How To Install Tor Browser on Rocky Linux 10

The digital privacy landscape has evolved dramatically in 2025, making anonymous browsing more critical than ever before. With increasing surveillance concerns and data collection practices, users need robust solutions to protect their online activities. Rocky Linux 10, as an enterprise-grade distribution, provides an excellent foundation for running privacy-focused applications like Tor Browser.
This comprehensive guide addresses the growing need for secure, anonymous web browsing on Rocky Linux 10 systems. Whether you’re a system administrator, privacy-conscious user, or security professional, this tutorial will walk you through multiple installation methods, configuration options, and best practices for deploying Tor Browser effectively.
You’ll learn three distinct installation approaches, from manual downloads to repository-based installations, along with essential security configurations, troubleshooting solutions, and optimization techniques. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a fully functional Tor Browser installation that maximizes both privacy and performance on your Rocky Linux 10 system.
Understanding Tor Browser and Its Importance
What is Tor Browser
Tor Browser represents the gold standard for anonymous web browsing, built upon the robust foundation of Mozilla Firefox. The browser implements sophisticated onion routing technology, which encrypts and routes internet traffic through multiple relay servers worldwide, effectively masking user identity and location.
The Tor network operates on a principle of layered encryption, where each relay only knows the previous and next hop in the chain, never the complete path from source to destination. This architecture ensures that no single point can compromise user anonymity, making it virtually impossible to trace browsing activities back to the original user.
Key Features and Benefits
Tor Browser incorporates numerous privacy-enhancing features designed to protect users from various tracking mechanisms. The browser includes built-in NoScript functionality, preventing malicious JavaScript execution, and HTTPS Everywhere integration, which forces secure connections whenever possible.
The browser’s isolation model ensures that each website session operates independently, preventing cross-site tracking and fingerprinting attempts. Additionally, Tor Browser automatically clears cookies, browsing history, and other identifying data upon closure, maintaining a clean slate for each browsing session.
Multi-layer encryption provides unprecedented protection against network surveillance, making it an essential tool for journalists, activists, researchers, and privacy-conscious individuals operating in restrictive environments or handling sensitive information.
Why Choose Tor on Rocky Linux 10
Rocky Linux 10 offers exceptional stability and security features that complement Tor Browser’s privacy objectives. The distribution’s enterprise-grade architecture provides robust system isolation, advanced security policies, and comprehensive audit capabilities that enhance overall anonymity protection.
The compatibility between Rocky Linux’s security-focused design and Tor’s privacy requirements creates an optimal environment for anonymous browsing activities while maintaining system integrity and performance.
Prerequisites and System Requirements
Rocky Linux 10 System Requirements
Before installing Tor Browser, ensure your Rocky Linux 10 system meets the minimum hardware specifications. A modern 64-bit processor with at least 2GB RAM and 1GB available disk space provides adequate performance for standard browsing activities.
Fresh operating system installations offer the best security posture, minimizing potential conflicts and ensuring clean dependency management. Root or sudo access remains essential for system-level configurations and package installations throughout this process.
Network connectivity requirements include stable internet access for downloading packages and establishing Tor network connections. Consider implementing proper firewall configurations that allow Tor traffic while maintaining system security.
Required Packages and Dependencies
The EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) repository provides essential packages not available in Rocky Linux’s base repositories. Installing EPEL enables access to additional tools and libraries required for various Tor Browser installation methods.
Essential utilities include wget for downloading files from command line, tar for archive extraction, and various development tools for compiling source packages when necessary. Network troubleshooting tools like curl and netstat prove invaluable for verifying Tor connectivity and diagnosing connection issues.
Security Preparation
System updates form the foundation of any secure installation process. Execute comprehensive system updates before beginning Tor Browser installation to ensure all security patches and bug fixes are applied.
Configure firewall rules appropriately to allow Tor traffic while blocking unnecessary services. Create dedicated user accounts for Tor Browser usage when operating in multi-user environments, implementing principle of least privilege for enhanced security isolation.
Installation Method 1: Manual Installation (Official Method)
Downloading Tor Browser
The official Tor Project website provides the most current and secure Tor Browser releases. Navigate to the download section and identify the latest version specifically compiled for Linux x86_64 architecture. As of 2025, Tor Browser 14.0 represents the current stable release with enhanced security features.
Use wget to download the browser package directly to your Rocky Linux system:
cd ~/Downloads
wget https://dist.torproject.org/torbrowser/14.5.5/tor-browser-linux-x86_64-14.5.5.tar.xzThis command downloads the compressed archive containing the complete Tor Browser installation package. The download size typically ranges from 100-150MB depending on the specific version and included components.
Signature Verification Process
Cryptographic signature verification ensures the downloaded package hasn’t been tampered with during transit. This critical security step prevents installation of compromised or malicious software that could compromise user privacy.
Download the corresponding signature file and GPG key:
wget https://dist.torproject.org/torbrowser/14.5.5/tor-browser-linux-x86_64-14.5.5.tar.xz.asc
gpg --auto-key-locate nodefault,wkd --locate-keys torbrowser@torproject.orgVerify the package integrity using GPG:
gpg --verify tor-browser-linux-x86_64-14.5.5.tar.xz.asc tor-browser-linux-x86_64-14.5.5.tar.xzA successful verification displays “Good signature” message, confirming the package authenticity. Never skip this verification step, as compromised Tor Browser installations can completely undermine anonymity protections.
Extraction and Installation
Extract the downloaded archive using tar with appropriate compression flags:
tar -xvJf tor-browser-linux-x86_64-14.5.5.tar.xzThis creates a tor-browser directory containing the complete browser installation. The extracted folder includes the browser executable, configuration files, and necessary libraries for standalone operation.
Navigate to the extracted directory and examine the contents:
cd tor-browser
ls -laThe directory structure includes the Browser folder containing Firefox-based components, Data folder for user preferences, and the start-tor-browser.desktop launcher script.
Desktop Integration
Register Tor Browser as a system application for convenient access:
./start-tor-browser.desktop --register-appThis command creates desktop entries and application menu shortcuts, integrating Tor Browser with the Rocky Linux desktop environment. The registration process adds Tor Browser to the applications menu and enables launching through graphical interfaces.
Create a symbolic link for command-line access:
sudo ln -s /home/$(whoami)/Downloads/tor-browser/start-tor-browser.desktop /usr/local/bin/tor-browserThis allows launching Tor Browser from any terminal location using the tor-browser command.
Installation Method 2: Using Flatpak
Flatpak Setup Prerequisites
Flatpak provides isolated application environments that enhance security and simplify dependency management. Install Flatpak on Rocky Linux 10 using the DNF package manager:
sudo dnf install flatpak -yConfigure the Flathub repository for access to Tor Browser Launcher:
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepoRestart your system or log out and back in to ensure Flatpak integration with the desktop environment functions properly.
Tor Browser Launcher Installation
Install Tor Browser Launcher through Flatpak:
flatpak install flathub com.github.micahflee.torbrowser-launcherThe Tor Browser Launcher handles automatic downloads, signature verification, and updates for Tor Browser installations. This approach simplifies maintenance while ensuring authentic software sources.
Monitor the installation progress and confirm when prompted. The initial installation downloads both the launcher application and the current Tor Browser release, requiring several minutes depending on network speed.
Running and Configuring
Launch Tor Browser Launcher using Flatpak:
flatpak run com.github.micahflee.torbrowser-launcherThe launcher automatically downloads and verifies the latest Tor Browser version during first run. This process includes signature verification and secure installation in an isolated Flatpak environment.
Configure automatic updates through the launcher interface to maintain current security patches. The Flatpak installation method provides excellent isolation while simplifying update management for users preferring automated maintenance.
Installation Method 3: Repository Installation
EPEL Repository Configuration
Enable the EPEL repository to access additional packages required for Tor installation:
sudo dnf install epel-release -y
sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled crbUpdate the package database to include EPEL packages:
sudo dnf updateVerify EPEL repository activation:
dnf repolist enabled | grep epelTor Repository Setup
Create a custom repository configuration for the official Tor packages:
sudo nano /etc/yum.repos.d/tor.repoAdd the following repository configuration:
[tor]
name=Tor for Enterprise Linux $releasever - $basearch
baseurl=https://rpm.torproject.org/centos/$releasever/$basearch
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://rpm.torproject.org/centos/public_gpg.key
cost=100Import the Tor Project GPG key:
sudo rpm --import https://rpm.torproject.org/centos/public_gpg.keyPackage Installation
Install Tor Browser components using DNF:
sudo dnf install tor torbrowser-launcherThis command installs both the Tor daemon and the browser launcher application. The repository method provides integration with Rocky Linux’s package management system, enabling automatic security updates through standard system maintenance procedures.
Verify the installation:
which tor
systemctl status torConfigure Tor service for automatic startup if desired:
sudo systemctl enable tor
sudo systemctl start torFirst Launch and Initial Configuration
Starting Tor Browser
Launch Tor Browser using your preferred installation method. For manual installations, execute the start script:
./start-tor-browser.desktopFlatpak users launch through the application menu or command line:
flatpak run com.github.micahflee.torbrowser-launcherRepository installations typically provide launcher shortcuts in the applications menu under Internet or Network categories.
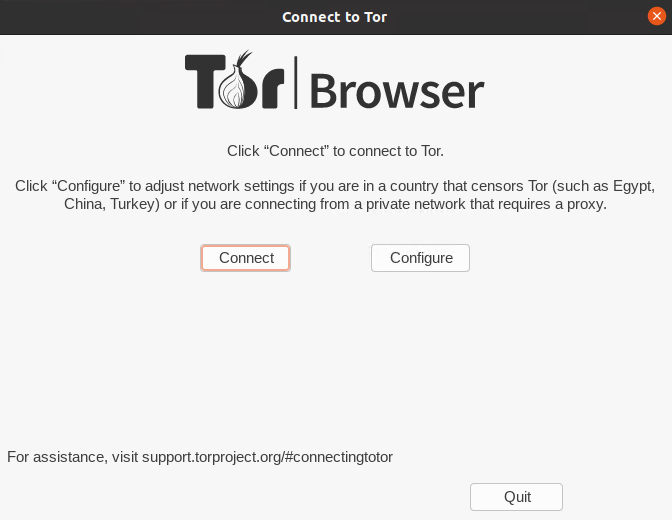
Connection Configuration
Tor Browser presents connection configuration options during initial startup. Standard connections work for most users, automatically connecting to the Tor network without additional configuration.
Users operating behind restrictive firewalls or in censored regions may require bridge configuration. Select “Configure” during startup to access bridge settings and obtain bridge addresses from the Tor Project’s bridge database.
Proxy configuration becomes necessary when connecting through corporate networks or additional privacy layers. Configure SOCKS5 proxies or HTTP proxies as required by your network environment.
Browser Settings Optimization
Access Tor Browser security settings through the shield icon in the address bar. Choose security levels based on your threat model: Standard provides balanced protection, Safer disables potentially dangerous features, and Safest offers maximum protection with reduced functionality.
Review privacy settings in the preferences menu, ensuring optimal configuration for your use case. Consider disabling JavaScript for maximum security, though this may break functionality on many websites.
Configure NoScript extension settings to allow necessary scripts while blocking potentially malicious content. Understanding NoScript configuration significantly improves both security and usability of Tor Browser sessions.
Security Best Practices and Verification
Post-Installation Security Checks
Verify your anonymity by checking your IP address through Tor-friendly services. Navigate to check.torproject.org to confirm successful Tor network connection and proper IP masking.
Test for DNS leaks using dedicated testing services like dnsleaktest.com or ipleak.net. Proper Tor configuration should route all DNS queries through the Tor network, preventing location disclosure through DNS resolution.
Examine browser fingerprinting protection by visiting fingerprinting test sites. Tor Browser should present identical fingerprints for all users, preventing unique identification through browser characteristics.
Safe Usage Guidelines
JavaScript handling requires careful consideration of security versus functionality trade-offs. Enable JavaScript only for trusted sites when necessary, maintaining disabled default settings for maximum protection.
Download precautions include scanning all files with antivirus software and avoiding executable files whenever possible. Downloads through Tor exit nodes may expose user activities to exit node operators, requiring additional care with sensitive files.
Plugin management focuses on maintaining Tor Browser’s default configuration. Installing additional plugins or extensions compromises anonymity by creating unique browser fingerprints that enable user tracking.
Regular Maintenance
Update procedures vary by installation method but remain critical for maintaining security. Manual installations require periodic downloads of new versions, while repository and Flatpak installations provide automatic update mechanisms.
Monitor Tor Project security announcements for critical updates requiring immediate attention. Security vulnerabilities in Tor Browser can compromise user anonymity, making timely updates essential for maintaining protection.
Backup important browser configurations and bookmarks regularly, while avoiding storage of sensitive data within Tor Browser profiles. Consider using external password managers and avoiding browser-stored credentials for enhanced security.
Common Troubleshooting Issues
Installation Problems
Permission errors frequently occur when extracting archives or executing installation scripts. Ensure proper file permissions and avoid running Tor Browser with root privileges, which compromises security and functionality.
Missing library issues manifest as dependency errors during startup. Install required libraries through DNF:
sudo dnf install libXt libXrender libXcomposite libXdamageDownload corruption causes signature verification failures or extraction errors. Re-download packages from official sources and verify checksums when signature verification fails consistently.
Launch and Runtime Issues
Desktop file execution problems prevent launching through graphical interfaces. Verify file permissions and executable flags:
chmod +x start-tor-browser.desktopBrowser startup failures often result from conflicting processes or corrupted user profiles. Remove user profile directories and restart Tor Browser to create fresh configurations:
rm -rf ~/.tor-browser/Connection establishment issues require checking network connectivity and firewall configurations. Verify that Tor can establish outbound connections on required ports (typically 443 and 80 for most configurations).
Network and Connectivity Problems
Tor network connection failures may indicate network restrictions or firewall blocking. Configure bridges or alternative connection methods for restrictive network environments.
Firewall configuration issues prevent Tor traffic flow. Configure iptables or firewalld to allow Tor connections:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=9050/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadProxy conflicts occur when multiple proxy configurations interfere with Tor connections. Disable system-wide proxy settings or configure Tor Browser to bypass existing proxy configurations.
Bridge configuration helps circumvent network censorship. Obtain bridge addresses from bridge.torproject.org and configure them in Tor Browser’s network settings for enhanced connectivity in restricted regions.
Advanced Configuration and Customization
Performance Optimization
Memory usage optimization involves adjusting browser cache settings and limiting concurrent connections. Access about:config and modify network.http.max-connections and browser.cache.disk.capacity for improved performance on resource-constrained systems.
Cache configuration balances security and performance requirements. Reduce cache sizes for enhanced security or increase for better performance on stable, trusted networks.
Network timeout adjustments accommodate slow Tor connections. Increase timeout values in about:config for improved reliability on congested networks.
Privacy Enhancement
Additional security extensions should be avoided in Tor Browser to maintain fingerprint uniformity. The browser’s default configuration provides optimal anonymity protection without additional modifications.
Advanced privacy settings include disabling WebRTC, restricting media device access, and configuring canvas fingerprinting protection. Access these settings through about:config for expert-level privacy customization.
Custom bridge configuration enables connection through private bridges for enhanced censorship resistance. Generate personal bridges through the Tor Project’s bridge infrastructure for improved reliability in restrictive environments.
Multi-User Setup
System-wide installation benefits include centralized management and consistent security policies across multiple users. Install Tor Browser in /opt/ for shared access while maintaining individual user profiles.
User-specific configurations allow personalized security settings while preserving system integrity. Create separate user accounts for different security requirements or operational needs.
Permission management ensures appropriate access controls for shared installations. Configure file permissions and directory access to prevent unauthorized modifications while enabling legitimate usage.
Comparison with Other Privacy Browsers
Tor vs. Standard Browsers
Privacy feature comparison reveals significant advantages of Tor Browser over conventional browsers. While standard browsers offer privacy modes and extensions, they cannot match Tor’s comprehensive anonymity protection through network-level routing.
Security advantage analysis demonstrates Tor Browser’s superior protection against advanced tracking techniques, fingerprinting, and network surveillance. Standard browsers remain vulnerable to various identification methods that Tor effectively mitigates.
Performance trade-offs include slower browsing speeds due to multi-hop routing, but this overhead provides essential anonymity protection unavailable in conventional browsers.
Integration with Rocky Linux Environment
System compatibility advantages include seamless integration with Rocky Linux’s security frameworks and audit capabilities. The distribution’s enterprise focus aligns well with Tor Browser’s security objectives.
Enterprise environment considerations encompass centralized management, policy enforcement, and compliance requirements that Rocky Linux addresses effectively when deploying Tor Browser across organizational networks.
Resource usage comparison shows Tor Browser consuming slightly more system resources than standard browsers due to encryption overhead and network routing complexity, though modern systems handle this efficiently.
Keeping Tor Browser Updated
Update Methods by Installation Type
Manual installation updates require downloading new versions and repeating the installation process. Check the Tor Project website regularly for security updates and new releases.
Flatpak automatic updates provide seamless maintenance through the Flatpak update mechanism:
flatpak update com.github.micahflee.torbrowser-launcherRepository-based updates integrate with Rocky Linux’s standard update procedures:
sudo dnf update tor torbrowser-launcherSecurity Update Importance
Critical security patches address vulnerabilities that could compromise user anonymity or system security. The Tor Project releases emergency updates for severe vulnerabilities, requiring immediate installation.
Update notification systems vary by installation method but should be monitored actively. Subscribe to Tor Project security announcements and Rocky Linux security advisories for timely update information.
Rollback procedures provide safety nets when updates cause compatibility issues. Maintain backup copies of working configurations and previous versions for emergency restoration if needed.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Tor Browser. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Tor Browser on your Rocky Linux 10 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Tor Browser website.