How To Install Webmin on Fedora 38

In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Webmin on Fedora 38. Webmin is an open-source web-based control panel that allows you to manage your Linux server through a user-friendly graphical interface. With Webmin, you can administer various aspects of your server, such as user accounts, software packages, file systems, and network settings, without the need for intricate command-line knowledge.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the Webmin web-based control panel on a Fedora 38.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Fedora 38.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- A stable internet connection is crucial as we’ll be downloading and installing various packages and dependencies from remote repositories.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Webmin on Fedora 38
Step 1. Before we can install Webmin on Fedora 38, it’s important to ensure that our system is up-to-date with the latest packages. This will ensure that we have access to the latest features and bug fixes and that we can install Webmin without any issues:
sudo dnf update
Step 2. Installing Required Dependencies.
Install the required dependencies by running the following command:
sudo dnf install perl perl-Net-SSLeay openssl perl-IO-Tty perl-Encode-Detect
Step 3. Installing Webmin on Fedora 38.
Begin by downloading the Webmin repository file using wget and moving it to the appropriate location:
wget https://onboardcloud.dl.sourceforge.net/project/webadmin/webmin/2.102/webmin-2.102-1.noarch.rpm
If the Webmin package was downloaded manually it can be installed:
sudo rpm -U webmin-2.102-1.noarch.rpm
Start the Webmin service by running the following command:
sudo systemctl start webmin
Enable the Webmin service to start automatically at boot time by running the following command:
sudo systemctl enable webmin
Step 4. Configure Firewall Rules.
If you have a firewall enabled, make sure to allow traffic to the Webmin port (default is 10000):
firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=10000/tcp firewall-cmd --reload
Step 5. Accessing Webmin Web UI.
Open your web browser and navigate to https://your-IP-address:10000. You will be prompted with a security warning, as the SSL certificate used by Webmin is self-signed. Click on “Advanced” and then “Proceed to localhost (unsafe)” to continue. Log in using your server’s root credentials.
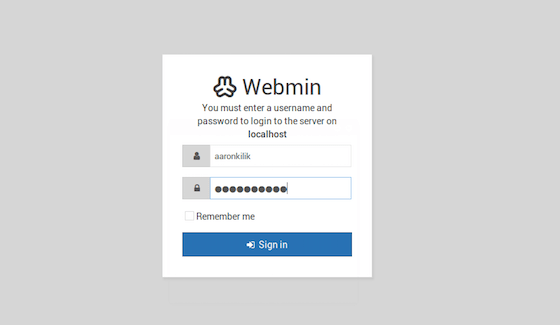
Step 6. Security Considerations.
Tips for Securing Your Webmin Installation:
- Regularly updating Webmin and your system.
- Enabling two-factor authentication for Webmin.
- Implementing strong passwords.
- Limiting access to trusted IP addresses.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Webmin. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Webmin web-based control panel on your Fedora 38 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Webmin website.