How To Install Viber on Fedora 41

Communicating with friends, family, and colleagues has never been easier thanks to messaging applications like Viber. As a cross-platform VoIP and instant messaging service, Viber allows users to make free calls, send messages, share media, and create group chats across multiple devices. While installing Viber on Windows or macOS might seem straightforward, Linux users often face unique challenges. This comprehensive guide will walk you through various methods to install Viber on Fedora 41, ensuring you can enjoy this powerful communication tool on your Linux system.
What is Viber?
Viber, also known as Rakuten Viber, is a free cross-platform voice over IP (VoIP) and instant messaging application that allows users to communicate with others regardless of their location. Initially launched in 2010, Viber has grown to become one of the most popular messaging platforms worldwide with over a billion users.
The application offers a rich feature set including:
- Free voice and video calls between Viber users
- Text messaging with support for GIFs, stickers, and emoji
- Photo and video sharing capabilities
- Group chats with up to 250 participants
- End-to-end encryption for enhanced security and privacy
- Disappearing messages for sensitive information
- Syncing between mobile and desktop devices
Unlike open-source alternatives, Viber is a closed-source application. However, it provides native executable clients for various Linux distributions, including Fedora. The desktop version integrates seamlessly with the mobile application, allowing you to continue conversations across devices without interruption.
Prerequisites for Installing Viber on Fedora 41
Before proceeding with the installation of Viber on your Fedora 41 system, ensure you meet the following requirements:
- An active internet connection
- Administrative (sudo) privileges on your Fedora system
- Viber application installed and activated on your mobile phone
- Fedora 41 with updated system packages
- Sufficient storage space (approximately 200MB)
Most importantly, you must have Viber installed on your mobile device first. The desktop version of Viber requires synchronization with your mobile account through a QR code scanning process.
To verify your Fedora version, open a terminal and run:
cat /etc/fedora-releaseThis command should return “Fedora Linux release 41” if you’re running the correct version.
Installation Methods Overview
There are several ways to install Viber on Fedora 41, each with its own advantages and potential challenges. The three primary installation methods are:
- RPM Package Installation: The traditional method using Fedora’s native package format
- AppImage Installation: A portable application format that doesn’t require installation
- Snap Package Installation: Using Snap, a universal package management system
Your choice may depend on factors such as your technical expertise, preference for system integration, and specific requirements. The following sections detail each method comprehensively.
Method 1: Installing Viber RPM Package
The RPM (Red Hat Package Manager) method is the most traditional way to install applications on Fedora systems. This approach integrates Viber directly into your system, making it easily accessible from your application menu.
Downloading the RPM Package
First, you need to download the official Viber RPM package. Open a terminal and use the wget command to download the package:
wget -c https://download.cdn.viber.com/desktop/Linux/viber.rpmIf wget isn’t installed on your system, you can install it using:
sudo dnf install wgetInstalling the RPM Package
Once the download is complete, navigate to the directory containing the downloaded file and install it using DNF (Dandified YUM), Fedora’s package manager:
sudo dnf localinstall viber.rpmAlternatively, you can use the traditional RPM command:
sudo rpm -i viber.rpmHandling Dependencies
During installation, you might encounter dependency-related issues. One common problem in Fedora 41 is the missing libcrypto.so.10 library. To resolve this, install the compat-openssl10 package:
sudo dnf install compat-openssl10If you encounter additional dependency issues, you can try installing them with:
sudo dnf install libXScrnSaver libnotifyVerifying the Installation
After successful installation, verify that Viber is properly installed by searching for it in your application menu or running:
viberThe application should launch, presenting you with a QR code to link with your mobile device.
Method 2: Using Viber AppImage
AppImage is a universal software packaging format that allows applications to run on various Linux distributions without installation. This method is ideal if you prefer not to modify your system or want to try Viber without committing to a full installation.
Understanding AppImage Benefits
AppImage offers several advantages:
- No installation required
- No system modification
- Easy portability between Linux systems
- Self-contained dependencies
- Simple to update or remove
Downloading Viber AppImage
To get the Viber AppImage, use wget to download it:
wget -c https://download.cdn.viber.com/desktop/Linux/viber.AppImageMaking the AppImage Executable
After downloading, you need to make the AppImage file executable. Run the following command:
chmod +x viber.AppImageRunning Viber via AppImage
You can now run Viber directly by executing the AppImage:
./viber.AppImageCreating a Desktop Shortcut
For convenience, you might want to create a desktop shortcut. Create a file named viber.desktop in ~/.local/share/applications/ with the following content:
[Desktop Entry]
Name=Viber
Comment=Viber VoIP and messaging application
Exec=/path/to/viber.AppImage
Icon=/path/to/viber-icon.png
Terminal=false
Type=Application
Categories=Network;InstantMessaging;Replace /path/to/viber.AppImage with the actual path to your AppImage file. You can download a Viber icon from the internet for use with the shortcut.
Method 3: Using Unofficial Snap Package
Snap is a universal package management system developed by Canonical. While there’s no official Viber snap package, an unofficial one is available that works well on Fedora 41.
Setting Up Snapd on Fedora 41
First, install the snap daemon (snapd) on your Fedora system:
sudo dnf install snapdAfter installation, enable the snapd service:
sudo systemctl enable --now snapd.socketTo enable classic snap support, create a symbolic link:
sudo ln -s /var/lib/snapd/snap /snapYou’ll need to log out and log back in, or restart your system, for the changes to take effect.
Installing Viber Snap Package
Once snapd is set up, install the unofficial Viber snap package:
sudo snap install viber-unofficialThe installation process may take a few minutes, depending on your internet connection speed.
Running Viber Snap
After installation, you can launch Viber either from your application menu or by running:
snap run viber-unofficialSetting Up Viber After Installation
Regardless of which installation method you chose, you’ll need to set up Viber on your desktop by linking it to your mobile device.
First-Time Launch
When you launch Viber for the first time, you’ll see a welcome screen with a QR code. This code is used to link your desktop installation with your mobile device.
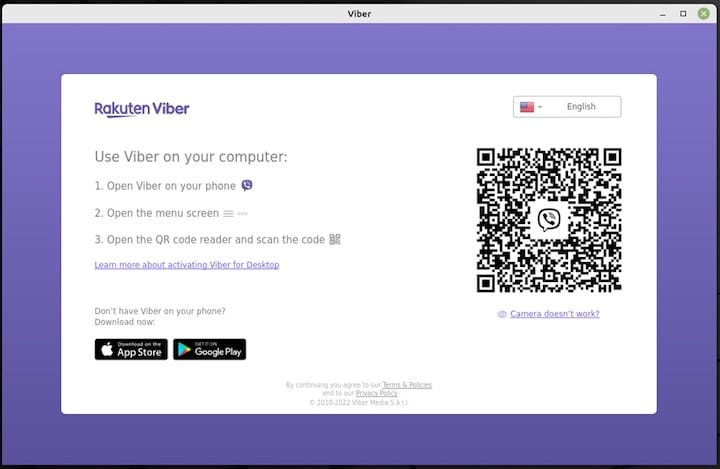
QR Code Scanning Process
To link your devices:
- Open Viber on your mobile phone
- Navigate to “More” (three dots or hamburger menu)
- Select “Settings” > “Viber for Desktop”
- Tap “Scan QR code”
- Point your phone’s camera at the QR code displayed on your desktop screen
Account Verification
After scanning the QR code, your desktop application will sync with your mobile device, importing your contacts, chat history, and settings. This process may take a few minutes, depending on the amount of data.
Configuring Initial Settings
Once the synchronization is complete, you can configure your Viber desktop settings:
- Adjust notification preferences
- Set up audio and video devices for calls
- Configure privacy settings
- Customize the chat appearance and background
- Set up backup options for your messages
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with careful installation, you might encounter some issues when using Viber on Fedora 41. Here are solutions to common problems:
Dependency Issues (libcrypto.so.10)
One of the most common issues is the missing libcrypto.so.10 library. This can be resolved by installing the compatibility package:
sudo dnf install compat-openssl10Wayland Compatibility Problems
Viber may have issues with Wayland, Fedora’s default display server. To run Viber on X11 instead:
- Log out of your current session
- On the login screen, click on the gear icon
- Select “Gnome on Xorg”
- Log in normally and launch Viber
Hyprland-Specific Issues
If you’re using Hyprland as your window manager (as mentioned in search result #2), you might encounter issues with Viber not opening. This is often related to the module “org.hyprland.style” errors. A potential workaround is to:
- Create a specific Viber launch script:
#!/bin/bash
XDG_SESSION_TYPE=x11 viber- Make it executable:
chmod +x ~/viber-launcher.sh- Use this script to launch Viber instead of the regular command.
Network Connection Problems
If Viber cannot connect to its servers, ensure:
- Your internet connection is working properly
- No firewall rules are blocking Viber
- The required ports are open (TCP/UDP: 5245, 4244, 5243, 7985, 80, 443)
To open these ports on Fedora’s firewall:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=5245/tcp --add-port=4244/tcp --add-port=5243/tcp --add-port=7985/tcp --add-port=80/tcp --add-port=443/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=5245/udp --add-port=4244/udp --add-port=5243/udp --add-port=7985/udp --add-port=80/udp --add-port=443/udp
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadQR Code Scanning Problems
If you’re having trouble scanning the QR code:
- Ensure your phone’s camera is clean and focused
- Adjust your screen brightness
- Try relaunching Viber on both devices
- Ensure both devices are connected to the internet
Audio/Video Configuration Issues
For problems with calls or video chats:
- Check your microphone and camera permissions
- Verify that audio devices are properly configured in Viber settings
- Test your microphone and camera with another application
Viber on Different Fedora Desktop Environments
Viber’s performance and appearance can vary across different desktop environments in Fedora 41.
GNOME vs KDE
Viber generally works well on both GNOME (Fedora’s default desktop environment) and KDE:
- GNOME: Provides a clean integration with Viber and generally fewer issues
- KDE: Offers better customization options but might require additional tweaking
Hyprland Considerations
As noted in search result #2, Hyprland users on Fedora 41 might experience issues with Viber not opening. This tiling window manager requires special considerations:
- Try launching Viber with X11 session type as mentioned in the troubleshooting section
- Consider using environment variables to force Viber to use specific UI toolkits
- Monitor the Fedora Forum and Hyprland GitHub issues for community solutions
X11 vs Wayland Compatibility
Viber was primarily developed for X11, which can lead to compatibility issues with Wayland:
- X11: Generally offers the most stable experience with Viber
- Wayland: May require additional configuration or workarounds
Tips for Optimal Performance
To get the most out of Viber on Fedora 41, consider these optimization tips:
Resource Management
Viber can be resource-intensive, especially during video calls. To improve performance:
- Close unnecessary applications while using Viber
- Consider increasing swap space if your system has limited RAM
- Monitor CPU usage with tools like
htopduring calls
Improving Call Quality
For better call experience:
- Use a wired internet connection if possible
- Close bandwidth-intensive applications during calls
- Configure Viber to use lower video quality if necessary
- Use a good quality headset with noise cancellation
Storage Management
Viber media files can quickly accumulate and consume storage space:
- Periodically clear the cache from Viber settings
- Set up automatic media deletion after a certain period
- Consider moving the Viber data directory to a partition with more space
Security and Privacy Considerations
As a closed-source application, Viber raises some privacy and security considerations:
Understanding Viber’s Privacy Policy
While Viber offers end-to-end encryption, it’s important to understand:
- What data is collected and stored
- How long your messages are retained
- What information is shared with third parties
End-to-End Encryption
Viber provides end-to-end encryption for messages and calls, but you should:
- Verify that encryption is enabled (check for the padlock icon)
- Use the “Trust this contact” feature for additional security
- Be aware that group chats have different encryption properties than one-on-one conversations
Required Permissions
The Viber desktop application requests various permissions, including:
- Access to your contacts
- Storage for media files
- Network connectivity
- Audio and video devices
Consider limiting these permissions when possible through Fedora’s security settings.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Viber. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Viber instant messaging and VoIP application on the Fedora 41 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Viber website.