
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install WildFly on Debian 11. For those of you who didn’t know, WildFly formerly known as JBoss is an application server written in Java and developed by Red Hat. WildFly is a flexible, lightweight, managed application runtime that helps you build amazing applications.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the WildFly (JBoss) on a Debian 11 (Bullseye).
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Debian 11 (Bullseye).
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install WildFly on Debian 11 Bullseye
Step 1. Before we install any software, it’s important to make sure your system is up to date by running the following apt commands in the terminal:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
Step 2. Installing Java.
WildFly (JBoss) requires Java to be installed on your server. Now run the following command to install Java:
sudo apt install default-jdk
Verify Java version using the following command:
java -version
Step 3. Create User and Group for Wildfly.
Now we create a user and group to run the Wildfly application using the following command:
groupadd -r wildfly useradd -r -g wildfly -d /opt/wildfly -s /sbin/nologin wildfly
Step 4. Installing WildFly on Debian 11.
By default, WildFly is not available on Debian 11 base repository. Now we download the latest stable release WildFly from GitHub:
wget https://github.com/wildfly/wildfly/releases/download/25.0.1.Final/wildfly-25.0.1.Final.zip
Next, extract the downloaded file:
unzip wildfly-25.0.1.Final.zip mv wildfly-25.0.1.Final /opt/wildfly
Then, change the directory ownership to user and group WildFly:
chown -RH wildfly:wildfly /opt/wildfly
Step 5. Configure WildFly.
Now we create a Wildfly configuration directory inside /etc using the following command below:
mkdir -p /etc/wildfly
After that, copy all necessary files from the Wildfly directory to the /etc/wildfly directory:
cp /opt/wildfly/docs/contrib/scripts/systemd/wildfly.conf /etc/wildfly/ cp /opt/wildfly/docs/contrib/scripts/systemd/wildfly.service /etc/systemd/system/ cp /opt/wildfly/docs/contrib/scripts/systemd/launch.sh /opt/wildfly/bin/
Next, set execution permission to all shell script files:
chmod +x /opt/wildfly/bin/*.sh
Finally, start and enable the Wildfly service using the following command below:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl start wildfly sudo systemctl enable wildfly
Step 6. Configure Wildfly Admin Console.
By default, the Wildfly admin console is disabled. We recommended enabling it to manage the Wildfly application:
nano /etc/wildfly/wildfly.conf
Change the following configuration lines:
WILDFLY_BIND=127.0.0.1 WILDFLY_CONSOLE_BIND=127.0.0.1
Save and close the file then edit the Wildfly launcher script and enable the admin console:
nano /opt/wildfly/bin/launch.sh
Change the following configuration lines:
if [[ "$1" == "domain" ]]; then
$WILDFLY_HOME/bin/domain.sh -c $2 -b $3 -bmanagement $4
else
$WILDFLY_HOME/bin/standalone.sh -c $2 -b $3 -bmanagement $4
fi
Save and close the file then edit the Wildfly systemd file:
nano /etc/systemd/system/wildfly.service
Change the following configuration lines:
ExecStart=/opt/wildfly/bin/launch.sh $WILDFLY_MODE $WILDFLY_CONFIG $WILDFLY_BIND $WILDFLY_CONSOLE_BIND
Finally, start and enable the Wildfly service using the following command below:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl restart wildfly sudo systemctl status wildfly
Step 7. Configure Wildfly Admin User.
Now we create an admin user to access the Wildfly admin console. You can create it by running the following command below:
sh /opt/wildfly/bin/add-user.sh
Step 8. Configure the Firewall.
If your server is protected by a firewall and you want to access the WildFly interface from the outside of your local network you need to open port 8080:
sudo ufw allow 8080/tcp
Step 9. Accessing WildFly Web Interface.
Once successfully installed, open your web browser and access the WildFly using the URL https://your-IP-address:8080. You will be redirected to the WildFly page:

To access the Wildfly admin console type the URL http://your-IP-address:9990/console in your web browser. You will be asked to provide an admin username and password as below:
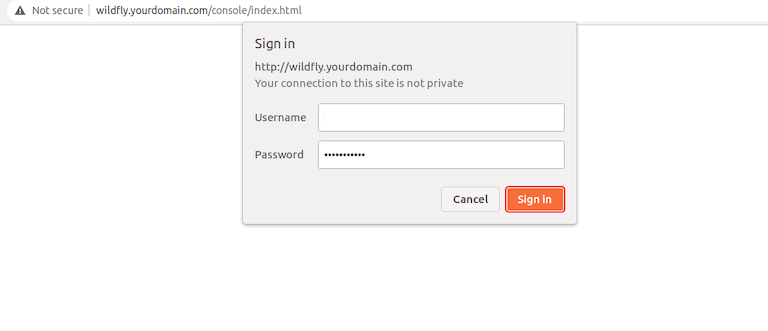
Congratulations! You have successfully installed WildFly. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the latest version of WildFly (JBoss) on Debian 11 Bullseye. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official WildFly website.