How To Install WordPress on Rocky Linux 10

Installing WordPress on Rocky Linux 10 provides a powerful, enterprise-grade foundation for modern websites. Rocky Linux 10, built from Red Hat Enterprise Linux sources, offers exceptional stability and security for WordPress deployments. This comprehensive guide covers both LAMP and LEMP stack installations, complete with security hardening and performance optimization techniques.
WordPress powers over 40% of websites globally, making it the world’s leading content management system. Combining it with Rocky Linux 10’s robust infrastructure creates an ideal platform for everything from personal blogs to enterprise applications. The installation process typically requires 30-45 minutes, depending on your configuration choices and optional security implementations.
Whether you’re building a development environment or preparing a production server, this detailed walkthrough ensures a secure, optimized WordPress installation that follows current industry best practices and Rocky Linux documentation standards.
Prerequisites and System Requirements
Essential System Requirements
Rocky Linux 10 installation demands specific minimum hardware specifications for optimal WordPress performance. Allocate at least 2GB RAM for basic installations, though 4GB provides better performance for production environments. Storage requirements include 20GB minimum disk space, with 50GB recommended for production deployments hosting multiple sites or extensive media libraries.
Network connectivity remains crucial throughout the installation process. Ensure reliable internet access for downloading packages, WordPress core files, and security updates. A stable connection prevents interruptions during critical installation phases.
Access Requirements and Tools
Administrative privileges through root access or sudo capabilities are mandatory for system-level modifications. Standard users cannot install packages or modify system configurations required for WordPress deployment.
Basic command-line proficiency significantly streamlines the installation process. Familiarity with text editors like vim or nano helps during configuration file modifications. SSH access should be properly secured before beginning the WordPress installation process.
Domain name configuration pointing to your server’s IP address is essential for production deployments. Development environments can utilize IP addresses directly, but production sites require proper DNS configuration for optimal functionality and SEO benefits.
Security Preparation Considerations
Implement SSH key-based authentication before proceeding with WordPress installation. Password-based authentication presents significant security risks, particularly for production servers. Configure fail2ban to prevent brute-force attacks against SSH and future WordPress login attempts.
Firewall configuration should be planned in advance, considering which ports require access for web traffic, SSH administration, and any additional services. Rocky Linux 10’s firewalld provides robust protection when properly configured.
System Preparation and Updates
Complete System Update Process
Begin WordPress installation with comprehensive system updates ensuring all security patches and software improvements are installed. Rocky Linux 10 utilizes DNF package manager for system maintenance and software installation.
Execute the following commands to update your system completely:
sudo dnf clean all
sudo dnf update -y
sudo dnf upgrade -yThe cleaning process removes cached package data, while updates install security patches and bug fixes. Upgrades handle major version changes for installed packages. This process typically requires 5-15 minutes depending on available updates.
Reboot the system after major updates to ensure kernel changes take effect:
sudo systemctl rebootEssential Package Installation
Install fundamental utilities required throughout the WordPress installation process. These tools facilitate file management, network operations, and text editing tasks.
sudo dnf install wget curl vim tar unzip git htop -yEach package serves specific purposes: wget and curl handle file downloads, vim provides text editing capabilities, tar and unzip manage compressed archives, git enables version control, and htop offers system monitoring.
Repository Configuration and Verification
Rocky Linux 10 includes standard repositories, but additional software sources enhance available packages. Install EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) repository for expanded software availability:
sudo dnf install epel-release -y
sudo dnf makecacheVerify repository configuration with:
sudo dnf repolist enabledThis command displays active repositories, confirming proper configuration before proceeding with web server and database installations.
Time Zone and Locale Configuration
Proper time zone configuration prevents timestamp discrepancies affecting WordPress functionality, security logs, and scheduled tasks. Set your appropriate time zone:
sudo timedatectl set-timezone America/New_York
sudo timedatectl statusConfigure system locale for proper character encoding and internationalization support:
sudo localectl set-locale LANG=en_US.UTF-8These settings ensure WordPress displays dates correctly and handles international content properly.
LAMP Stack Installation (Apache, MySQL, PHP)
Apache Web Server Installation and Configuration
Apache HTTP Server provides the foundation for WordPress hosting with the LAMP stack configuration. Install Apache with essential modules:
sudo dnf install httpd httpd-tools mod_ssl -yEnable and start Apache services immediately:
sudo systemctl enable httpd
sudo systemctl start httpdVerify Apache installation and service status:
sudo systemctl status httpd
httpd -vThe status command confirms Apache is running properly, while the version command displays installed Apache version information.
Configure basic Apache settings for WordPress compatibility:
sudo vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.confLocate and modify these directives for optimal WordPress performance:
ServerTokens Prod
ServerSignature Off
KeepAlive On
MaxKeepAliveRequests 100
KeepAliveTimeout 5These settings enhance security by hiding server information and improve performance through persistent connections.
MariaDB Database Server Setup and Security
MariaDB serves as the database backend for WordPress content storage, user management, and configuration data. Install MariaDB server and client packages:
sudo dnf install mariadb-server mariadb -yEnable automatic startup and start MariaDB immediately:
sudo systemctl enable mariadb
sudo systemctl start mariadbSecure MariaDB installation using the included security script:
sudo mysql_secure_installationFollow the interactive prompts carefully:
- Set root password (use strong, unique password)
- Remove anonymous users (answer ‘Y’)
- Disallow root login remotely (answer ‘Y’)
- Remove test database (answer ‘Y’)
- Reload privilege tables (answer ‘Y’)
Test database connectivity:
sudo mysql -u root -pThis command verifies successful MariaDB installation and root password configuration.
PHP Installation with WordPress Extensions
PHP powers WordPress’s dynamic content generation and database interactions. Install PHP with essential extensions for complete WordPress functionality:
sudo dnf install php php-mysqlnd php-gd php-xml php-mbstring php-curl php-zip php-intl php-json php-fpm -yEach extension serves specific WordPress functions:
- php-mysqlnd: Database connectivity
- php-gd: Image processing and manipulation
- php-xml: XML parsing for feeds and imports
- php-mbstring: Multi-byte string handling
- php-curl: HTTP requests for plugins and themes
- php-zip: Archive handling for updates
- php-intl: Internationalization support
Configure PHP for WordPress optimization:
sudo nano /etc/php.iniModify these settings for better WordPress performance:
memory_limit = 256M
upload_max_filesize = 64M
post_max_size = 64M
max_execution_time = 300
max_input_vars = 3000Restart Apache to load PHP modules:
sudo systemctl restart httpdLAMP Stack Verification and Testing
Create a PHP information file to verify complete LAMP stack functionality:
sudo echo "<?php phpinfo(); ?>" > /var/www/html/info.phpAccess the PHP info page through your web browser at http://your-server-ip/info.php. This page displays PHP configuration, loaded extensions, and system information confirming successful LAMP installation.
Remove the info file after verification for security purposes:
sudo rm /var/www/html/info.phpTest database connectivity from PHP:
sudo nano /var/www/html/db-test.phpAdd this simple database connection test:
<?php
$connection = new mysqli("localhost", "root", "your-root-password", "mysql");
if ($connection->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $connection->connect_error);
}
echo "Database connection successful!";
$connection->close();
?>Alternative: LEMP Stack Installation (Nginx, MySQL, PHP)
Nginx Web Server Installation
Nginx offers superior performance for high-traffic WordPress sites through efficient resource utilization and concurrent connection handling. Install Nginx web server:
sudo dnf install nginx -yEnable automatic startup and start Nginx service:
sudo systemctl enable nginx
sudo systemctl start nginxVerify Nginx installation and configuration:
sudo systemctl status nginx
nginx -vTest Nginx configuration syntax:
sudo nginx -tThis command validates configuration files before applying changes, preventing service disruption from syntax errors.
MariaDB Installation for LEMP
Database installation remains identical between LAMP and LEMP stacks. Install MariaDB server components:
sudo dnf install mariadb-server mariadb -y
sudo systemctl enable mariadb
sudo systemctl start mariadb
sudo mysql_secure_installationFollow the same security hardening procedures outlined in the LAMP section for consistent database protection.
PHP-FPM Configuration for Nginx
LEMP stack utilizes PHP-FPM (FastCGI Process Manager) for improved PHP performance and resource management compared to Apache’s mod_php:
sudo dnf install php php-fpm php-mysqlnd php-gd php-xml php-mbstring php-curl php-zip php-intl -yConfigure PHP-FPM for optimal performance:
sudo vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.confModify these critical settings:
user = nginx
group = nginx
listen = /run/php-fpm/www.sock
listen.owner = nginx
listen.group = nginx
pm = dynamic
pm.max_children = 50
pm.start_servers = 5
pm.min_spare_servers = 5
pm.max_spare_servers = 35Enable and start PHP-FPM:
sudo systemctl enable php-fpm
sudo systemctl start php-fpmNginx PHP Processing Configuration
Configure Nginx to process PHP files through PHP-FPM. Create a default server block:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.confAdd comprehensive PHP processing configuration:
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
server_name _;
root /var/www/html;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$args;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
try_files $uri =404;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php-fpm/www.sock;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
location ~ /\.ht {
deny all;
}
}Test configuration and restart services:
sudo nginx -t
sudo systemctl restart nginx
sudo systemctl restart php-fpmDatabase Configuration for WordPress
WordPress Database Creation
Access MariaDB as root user to create dedicated WordPress database:
sudo mysql -u root -pCreate WordPress database with UTF-8 character set for proper international character support:
CREATE DATABASE wordpress CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;The utf8mb4 character set supports full Unicode including emoji characters, preventing database errors with modern content.
Dedicated WordPress User Creation
Create a specific database user for WordPress with limited privileges following security best practices:
CREATE USER 'wpuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'StrongPassword123!@#';Use complex passwords containing uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid dictionary words and predictable patterns.
Grant necessary privileges to the WordPress user:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON wordpress.* TO 'wpuser'@'localhost';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Verify user creation and privileges:
SHOW GRANTS FOR 'wpuser'@'localhost';
EXIT;Database Security Hardening
Test the new user account connectivity:
mysql -u wpuser -p wordpressThis command verifies successful user creation and database access permissions.
Implement additional database security measures:
sudo nano /etc/my.cnf.d/security.cnfAdd security-focused configuration:
[mysqld]
local-infile=0
skip-show-database
skip-networkingThese settings disable local file imports, hide database lists from unauthorized users, and prevent network-based attacks.
Database Performance Optimization
Configure MariaDB for WordPress performance optimization:
sudo vim /etc/my.cnf.d/performance.cnfAdd performance tuning parameters based on available system resources:
[mysqld]
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 1G
innodb_log_file_size = 256M
query_cache_size = 64M
query_cache_type = 1
max_connections = 150Adjust buffer pool size to approximately 70% of available RAM for database-intensive applications.
Restart MariaDB to apply configuration changes:
sudo systemctl restart mariadbWordPress Download and Installation
Official WordPress Download
Download the latest WordPress release directly from the official repository ensuring authenticity and security:
cd /tmp
wget https://wordpress.org/latest.tar.gzVerify download integrity using checksums when available:
wget https://wordpress.org/latest.tar.gz.sha1
sha1sum -c latest.tar.gz.sha1WordPress File Extraction and Placement
Extract the WordPress archive to a temporary location:
tar -xzf latest.tar.gzFor Apache (LAMP stack), move files to the default document root:
sudo cp -R wordpress/* /var/www/html/For Nginx (LEMP stack), create domain-specific directories:
sudo mkdir -p /var/www/html/example.com/public_html
sudo mv wordpress/* /var/www/html/example.com/public_html/Clean up temporary files:
rm -rf /tmp/wordpress /tmp/latest.tar.gzFile Permissions and Ownership Configuration
Set appropriate file permissions and ownership for security and functionality. For Apache installations:
sudo chown -R apache:apache /var/www/html/
sudo find /var/www/html/ -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;
sudo find /var/www/html/ -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;For Nginx installations:
sudo chown -R nginx:nginx /var/www/html/example.com/public_html/
sudo find /var/www/html/example.com/public_html/ -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;
sudo find /var/www/html/example.com/public_html/ -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;Set specific permissions for wp-content directory to enable uploads and plugin installations:
sudo chmod -R 775 /var/www/html/wp-content/WordPress Configuration File Setup
Copy the sample configuration file:
sudo cp /var/www/html/wp-config-sample.php /var/www/html/wp-config.phpSecure the configuration file permissions:
sudo chmod 600 /var/www/html/wp-config.php
sudo chown apache:apache /var/www/html/wp-config.phpFor Nginx, replace “apache” with “nginx” in the ownership command.
WordPress Configuration and Security
Database Connection Configuration
Edit the WordPress configuration file to establish database connectivity:
sudo nano /var/www/html/wp-config.phpUpdate database connection constants with previously created credentials:
define('DB_NAME', 'wordpress');
define('DB_USER', 'wpuser');
define('DB_PASSWORD', 'StrongPassword123!@#');
define('DB_HOST', 'localhost');
define('DB_CHARSET', 'utf8mb4');
define('DB_COLLATE', 'utf8mb4_unicode_ci');WordPress Security Keys Generation
Generate unique security keys using the WordPress secret key generator:
curl -s https://api.wordpress.org/secret-key/1.1/salt/Replace the placeholder keys in wp-config.php with the generated values. These keys encrypt cookies, sessions, and passwords, enhancing overall security.
Advanced WordPress Security Configuration
Add security-focused configuration options to wp-config.php:
// Disable file editing from WordPress admin
define('DISALLOW_FILE_EDIT', true);
// Hide WordPress version information
remove_action('wp_head', 'wp_generator');
// Disable XML-RPC functionality
add_filter('xmlrpc_enabled', '__return_false');
// Force SSL for admin area
define('FORCE_SSL_ADMIN', true);
// Increase memory limit
ini_set('memory_limit', '256M');
// Enable automatic updates for security releases
define('WP_AUTO_UPDATE_CORE', 'minor');WordPress Debug Configuration
Configure debugging settings appropriately for your environment:
For development environments:
define('WP_DEBUG', true);
define('WP_DEBUG_LOG', true);
define('WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY', false);For production environments:
define('WP_DEBUG', false);
define('WP_DEBUG_LOG', false);
define('WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY', false);SELinux Configuration and Security Context
Understanding SELinux in Rocky Linux 10
Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux) provides mandatory access control protecting system resources from unauthorized access. Rocky Linux 10 enables SELinux by default, requiring specific configuration for WordPress functionality.
Check current SELinux status:
sestatus
getenforceSELinux operates in three modes: Enforcing (active protection), Permissive (logging only), and Disabled (inactive).
WordPress SELinux Context Configuration
Set appropriate SELinux contexts for WordPress files enabling web server access:
sudo setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect true
sudo setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect_db trueConfigure file contexts for WordPress directory:
sudo semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_exec_t "/var/www/html(/.*)?"
sudo semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t "/var/www/html/wp-content(/.*)?"
sudo restorecon -Rv /var/www/html/SELinux Boolean Settings for WordPress
Enable additional SELinux booleans for complete WordPress functionality:
sudo setsebool -P httpd_execmem on
sudo setsebool -P httpd_unified on
sudo setsebool -P httpd_can_sendmail onThese settings allow memory execution, unified file contexts, and email functionality respectively.
SELinux Troubleshooting and Monitoring
Monitor SELinux access violations using audit logs:
sudo ausearch -m avc -ts recentGenerate custom SELinux policies for legitimate access denials:
sudo ausearch -m avc -ts recent | audit2allow -M wordpress-policy
sudo semodule -i wordpress-policy.ppInstall setroubleshoot for user-friendly SELinux problem reporting:
sudo dnf install setroubleshoot-server -yFirewall Configuration and Network Security
Firewalld Service Management
Rocky Linux 10 utilizes firewalld for network security management. Verify firewall status and configuration:
sudo systemctl status firewalld
sudo firewall-cmd --stateEnable firewalld if not already active:
sudo systemctl enable firewalld
sudo systemctl start firewalldHTTP and HTTPS Traffic Configuration
Open necessary ports for web traffic and secure connections:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=httpsAlternatively, specify ports directly:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=80/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=443/tcpSSH Security Enhancement
Modify SSH configuration for enhanced security:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_configImplement these security improvements:
Port 2222
PermitRootLogin no
MaxAuthTries 3
ClientAliveInterval 300
ClientAliveCountMax 2Update firewall rules for new SSH port:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=2222/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --remove-service=sshAdvanced Firewall Security
Create custom firewall zones for enhanced security:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --new-zone=webserver
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=webserver --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=webserver --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=webserver --add-interface=eth0Apply all firewall changes:
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
sudo firewall-cmd --list-allIntrusion Prevention with Fail2ban
Install and configure fail2ban for automated intrusion prevention:
sudo dnf install fail2ban -y
sudo systemctl enable fail2ban
sudo systemctl start fail2banCreate WordPress-specific fail2ban configuration:
sudo nano /etc/fail2ban/jail.localAdd WordPress protection rules:
[wordpress]
enabled = true
port = http,https
filter = wordpress
logpath = /var/log/httpd/access_log
maxretry = 3
bantime = 3600Web Server Virtual Host Configuration
Apache Virtual Host for WordPress
Create dedicated virtual host configuration for production WordPress sites:
sudo nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/wordpress.confConfigure comprehensive virtual host settings:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName example.com
ServerAlias www.example.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/html
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/wordpress_error.log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/wordpress_access.log combined
<Directory "/var/www/html">
Options -Indexes +FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
# Security headers
Header always set X-Content-Type-Options nosniff
Header always set X-Frame-Options DENY
Header always set X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block"
Header always set Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains"
</Directory>
# Block access to sensitive files
<Files "wp-config.php">
Require all denied
</Files>
<Files ".htaccess">
Require all denied
</Files>
</VirtualHost>Nginx Server Block Configuration
Create Nginx server block for LEMP stack deployments:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/wordpress.confConfigure optimized server block:
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com www.example.com;
root /var/www/html/example.com/public_html;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
# Security headers
add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff;
add_header X-Frame-Options DENY;
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block";
# WordPress permalink support
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$args;
}
# PHP processing
location ~ \.php$ {
try_files $uri =404;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php-fpm/www.sock;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_read_timeout 300;
}
# Security restrictions
location ~ /\.(htaccess|htpasswd) {
deny all;
}
location ~ /wp-config.php {
deny all;
}
# Cache static files
location ~* \.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif|ico|css|js)$ {
expires 1y;
add_header Cache-Control "public, immutable";
}
}Configuration Testing and Service Restart
Test configuration syntax before applying changes:
For Apache:
sudo httpd -t
sudo systemctl restart httpdFor Nginx:
sudo nginx -t
sudo systemctl restart nginx
sudo systemctl restart php-fpmVerify services are running correctly:
sudo systemctl status httpd # For Apache
sudo systemctl status nginx # For Nginx
sudo systemctl status php-fpm # For LEMP stackWordPress Web-Based Installation Wizard
Accessing WordPress Installation
Open a web browser and navigate to your server to begin WordPress installation:
For IP-based access:
http://your-server-ip/For domain-configured installations:
http://example.com/The WordPress installation wizard automatically detects incomplete installations and guides you through the setup process.
Language and Regional Settings
Select your preferred language from the comprehensive list of available options. WordPress supports over 70 languages with full localization including:
- User interface translation
- Date and time formatting
- Currency symbols
- Number formatting conventions
Language selection affects admin interface appearance and can be modified post-installation through Settings → General.
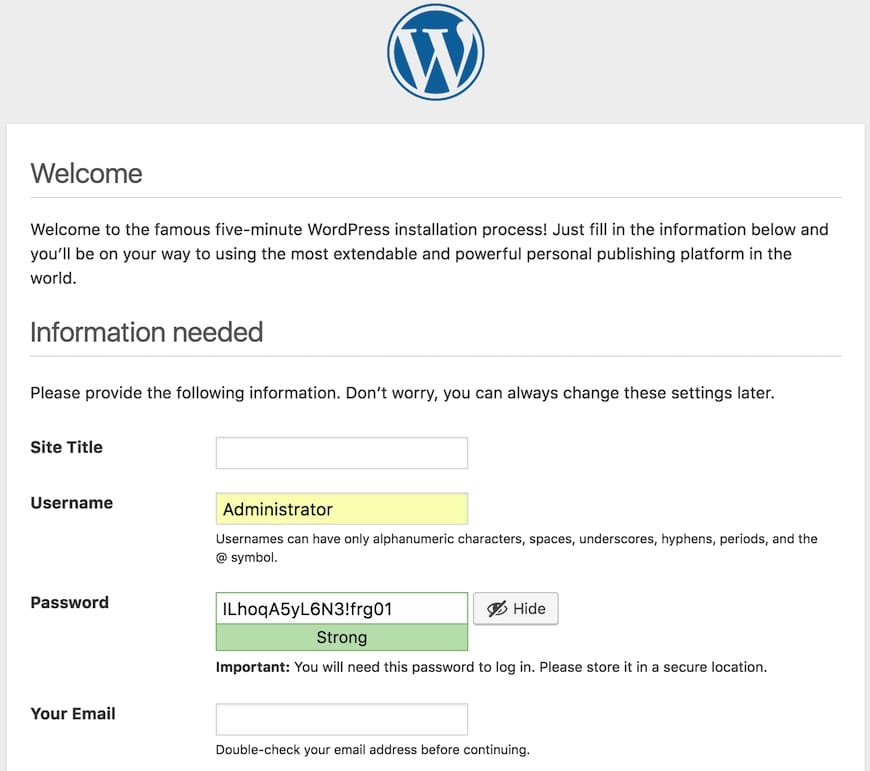
Site Information and Administrator Account
Complete the WordPress installation form with essential site information:
Site Title: Enter descriptive website name appearing in browser titles and search results. Choose meaningful titles that reflect your site’s purpose and content focus.
Username: Create administrator username avoiding common names like “admin” or “administrator” for security reasons. Use unique, memorable usernames not easily guessable by attackers.
Password: Generate strong passwords containing minimum 12 characters with mixed case letters, numbers, and special characters. WordPress provides password strength indicators helping create secure credentials.
Email Address: Provide valid administrator email address for important notifications, password resets, and security alerts. Use dedicated email addresses for website administration.
Search Engine Visibility: Check this option only for development or staging environments. Production sites should leave this unchecked to allow search engine indexing and discovery.
Installation Process Completion
Click “Install WordPress” to finalize the setup process. Installation typically completes within 30-60 seconds depending on server performance and network connectivity.
WordPress creates necessary database tables, default content, and administrative user account during this phase. Monitor for error messages indicating database connectivity or file permission issues.
Initial WordPress Login and Dashboard
Access the WordPress admin dashboard using created credentials at:
http://example.com/wp-admin/The dashboard provides comprehensive site management capabilities including:
- Content creation and editing
- Theme and plugin management
- User account administration
- Site settings configuration
- Security monitoring tools
Performance Optimization and Caching
WordPress Caching Solutions
Implement comprehensive caching strategies to optimize WordPress performance and reduce server resource consumption:
Page Caching: Store complete HTML pages as static files reducing database queries and PHP processing time. Popular solutions include:
- WP Rocket (Premium): Advanced caching with automatic optimization
- W3 Total Cache (Free): Comprehensive caching suite
- WP Super Cache (Free): Simple, effective page caching
Configure basic page caching through plugin installation and activation from WordPress admin dashboard.
Database Optimization Techniques
Regular database maintenance improves WordPress performance by removing unnecessary data and optimizing table structures:
Install database optimization plugins like WP-Optimize or WP Sweep for automated cleanup including:
- Revision cleanup and limitation
- Spam comment removal
- Transient data clearing
- Database table optimization
Manual database optimization using command line tools:
sudo mysql -u root -p -e "OPTIMIZE TABLE wordpress.wp_posts, wordpress.wp_options, wordpress.wp_comments;"Image Optimization and Compression
Implement image optimization to reduce bandwidth usage and improve page load times:
Automatic Image Compression: Install plugins like Smush, ShortPixel, or Imagify for automatic image optimization including:
- Lossless compression reducing file sizes
- WebP format conversion for modern browsers
- Lazy loading implementation for improved performance
- Bulk optimization for existing media libraries
Configure image compression settings balancing quality and file size based on content requirements.
PHP Performance Tuning
Optimize PHP configuration for WordPress-specific performance improvements:
sudo nano /etc/php.iniAdjust these critical performance parameters:
memory_limit = 512M
max_execution_time = 300
upload_max_filesize = 128M
post_max_size = 128M
max_input_vars = 5000
opcache.enable = 1
opcache.memory_consumption = 128
opcache.max_accelerated_files = 4000Enable OPcache for significant performance improvements through PHP bytecode caching:
sudo nano /etc/php.d/10-opcache.iniAdd OPcache optimization settings:
opcache.enable = 1
opcache.enable_cli = 1
opcache.memory_consumption = 256
opcache.interned_strings_buffer = 8
opcache.max_accelerated_files = 10000
opcache.revalidate_freq = 2Content Delivery Network Integration
Implement CDN services for global content distribution and reduced server load:
Popular CDN Services:
- Cloudflare: Free tier with DDoS protection and global caching
- MaxCDN/StackPath: High-performance content delivery
- Amazon CloudFront: Scalable AWS-integrated solution
Configure CDN integration through WordPress plugins or manual DNS configuration depending on chosen service.
Security Hardening and Best Practices
Essential WordPress Security Plugins
Install and configure comprehensive security plugins protecting against common threats:
Wordfence Security: Industry-leading WordPress security solution providing:
- Real-time malware scanning and removal
- Firewall protection against attacks
- Brute force protection with login attempt limiting
- Two-factor authentication implementation
- Security monitoring and threat intelligence
iThemes Security: Alternative security suite offering:
- Strong password enforcement policies
- File change detection and monitoring
- Database backup and restoration capabilities
- Malware scanning and cleanup tools
- Security hardening recommendations
Configure security plugins immediately after WordPress installation for maximum protection.
File System Security Implementation
Implement file system-level security measures protecting WordPress core files and sensitive data:
# Secure wp-config.php permissions
sudo chmod 600 /var/www/html/wp-config.php
# Protect sensitive WordPress files
sudo chmod 444 /var/www/html/index.php
sudo chmod 644 /var/www/html/.htaccess
# Set restrictive directory permissions
sudo find /var/www/html/ -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;
sudo find /var/www/html/ -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;
# Secure wp-content directory
sudo chmod 755 /var/www/html/wp-content/
sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www/html/wp-content/themes/
sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www/html/wp-content/plugins/WordPress Configuration Security Enhancements
Add security-focused directives to wp-config.php preventing common attack vectors:
// Disable file editing through WordPress admin
define('DISALLOW_FILE_EDIT', true);
define('DISALLOW_FILE_MODS', true);
// Hide WordPress version information
remove_action('wp_head', 'wp_generator');
// Disable XML-RPC functionality if not needed
add_filter('xmlrpc_enabled', '__return_false');
// Force SSL for admin area and login
define('FORCE_SSL_ADMIN', true);
// Limit login attempts
define('LIMIT_LOGIN_ATTEMPTS', true);
// Disable user registration if not required
define('AUTOMATIC_UPDATER_DISABLED', true);Regular Security Maintenance Procedures
Establish routine security maintenance procedures ensuring ongoing protection:
Weekly Security Tasks:
- Install WordPress core, theme, and plugin updates
- Review security scan results and address issues
- Monitor failed login attempts and suspicious activity
- Check file integrity and unauthorized modifications
Monthly Security Reviews:
- Audit user accounts and permissions
- Review security plugin settings and logs
- Perform complete malware scans
- Update security passwords and access keys
Quarterly Security Audits:
- Comprehensive security assessment
- Review and update security policies
- Test backup restoration procedures
- Evaluate security plugin effectiveness
Backup Strategy Implementation
Configure automated backup solutions for disaster recovery and security incident response:
Recommended Backup Plugins:
- UpdraftPlus: Comprehensive backup with cloud storage integration
- BackWPup: Professional backup solution with scheduling
- Duplicator: Site migration and backup capabilities
Implement 3-2-1 backup strategy: 3 copies of data, 2 different storage media, 1 offsite location for optimal data protection.
Troubleshooting Common Installation Issues
Permission and Ownership Problems
WordPress file permission errors frequently occur during installation and updates. Diagnose permission issues:
ls -la /var/www/html/Reset WordPress permissions systematically:
# Set correct ownership
sudo chown -R apache:apache /var/www/html/ # For Apache
sudo chown -R nginx:nginx /var/www/html/ # For Nginx
# Set directory permissions
sudo find /var/www/html/ -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;
# Set file permissions
sudo find /var/www/html/ -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;
# Special permissions for wp-content
sudo chmod -R 775 /var/www/html/wp-content/Database Connection Troubleshooting
Database connectivity issues prevent WordPress installation completion. Troubleshoot database problems:
Test database connectivity manually:
mysql -u wpuser -p wordpressVerify database service status:
sudo systemctl status mariadb
sudo systemctl restart mariadbCheck database credentials in wp-config.php:
sudo vim /var/www/html/wp-config.phpEnsure database name, username, password, and host information match created database configuration.
SELinux Access Denial Resolution
SELinux access denials block WordPress functionality requiring policy adjustments:
Check recent SELinux denials:
sudo ausearch -m avc -ts recentGenerate custom SELinux policies for legitimate access:
sudo ausearch -m avc -ts recent | audit2allow -M wordpress-custom
sudo semodule -i wordpress-custom.ppVerify SELinux booleans for web server operations:
getsebool -a | grep httpd
sudo setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect on
sudo setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect_db onPHP Memory and Execution Limits
PHP resource limits cause installation failures and plugin errors:
Increase PHP memory limits in configuration:
sudo vim /etc/php.iniModify resource allocation settings:
memory_limit = 512M
max_execution_time = 600
max_input_time = 600
post_max_size = 128M
upload_max_filesize = 128MAlternative method through wp-config.php:
ini_set('memory_limit', '512M');
set_time_limit(300);Web Server Configuration Issues
Apache and Nginx configuration errors prevent proper WordPress operation:
Test Apache configuration syntax:
sudo httpd -t
sudo systemctl restart httpdTest Nginx configuration:
sudo nginx -t
sudo systemctl restart nginx
sudo systemctl restart php-fpmReview error logs for specific issues:
sudo tail -f /var/log/httpd/error_log # Apache
sudo tail -f /var/log/nginx/error.log # NginxPlugin and Theme Compatibility
Plugin conflicts cause WordPress malfunctions requiring systematic troubleshooting:
Deactivate all plugins through database when admin access is unavailable:
UPDATE wp_options SET option_value = '' WHERE option_name = 'active_plugins';Manually deactivate problematic plugins:
sudo mv /var/www/html/wp-content/plugins/problematic-plugin /var/www/html/wp-content/plugins/problematic-plugin.disabledMaintenance and Long-term Management
Automated Update Configuration
Configure WordPress automatic updates balancing security and stability:
Enable minor security updates through wp-config.php:
// Enable automatic updates for security releases
add_filter('allow_minor_auto_core_updates', '__return_true');
// Enable selective plugin updates
add_filter('auto_update_plugin', '__return_true');
// Enable theme updates for security patches
add_filter('auto_update_theme', '__return_true');Selective update control for production environments:
// Disable automatic updates for major releases
add_filter('allow_major_auto_core_updates', '__return_false');
// Enable updates for specific plugins only
function auto_update_specific_plugins($update, $item) {
$plugins = array('akismet/akismet.php', 'jetpack/jetpack.php');
return in_array($item->plugin, $plugins);
}
add_filter('auto_update_plugin', 'auto_update_specific_plugins', 10, 2);Regular Maintenance Schedules
Establish comprehensive maintenance routines ensuring optimal WordPress performance and security:
Daily Monitoring Tasks:
- Check site availability and performance
- Review security alerts and suspicious activity
- Monitor server resource utilization
- Verify backup completion status
Weekly Maintenance Procedures:
- Install available security updates
- Review and moderate user comments
- Check broken links and fix issues
- Analyze traffic statistics and performance metrics
Monthly Optimization Activities:
- Database cleanup and optimization
- Image library management and optimization
- Plugin and theme audit for unused components
- Security scan and vulnerability assessment
Quarterly System Reviews:
- Complete system backup verification
- User account audit and permission review
- Performance optimization and caching review
- Disaster recovery procedure testing
System-Level Updates and Security
Maintain Rocky Linux system packages ensuring security patches and performance improvements:
# Update all system packages
sudo dnf update -y
# Clean package cache
sudo dnf clean all
# Remove unnecessary packages
sudo dnf autoremove -y
# Update security packages specifically
sudo dnf upgrade --security -yMonitor system logs for issues:
# Monitor WordPress-specific logs
sudo tail -f /var/www/html/wp-content/debug.log
# Monitor web server logs
sudo tail -f /var/log/httpd/error_log # Apache
sudo tail -f /var/log/nginx/error.log # Nginx
# Monitor system security logs
sudo tail -f /var/log/securePerformance Monitoring and Optimization
Implement comprehensive performance monitoring identifying optimization opportunities:
Server Performance Monitoring:
- CPU utilization and load averages
- Memory usage and swap activity
- Disk I/O and space utilization
- Network traffic and connection counts
WordPress Performance Metrics:
- Page load times and response speeds
- Database query performance
- Plugin performance impact
- Cache hit rates and effectiveness
Use monitoring tools like htop, iotop, nload, and MySQL Performance Schema for detailed system analysis.
Backup Verification and Recovery Testing
Regular backup verification ensures data recovery capabilities during emergencies:
Backup Verification Procedures:
- Test backup file integrity and completeness
- Verify backup restoration on test environments
- Validate database backup consistency
- Confirm offsite backup accessibility
Recovery Testing Schedule:
- Monthly partial recovery tests
- Quarterly complete site restoration
- Annual disaster recovery simulation
- Documentation update and staff training
Maintain detailed recovery procedures documenting step-by-step restoration processes for various failure scenarios.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed WordPress. Thanks for using this tutorial to install the latest version of WordPress on Rocky Linux 10. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official WordPress website.