How To Install VNC Server on Linux Mint 20

In this tutorial, we will show you how to install VNC Server on Linux Mint 20. For those of you who didn’t know, Node.js is a Javascript platform for programming that enables users to build network applications very quickly. If you are using Javascript on both the front-end and the back-end, it means your development can be much more consistent and be designed within the same system.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you through the step-by-step installation of the VNC Server on a Linux Mint 20 (Ulyana).
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Linux Mint 20 (Ulyana).
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install VNC Server on Linux Mint 20 Ulyana
Step 1. Before running the tutorial below, it’s important to make sure your system is up to date by running the following apt commands in the terminal:
sudo apt update
Step 2. Installing the Desktop environment.
Run the following command to install the XFCE desktop:
sudo apt install xfce4 xfce4-goodies
Step 3. Installing VNC Server on Linux Mint 20.
Install the TightVNC server using the following command:
sudo apt install tightvncserver
Once that installation completes, issue the following command:
vncserver
You will be prompted to set a password for the VNC server. Enter the password and then confirm it by entering it again.
Step 4. Configure the VNC.
First, stop the VNC session using the following command:
vncserver -kill :1
Next, create a backup of its default startup script file:
mv ~/.vnc/xstartup ~/.vnc/xstartup.bak
Now edit xstartup the file:
nano ~/.vnc/xstartup
Insert the following lines in this file:
#!/bin/bash xrdb $HOME/.Xresources startxfce4 &
Make the xstartup file executable:
sudo chmod +x ~/.vnc/xstartup
And finally, start vncserver again:
vncserver
Step 5. Create a VNC server system startup script.
One more time, let’s stop the VNC server so we can change configuration files:
vncserver -kill :1
Now create a new unit file for VNC. A unit file encodes information about a service:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/vncserver@.service
Paste in the following, replacing idroot it with your own user name. You can also change 1280x800 to your desired resolution:
[Unit] Description=Start TightVNC server at startup After=syslog.target network.target [Service] Type=forking User=idroot Group=idroot WorkingDirectory=/home/idroot PIDFile=/home/idroot/.vnc/%H:%i.pid ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/vncserver -kill :%i > /dev/null 2>&1 ExecStart=/usr/bin/vncserver -depth 24 -geometry 1280x800 :%i ExecStop=/usr/bin/vncserver -kill :%i [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Now reload the systemd processes using the following command for the changes to take effect:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl enable vncserver@1.service sudo systemctl start vncserver@1
Step 6. Connecting to VNC server.
To access the remote desktop on the VNC server from the windows system, you must have a VNC viewer installed on your system. There is various VNC viewer available to use. Download any one and install it on your system, for example:
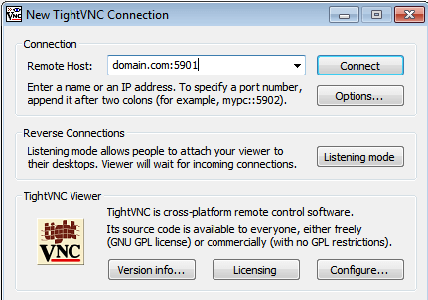
Congratulations! You have successfully installed VNC. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the latest version of VNC Server on the Linux Mint system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official VNC website.