How To Install Wiki.js on Debian 13

Wiki.js represents a modern approach to knowledge management and documentation. This powerful, open-source wiki software built on Node.js provides organizations and individuals with a lightweight yet feature-rich platform for creating collaborative documentation, knowledge bases, and team wikis. Unlike traditional wiki solutions, Wiki.js offers an intuitive interface, Markdown editing capabilities, Git integration, and exceptional resource efficiency. The software is designed for performance while conserving CPU resources, making it an ideal choice for Debian 13 servers. This comprehensive guide walks through every step required to deploy Wiki.js on Debian 13, from initial system preparation through SSL certificate configuration and production-ready optimization.
Prerequisites and Requirements
Before beginning the Wiki.js installation process on Debian 13, several essential prerequisites must be in place.
System Requirements
A Debian 13 server with root or sudo privileges forms the foundation for this installation. The system should have a minimum of 1GB RAM, though 2GB is recommended for optimal performance and smooth operation under load. Storage requirements are modest, with at least 1GB of free disk space needed for the application and its dependencies. A non-root user account with administrator privileges provides better security practices than operating as root. An active internet connection is necessary for downloading packages, dependencies, and Wiki.js itself.
Software Requirements
Wiki.js requires specific software components to function properly. Node.js version 18.x, 20.x, or 22.x (latest LTS recommended) serves as the JavaScript runtime engine. PostgreSQL 11 or later acts as the database backend, with PostgreSQL 15 or newer recommended for best performance and feature compatibility. Nginx web server functions as a reverse proxy to handle incoming requests efficiently. An SSL/TLS certificate from Let’s Encrypt secures production deployments with encrypted HTTPS connections. Finally, a domain name or subdomain pointing to the server IP address (such as wiki.example.com) enables proper web access.
Step 1: Update System and Install Essential Packages
System preparation begins with ensuring all existing packages are current. Execute the following command to refresh the package index and retrieve the latest package information from Debian repositories:
sudo apt updateNext, upgrade all installed packages to their newest versions to patch security vulnerabilities and improve stability:
sudo apt upgrade -yEssential build tools and dependencies must be installed before proceeding with Wiki.js components. These packages include curl for downloading resources, wget for file retrieval, git for version control capabilities, build-essential for compiling software, gnupg for cryptographic key management, and ca-certificates for SSL certificate validation:
sudo apt install -y curl wget git build-essential gnupg ca-certificatesAfter applying major system updates, particularly kernel upgrades, a system reboot ensures all changes take effect properly. The command sudo reboot accomplishes this, though it may not always be necessary for minor updates.
Step 2: Install Node.js on Debian 13
Node.js powers Wiki.js as its underlying JavaScript runtime environment, making it an absolutely critical component. The NodeSource repository provides the most recent and well-maintained Node.js packages for Debian systems.
Begin by creating the keyrings directory where repository signing keys will be stored:
sudo mkdir -p /etc/apt/keyringsDownload and add the NodeSource GPG key for package verification and security:
curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/gpgkey/nodesource-repo.gpg.key | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/nodesource.gpgAdd the NodeSource repository for Node.js 22.x to your APT sources list:
echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/nodesource.gpg] https://deb.nodesource.com/node_22.x nodistro main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nodesource.listUpdate the package index again to include packages from the newly added repository:
sudo apt updateInstall Node.js and npm (Node Package Manager) with a single command:
sudo apt install -y nodejsVerify successful Node.js installation by checking the version:
node -vSimilarly, confirm npm installation with its version check:
npm -vWiki.js version 2.x supports Node.js versions 18.x, 20.x, and 22.x, providing flexibility in choosing your runtime version. If version verification fails, double-check that the repository was added correctly and that the installation completed without errors.
Step 3: Install and Configure PostgreSQL Database
Install PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL serves as the recommended database engine for Wiki.js due to its superior performance, advanced search capabilities, and comprehensive feature set. Wiki.js 3.0 will exclusively support PostgreSQL, abandoning other database engines entirely.
Install PostgreSQL server and its contributed extensions package:
sudo apt install -y postgresql postgresql-contribStart the PostgreSQL service immediately:
sudo systemctl start postgresqlEnable PostgreSQL to launch automatically on system boot:
sudo systemctl enable postgresqlVerify that PostgreSQL is running correctly by checking its service status:
sudo systemctl status postgresqlCreate Database and User
PostgreSQL requires a dedicated database and user account for Wiki.js to maintain security isolation and proper access control. Switch to the postgres system user to execute administrative database commands:
sudo -i -u postgresAccess the PostgreSQL interactive terminal:
psqlCreate a new database named “wikijs” specifically for Wiki.js data storage:
CREATE DATABASE wikijs;Create a database user with a strong, unique password (replace ‘secure_password’ with your chosen password):
CREATE USER wikijs WITH PASSWORD 'secure_password';Grant comprehensive privileges on the wikijs database to the wikijs user:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE wikijs TO wikijs;For PostgreSQL 15 and later versions, additional schema privileges must be granted explicitly:
GRANT ALL ON SCHEMA public TO wikijs;Exit the PostgreSQL prompt by typing \q and return to your regular user account with exit. Test database connectivity using the credentials just created to ensure proper configuration. Store database passwords securely and use strong, randomly generated passwords containing uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
Step 4: Install Nginx as Reverse Proxy
Nginx acts as a reverse proxy, sitting between client requests and the Wiki.js application server. This architecture provides SSL termination, load balancing capabilities, enhanced security, and improved performance through caching.
Install the Nginx web server package from Debian repositories:
sudo apt install -y nginxFor environments requiring the absolute latest Nginx features, consider adding the official Nginx repository instead of using Debian’s package. Start the Nginx service:
sudo systemctl start nginxConfigure Nginx to start automatically at boot time:
sudo systemctl enable nginxVerify successful Nginx installation by accessing your server’s IP address in a web browser, where you should see the default Nginx welcome page. Configure your firewall to allow HTTP (port 80) and HTTPS (port 443) traffic for web access:
sudo ufw allow 'Nginx Full'The actual Nginx virtual host configuration will be created later in this guide after Wiki.js installation is complete.
Step 5: Download and Install Wiki.js
Download Wiki.js
Navigate to a temporary working directory in your home folder:
cd ~Download the latest stable Wiki.js release directly from the official GitHub repository:
wget https://github.com/Requarks/wiki/releases/latest/download/wiki-js.tar.gzVerify that the download completed successfully by checking the file size with ls -lh wiki-js.tar.gz. If wget fails due to network issues, curl can serve as an alternative download method.
Extract and Setup Wiki.js
Create the installation directory where Wiki.js application files will reside:
sudo mkdir -p /opt/wikijsFor better security practices, create a dedicated system user for running Wiki.js:
sudo useradd -m -s /bin/false wikijsExtract the Wiki.js archive contents to the installation directory:
sudo tar xzf wiki-js.tar.gz -C /opt/wikijsNavigate into the Wiki.js installation directory:
cd /opt/wikijsList directory contents to verify successful extraction and examine the file structure:
ls -laThe directory should contain configuration files, server scripts, and application code. Set proper ownership of all files to the wikijs user for security:
sudo chown -R wikijs:wikijs /opt/wikijsRename the sample configuration file to create your active configuration:
sudo -u wikijs cp config.sample.yml config.ymlStep 6: Configure Wiki.js
Edit Configuration File
The config.yml file contains all essential configuration parameters for Wiki.js operation. Open the configuration file with a text editor using the wikijs user:
sudo -u wikijs nano config.ymlLocate the database configuration section and set the database type to postgres:
db:
type: postgres
host: localhost
port: 5432
user: wikijs
pass: secure_password
db: wikijs
ssl: falseConfigure the port on which Wiki.js will listen (default 3000 is recommended):
port: 3000Set the bind IP address to 127.0.0.1 to restrict access to localhost only, as Nginx will handle external connections:
bindIP: 127.0.0.1The logLevel parameter controls verbosity of application logs, with options including ‘info’, ‘warn’, and ‘error’. The dataPath specifies where uploaded files and temporary data are stored. Save the configuration file with Ctrl+X, then Y, then Enter.
Initialize Wiki.js Database
Wiki.js performs automatic database initialization when first launched, creating necessary tables and schema structures. Run the following command as the wikijs user to start the server and initialize the database:
sudo -u wikijs node serverMonitor the console output carefully for any error messages during initialization. Successful initialization will display messages indicating database migrations completed and the server is ready. After seeing confirmation that Wiki.js has started successfully, stop the process with Ctrl+C. This manual start was only for testing and initialization; the next step configures Wiki.js as a persistent system service.
Step 7: Create Systemd Service for Wiki.js
Running Wiki.js as a systemd service ensures automatic startup, process management, and easy administration through standard system tools. Create a new systemd service file:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/wikijs.serviceInsert the following comprehensive service configuration:
[Unit]
Description=Wiki.js
After=network.target postgresql.service
[Service]
Type=simple
ExecStart=/usr/bin/node server
Restart=always
User=wikijs
Environment=NODE_ENV=production
WorkingDirectory=/opt/wikijs
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetThe [Unit] section defines service dependencies, ensuring Wiki.js starts only after networking and PostgreSQL are available. The [Service] section specifies how the service runs, including the execution command, restart policy, and operating environment. The [Install] section determines when the service activates during the boot process. Save and close the file after entering the configuration.
Reload the systemd daemon to recognize the new service file:
sudo systemctl daemon-reloadStart the Wiki.js service:
sudo systemctl start wikijsEnable the service to launch automatically at system boot:
sudo systemctl enable wikijsVerify the service is running without errors:
sudo systemctl status wikijsView real-time service logs to monitor application behavior:
sudo journalctl -u wikijs -fConfirm Wiki.js is listening on port 3000:
ss -tulpn | grep 3000Step 8: Configure Nginx Reverse Proxy
Nginx reverse proxy configuration enables secure, efficient routing of web requests to the Wiki.js application. Create a new Nginx server block configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/wikijsInsert the following comprehensive reverse proxy configuration, replacing wiki.example.com with your actual domain:
server {
listen 80;
server_name wiki.example.com;
access_log /var/log/nginx/wikijs.access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/wikijs.error.log;
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:3000;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
client_max_body_size 50M;
}
}Essential proxy headers ensure Wiki.js receives accurate client information. The Upgrade and Connection headers enable WebSocket support for real-time collaboration features. The client_max_body_size directive allows file uploads up to 50MB. Save and exit the configuration file.
Enable the site by creating a symbolic link in sites-enabled:
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/wikijs /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/Test the Nginx configuration syntax for errors:
sudo nginx -tA successful test displays “syntax is ok” and “test is successful”. Reload Nginx to apply the new configuration:
sudo systemctl reload nginxIf configuration errors occur, carefully review the server block for typos, incorrect paths, or missing semicolons.
Step 9: Secure Wiki.js with SSL/TLS Certificate
Install Certbot
Certbot automates the process of obtaining and renewing free SSL/TLS certificates from Let’s Encrypt. Install Certbot and its Nginx plugin:
sudo apt install -y certbot python3-certbot-nginxThe python3-certbot-nginx package enables Certbot to automatically modify Nginx configurations for HTTPS. Verify Certbot installation by checking its version with certbot --version.
Obtain SSL Certificate
Run Certbot with the Nginx plugin to obtain and install an SSL certificate, replacing wiki.example.com with your domain and [email protected] with your email address:
sudo certbot --nginx --agree-tos --redirect --hsts --staple-ocsp --email [email protected] -d wiki.example.comThe –agree-tos flag accepts Let’s Encrypt terms of service automatically. The –redirect option forces HTTPS by redirecting all HTTP traffic. The –hsts flag adds HTTP Strict Transport Security headers for enhanced security. The –staple-ocsp option enables OCSP stapling for improved SSL performance. Follow any interactive prompts during the certificate issuance process.
Upon successful completion, SSL certificates are stored in /etc/letsencrypt/live/wiki.example.com/. Certbot automatically modifies the Nginx configuration to enable HTTPS. Test automatic certificate renewal to ensure certificates won’t expire unexpectedly:
sudo certbot renew --dry-runLet’s Encrypt certificates expire after 90 days, but Certbot’s systemd timer automatically renews them before expiration. Verify HTTPS is functioning by accessing https://wiki.example.com in a browser; the connection should show as secure with a valid certificate.
Step 10: Complete Wiki.js Setup Wizard
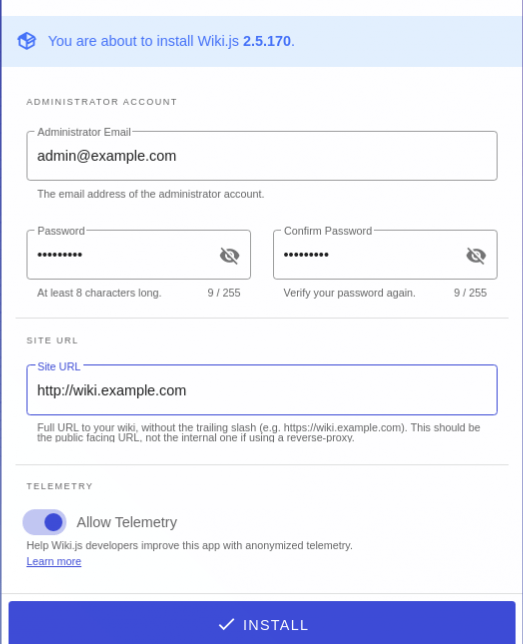
Access the Wiki.js web interface through your domain name in a browser: https://wiki.example.com. The initial setup wizard guides through final configuration steps.
Configure the administrator account by entering an email address, username, and strong password. This account will have full administrative privileges over the wiki. Select the site URL, which should match your domain name exactly. Choose the default locale and timezone settings appropriate for your location and user base.
Wiki.js requests permission to send anonymous telemetry data to help developers improve the software; this is optional and can be disabled. Click the Install button to complete the initialization process. Wait while Wiki.js performs final configuration and setup tasks, which typically takes only a few moments.
After installation completes, log in using the administrator credentials just created. The admin dashboard provides access to all configuration options, user management, and system settings. Create your first home page by clicking the “Create Home Page” button, which opens the Markdown editor interface.
Post-Installation Configuration
Configure Authentication
Navigate to the Administration panel and select the Authentication section. Wiki.js supports multiple authentication methods including local accounts, LDAP directory services, OAuth2 providers, and SAML single sign-on. Configure local authentication settings to control password requirements and policies.
Set minimum password length, require special characters, and enforce password complexity rules to enhance security. Enable two-factor authentication for administrator accounts and sensitive users to provide an additional security layer. To make the wiki completely private and require authentication for all pages, modify the Guest group permissions and remove all access rights.
Storage Configuration
Navigate to Administration > Storage to configure content backup and synchronization options. Wiki.js supports Git storage for version control, allowing automatic commits and synchronization with remote repositories like GitHub or GitLab. Set up a remote Git repository connection by providing the repository URL and authentication credentials.
Configure a backup strategy and schedule to protect against data loss. Local file system storage options allow attachments and media files to be stored on the server or external cloud services like AWS S3.
Performance Optimization and Maintenance
Configure Wiki.js search engine in the Administration panel, with PostgreSQL’s built-in full-text search recommended for optimal performance. PostgreSQL offers advanced search capabilities that rival dedicated search engines like Elasticsearch in many scenarios. Enable application caching to reduce database queries and improve page load times.
Database optimization for PostgreSQL includes tuning parameters like shared_buffers, work_mem, and effective_cache_size based on available system memory. Regular VACUUM and ANALYZE operations maintain database performance by removing dead tuples and updating query planner statistics. Implement regular backup procedures for both database content and uploaded files.
Update Wiki.js to the latest version by downloading new releases, stopping the service, extracting files, and restarting. Monitor system resources including CPU usage, RAM consumption, and disk space to prevent performance degradation. Configure log rotation with journalctl to prevent log files from consuming excessive disk space. Performance tuning for Nginx reverse proxy includes adjusting worker processes, connection limits, and buffer sizes.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When the Wiki.js service fails to start, check system logs with sudo journalctl -u wikijs -xe for detailed error messages. Database connection errors typically indicate incorrect credentials or PostgreSQL service not running; verify credentials in config.yml match the database user created earlier.
Nginx reverse proxy issues often stem from incorrect proxy headers or port mismatches; ensure proxy_pass points to the correct localhost address and port. Port conflicts occur when another application uses port 3000; either change Wiki.js port in config.yml or stop the conflicting service. File permission errors prevent Wiki.js from reading configuration or writing logs; ensure the wikijs user owns all files in /opt/wikijs.
Memory issues manifest as slow performance or crashes under load; increase available RAM or optimize PostgreSQL memory settings. SSL certificate renewal failures require manual intervention; check Certbot logs and ensure DNS records remain correct. Node.js version compatibility problems occur with unsupported versions; Wiki.js requires Node.js 18.x, 20.x, or 22.x.
Security Best Practices
Keep Wiki.js and all system packages updated regularly to patch security vulnerabilities and bugs. Configure firewall rules using UFW to allow only necessary ports (80, 443, SSH). Use strong, randomly generated passwords for database accounts and administrator users, storing them securely in a password manager.
Enable HTTPS-only access by configuring Nginx to redirect all HTTP traffic to HTTPS automatically. Implement a comprehensive backup strategy with automated daily backups stored both locally and offsite. Configure Nginx security headers including HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS), X-Frame-Options, X-Content-Type-Options, and Content Security Policy (CSP).
Limit database user privileges to only what Wiki.js requires, avoiding unnecessary superuser permissions. Monitor access logs regularly for suspicious activity, failed login attempts, and unusual traffic patterns. Perform regular security audits reviewing user permissions, authentication settings, and system configurations. Disable or remove unnecessary services and applications to reduce the attack surface.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Wiki.js. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Wiki.js on Debian 13 “Trixie” system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Wiki.js website.