the installation progress as DNF downloads packages and configures the system. Package verification occurs automatically, ensuring file integrity and authenticity. Large dependency chains may require several minutes for complete installation.
Common installation issues include repository synchronization failures or conflicting packages. Network connectivity problems can interrupt downloads, requiring installation restart. Disk space limitations may prevent successful installation completion.
Post-Installation Verification
Confirm successful Timeshift installation by checking the installed version:
timeshift --versionThis command displays the installed Timeshift version and confirms proper binary installation. Verify installation completeness by listing installed files:
rpm -ql timeshiftService status verification ensures Timeshift integrates properly with the system. Check for configuration files in /etc/timeshift/ and verify binary accessibility in the system PATH.
Alternative Installation Troubleshooting
Repository conflicts may prevent standard installation, requiring manual resolution. Clear DNF cache and retry installation if initial attempts fail:
sudo dnf clean all
sudo dnf install timeshiftDependency conflicts occasionally occur with third-party software installations. Use DNF’s troubleshooting features to identify and resolve conflicting packages. Manual package downloads from EPEL repositories provide fallback installation options when automatic installation fails.
Source compilation serves as the ultimate fallback for systems with unique requirements or repository access issues. Download source code from official repositories and follow compilation instructions for custom installations.
Initial Timeshift Configuration
First Launch and Setup Wizard
Launch Timeshift’s graphical interface for initial configuration:
sudo timeshift-gtkThe setup wizard guides new users through essential configuration decisions. First-time launches present snapshot type selection, storage location configuration, and scheduling options. The intuitive interface simplifies complex backup concepts for administrators.
Navigation through setup screens requires careful consideration of each option’s implications. Configuration choices made during initial setup affect system performance and backup effectiveness. Document your selections for future reference and system documentation.
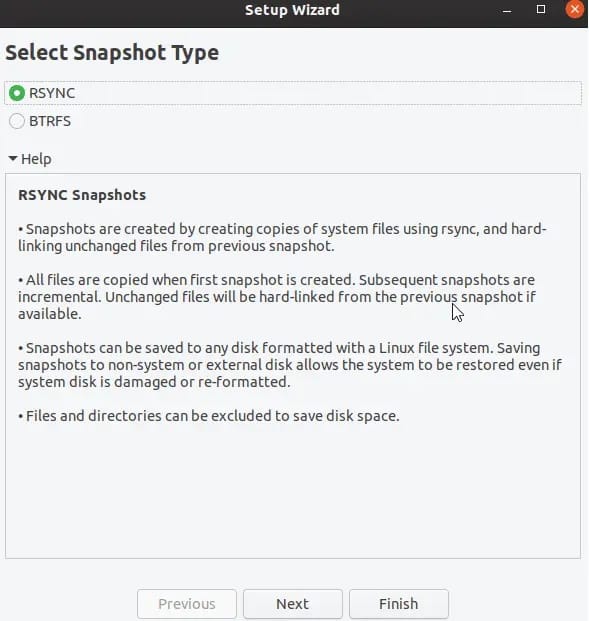
Snapshot Type Selection
Choose between RSYNC and BTRFS snapshot types based on your filesystem and requirements. RSYNC mode works universally across all Linux filesystems, creating hardlink-based snapshots that are reliable and space-efficient. This mode suits most Rocky Linux installations using EXT4 filesystems.
BTRFS mode leverages filesystem-level snapshots for faster creation and restoration. This option requires BTRFS filesystems and provides near-instantaneous snapshot operations. However, BTRFS mode limitations include filesystem dependency and reduced cross-system compatibility.
RSYNC snapshots offer superior compatibility and restoration flexibility, making them ideal for enterprise environments. Performance implications favor BTRFS for large systems with frequent snapshot requirements, though RSYNC remains adequate for most use cases.
Backup Location Configuration
Select appropriate storage locations for Timeshift snapshots, considering space requirements and accessibility. Internal drives provide fast access but risk simultaneous failure with the main system. External storage offers better disaster recovery protection but may impact snapshot speed.
Partition considerations include dedicating specific storage areas for snapshots. Separate partitions or drives prevent snapshot storage from consuming system space needed for normal operations. Calculate storage requirements based on expected snapshot frequency and retention periods.
Security implications affect backup location decisions. Protected storage areas prevent accidental deletion or unauthorized access to critical snapshots. Network-attached storage provides centralized backup management for multiple systems.
Advanced Configuration and Scheduling
Backup Schedule Configuration
Configure automated snapshot schedules to ensure consistent system protection without manual intervention. Timeshift supports hourly, daily, weekly, and monthly snapshot frequencies, allowing administrators to balance protection levels with storage consumption.
Retention policies automatically manage snapshot lifecycle, removing old snapshots while maintaining adequate backup history. Configure retention counts for each schedule type based on recovery requirements and available storage. Boot snapshots provide additional protection during system startup.
Performance considerations during scheduled backups affect system responsiveness. Schedule snapshot creation during low-usage periods to minimize impact on production workloads. Monitor system resources during backup operations to optimize scheduling.
Include/Exclude Directory Settings
Timeshift default exclusion patterns omit temporary files, caches, and user data directories. These exclusions reduce snapshot size and focus protection on system-critical files. Review default patterns to ensure they align with your specific requirements.
Including home directories requires careful consideration of storage implications and privacy concerns. System administrators may choose to include configuration files while excluding large media collections. Custom exclusion rules optimize snapshot efficiency for specific use cases.
Directory exclusions significantly impact snapshot size and creation time. Exclude log files, temporary directories, and cache folders that regenerate automatically. Include critical configuration directories and custom system modifications requiring protection.
Advanced Settings and Options
Cron job integration enables fine-grained scheduling control beyond the standard interface. Advanced users can create custom backup schedules using cron syntax for complex timing requirements. Monitor cron job execution through system logs.
Compression settings reduce snapshot storage requirements at the cost of increased CPU usage during creation. Network backup configurations enable remote snapshot storage for enhanced disaster recovery. Notification settings alert administrators to backup success or failure conditions.
Creating and Managing Snapshots
Manual Snapshot Creation
Create on-demand snapshots before major system changes or software installations. The graphical interface provides intuitive snapshot creation with comment fields for change documentation. Command-line snapshot creation offers scripting integration:
sudo timeshift --createSnapshot naming conventions help identify specific system states during restoration. Include dates, change descriptions, or version information in snapshot comments. Monitor creation progress through the interface or log files.
Verification procedures ensure snapshot integrity and completeness. Check snapshot file counts and sizes against expectations. Test restoration capabilities periodically to validate backup effectiveness.
Snapshot Management and Organization
Browse snapshots through the Timeshift interface to explore backed-up file versions. The file browser enables selective file restoration without full system rollback. Snapshot organization features help manage large backup catalogs.
Storage monitoring prevents snapshot storage exhaustion that could impact system stability. Regular cleanup of obsolete snapshots maintains optimal storage utilization. Automated retention policies reduce manual maintenance requirements.
Automated Backup Verification
Monitor scheduled backups through Timeshift logs and system notifications. Log analysis reveals backup success rates and identifies recurring issues. Performance monitoring during automated operations ensures minimal system impact.
Integrity verification confirms snapshot completeness and restoration capability. Implement regular restoration tests in non-production environments to validate backup reliability. Document verification procedures for operational consistency.
System Restoration Procedures
Restoration Planning and Preparation
Pre-restoration assessment involves identifying the specific issue requiring system rollback. Document current system state and backup available data not included in Timeshift snapshots. Create additional snapshots before restoration to preserve recent changes.
Backup verification ensures selected snapshots contain the desired system state. Review snapshot creation dates and comments to select appropriate restoration points. Consider restoration implications for running services and user data.
GUI-Based System Restoration
Access restoration interface through the Timeshift application, selecting desired snapshots from the available list. The graphical restoration process provides progress monitoring and confirmation dialogs. Review restoration scope before proceeding with system rollback.
Restoration monitoring tracks progress and identifies potential issues during the rollback process. Post-restoration verification confirms system functionality and proper file restoration. Handle restoration failures through alternative snapshot selection or manual intervention.
Command-Line Restoration Methods
Command-line restoration enables automated recovery procedures and emergency restoration scenarios:
sudo timeshift --restoreRecovery scripting integrates restoration into disaster recovery procedures. Emergency restoration from live media provides system recovery when normal boot fails. Document command-line procedures for emergency reference.
Troubleshooting and Best Practices
Common Installation Issues
Repository availability problems often stem from network connectivity or repository configuration errors. Verify internet access and repository configuration files in /etc/yum.repos.d/. Clear DNF cache and retry installation after resolving connectivity issues.
Dependency resolution failures may occur with conflicting packages or missing repositories. Review DNF error messages to identify specific dependency issues. Enable additional repositories or resolve package conflicts before retrying installation.
Permission issues prevent proper installation or configuration. Ensure sudo access and verify user permissions for system modification. SELinux policies may require adjustment for proper Timeshift operation.
Configuration and Operation Troubleshooting
Snapshot creation failures typically result from insufficient storage space or permission issues. Monitor disk space during snapshot operations and verify write permissions for backup locations. Review Timeshift logs for specific error messages.
Schedule malfunctions may require cron service verification and log analysis. Check cron daemon status and review scheduled job execution. Validate Timeshift service permissions for automated operation.
Best Practices and Recommendations
Optimal backup schedules balance protection requirements with system resources and storage capacity. Enterprise environments typically benefit from daily snapshots with weekly retention. Test different schedules to find the optimal configuration for your specific use case.
Storage management prevents backup-related disk space issues that could impact system stability. Monitor snapshot growth and implement retention policies that maintain adequate free space. Regular storage cleanup maintains optimal system performance.
Security considerations include protecting backup files from unauthorized access and ensuring snapshot integrity. Implement access controls for Timeshift configuration and backup locations. Regular security audits verify backup system integrity.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Timeshift. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Timeshift on the Rocky Linux 10 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Timeshift website.