How To Install VNC Server on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS

In this tutorial, we will show you how to install a VNC server on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS. In today’s fast-paced digital world, remote access to computers has become an essential requirement for many users. Whether you’re a system administrator managing servers, a developer working on remote projects, or simply someone who needs to access their desktop from another location, Virtual Network Computing (VNC) provides a convenient and efficient solution. VNC allows you to remotely control and interact with a computer’s desktop environment over a network connection.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the VNC server on Ubuntu 22.04 (Jammy Jellyfish). You can follow the same instructions for Ubuntu 22.04 and any other Debian-based distribution like Linux Mint, Elementary OS, Pop!_OS, and more as well.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Ubuntu 22.04, 20.04, and any other Debian-based distribution like Linux Mint.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- A stable internet connection is crucial for downloading and installing packages. Verify your connection before proceeding.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install VNC Server on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS Jammy Jellyfish
Step 1. To ensure a smooth installation process and maintain the security of your Ubuntu system, it’s crucial to update the system packages to their latest versions. Open a terminal and run the following commands:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade sudo apt install wget apt-transport-https gnupg2
Step 2. Installing Desktop Environment.
While VNC can work with various desktop environments, it’s recommended to use a lightweight option to ensure optimal performance and responsiveness. Two popular choices are XFCE and MATE. For this tutorial, we will focus on installing the XFCE desktop environment.
sudo apt install xfce4 xfce4-goodies
During installation, You will see a prompt to select a display manager for your newly installed XFCE Desktop Environment:
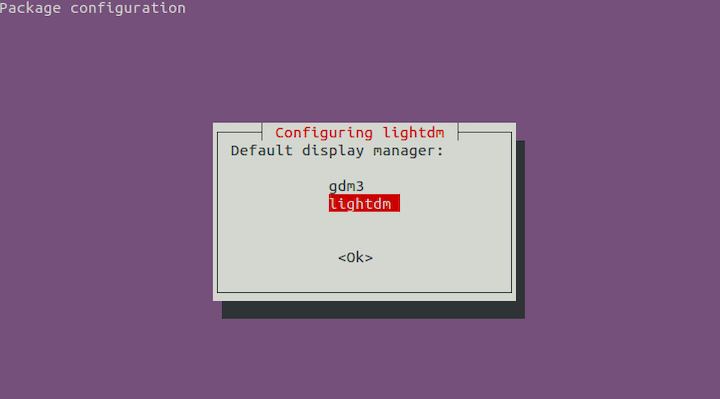
Step 3. Installing the VNC server on Ubuntu 22.04.
By default, the VNC server is not available on the Ubuntu 22.04 base repository. Now run the following command below to install TigerVNC to your Ubuntu system:
sudo apt install tigervnc-standalone-server tigervnc-common tigervnc-tools
After that, run the vncserver the command to set a VNC access password, create the initial configuration files, and start a VNC server instance:
vncserver
Once upon set up the password, you will get a prompt to set a View-Only password. That means anybody who accesses the VNC server with a view-only password will not be able to VNC desktop with either a Mouse or Keyboard:
Would you like to enter a view-only password (y/n)? N /usr/bin/xauth: file /home/idroot/.Xauthority does not exist New 'idroot:1 (idroot)' desktop at :1 on machine idroot Starting applications specified in /etc/X11/Xvnc-session Log file is /home/idroot/.vnc/idroot:1.log Use xtigervncviewer -SecurityTypes VncAuth -passwd /home/idroot/.vnc/passwd :1 to connect to the VNC server.
Note that if you ever want to change your password or add a view-only password, you can do so with the vncpasswd command:
vncpasswd
Step 4. Configure the VNC server.
First, stop the VNC server instance that is running on port 5901 with the following command:
vncserver -kill :1
Next, we need to edit the xstartup file:
mv ~/.vnc/xstartup ~/.vnc/xstartup.bak nano ~/.vnc/xstartup
Add the following lines below:
#!/bin/sh # Start up the standard system desktop unset SESSION_MANAGER unset DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS /usr/bin/startxfce4 [ -x /etc/vnc/xstartup ] && exec /etc/vnc/xstartup [ -r $HOME/.Xresources ] && xrdb $HOME/.Xresources x-window-manager &
Save and close the file, then make this file executable:
chmod +x ~/.vnc/xstartup
Next, restart the VNC server:
vncserver -localhost no :1
Step 5. Set Up VNC as a System Service.
Running VNC as a system service provides several benefits, such as automatic startup on boot and easier management. To set up VNC as a service, create a new systemd unit file:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/vncserver@.service
In the unit file, add the following content:
[Unit] Description=Start TightVNC server at startup After=syslog.target network.target [Service] Type=forking User=yourusername PAMName=login PIDFile=/home/yourusername/.vnc/%H:%i.pid ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/vncserver -kill :%i > /dev/null 2>&1 ExecStart=/usr/bin/vncserver -depth 24 -geometry 1280x800 :%i ExecStop=/usr/bin/vncserver -kill :%i [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Replace yourusername with your actual username and adjust the geometry option to set the desired screen resolution.
Save the file and reload the systemd configuration:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
Enable the VNC service to start automatically on boot:
sudo systemctl enable vncserver@1.service
Start the VNC service:
sudo systemctl start vncserver@1.service
Step 6. Configure Firewall.
Next, open the required firewall ports for VNC communication. By default, VNC uses port 5900 for the first display (:0), 5901 for the second display (:1), and so on. To allow incoming VNC connections, run the following command:
sudo ufw allow 5900/tcp sudo ufw allow 5901/tcp
Step 7. Connecting to your VNC Remote Desktop.
You’re probably familiar with your terminal if you are on Linux or macOS. Create an SSH connection on your local computer that securely forwards to the localhost connection for VNC:
ssh -L 59000:localhost:5901 -C -N -l server_user_name server_ip_address
To access the remote desktop on the VNC server from the Windows system, you must have a VNC viewer installed on your system. There are various VNC viewers available to use. Download anyone and install it on your system, for example:
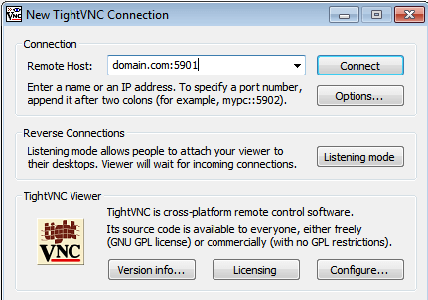
Congratulations! You have successfully installed VNC. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the VNC server on the Ubuntu 22.04 LTS Jammy Jellyfish system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official VNC website.