How To Install Xrdp on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS

Remote desktop access has become essential for system administrators, developers, and IT professionals managing Ubuntu servers. Xrdp provides a seamless solution for connecting to Ubuntu systems using the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), allowing users to access their Linux machines from Windows, macOS, or other operating systems. This comprehensive guide walks through the complete installation and configuration process for Xrdp on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS, ensuring secure and reliable remote desktop connectivity.
Whether managing cloud servers, accessing workstations remotely, or providing technical support, Xrdp delivers a familiar interface for Windows users while maintaining the power and flexibility of Linux. The installation process is straightforward, but proper configuration ensures optimal performance and security.
What is Xrdp?
Xrdp is an open-source implementation of Microsoft’s Remote Desktop Protocol server for Unix-like operating systems. It acts as a bridge between RDP clients and Linux desktop environments, enabling graphical remote access without requiring proprietary software. Unlike VNC-based solutions, Xrdp leverages the native RDP protocol built into Windows, making it immediately accessible without additional client installations.
The software supports multiple simultaneous sessions, allowing different users to connect concurrently without interfering with each other. Xrdp integrates seamlessly with various desktop environments including GNOME, Xfce, LXDE, and KDE, providing flexibility for different performance requirements and user preferences.
Key advantages include network bandwidth optimization through compression, support for audio redirection, clipboard sharing, and drive mapping capabilities that enhance the remote desktop experience. The protocol’s widespread adoption ensures compatibility across platforms and devices.
Prerequisites
Before beginning the installation process, ensure the system meets the following requirements. Ubuntu 24.04 LTS must be installed and fully operational with a desktop environment configured. Administrative privileges through sudo access are necessary for installing packages and modifying system configurations.
An active internet connection is required to download Xrdp packages and dependencies from Ubuntu repositories. The default GNOME desktop environment works with Xrdp, though lighter alternatives like Xfce or LXDE can improve remote performance.
Basic familiarity with terminal commands and Linux system administration helps navigate the configuration process smoothly. Access to a remote desktop client on another machine for testing the connection after installation is also recommended.
Step 1: Update System Packages
Keeping system packages current prevents compatibility issues and ensures access to the latest security patches. Begin by opening a terminal window and updating the package repository information with the following command:
sudo apt updateThis command refreshes the local package index, synchronizing it with Ubuntu’s software repositories. The system retrieves the latest package versions available for installation, ensuring Xrdp and its dependencies install correctly.
Following the update, upgrading existing packages is recommended though optional:
sudo apt upgrade -yThe upgrade process applies security updates and bug fixes to installed software. The -y flag automatically confirms installation prompts, streamlining the process. Wait for the upgrade to complete before proceeding to the Xrdp installation.
Step 2: Install Xrdp Package
Installing Xrdp on Ubuntu 24.04 is accomplished with a single command. Execute the following in the terminal:
sudo apt install xrdp -yThe package manager downloads Xrdp along with required dependencies including xorgxrdp, which provides the X server backend for RDP sessions. The installation typically completes within minutes depending on internet connection speed and system performance.
During installation, the system automatically creates the xrdp service and configures it to use the default RDP port 3389. Additional components like TigerVNC or X11VNC may be installed as dependencies to handle session management.
After installation completes, verify the package installed successfully by checking the installed version:
xrdp --versionThe output displays the Xrdp version number, confirming successful installation. Ubuntu 24.04 typically includes Xrdp version 0.9.x or newer, which offers improved compatibility with modern desktop environments.
Step 3: Verify Xrdp Service Status
Once installed, Xrdp runs as a systemd service that manages remote desktop connections. Check the service status with the following command:
sudo systemctl status xrdpThe output shows whether the service is active and running. Look for the “active (running)” status indicator in green text, confirming the service started successfully. The status display also shows recent log entries and process information.
If the service appears inactive or stopped, start it manually:
sudo systemctl start xrdpTo ensure Xrdp starts automatically when the system boots, enable the service:
sudo systemctl enable xrdpThis command creates the necessary systemd links to launch Xrdp during the boot sequence. Enabling the service prevents the need to manually start it after system restarts, essential for maintaining consistent remote access availability.
Step 4: Configure Xrdp User Permissions
A critical configuration step involves adding the xrdp user to the ssl-cert group. This membership grants Xrdp access to SSL certificates required for secure RDP connections. Execute the following command:
sudo adduser xrdp ssl-certThe command modifies group membership, allowing the Xrdp service to read certificate files stored in protected directories. Without this permission, connections may fail or operate in a less secure mode.
After modifying user permissions, restart the Xrdp service to apply changes:
sudo systemctl restart xrdpThe restart ensures the service reloads with updated permissions and group memberships. This step takes only a few seconds and temporarily disconnects any active remote sessions.
Step 5: Configure Firewall Settings
Ubuntu’s Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW) protects the system by blocking unauthorized network connections. Opening port 3389 allows RDP traffic to reach the Xrdp service. First, check the current firewall status:
sudo ufw statusIf UFW is active, configure it to permit RDP connections. For maximum security, restrict access to specific IP addresses:
sudo ufw allow from 192.168.1.100 to any port 3389Replace 192.168.1.100 with the actual IP address of the computer used for remote connections. This approach limits exposure by preventing unauthorized access attempts from unknown sources.
Alternatively, allow connections from any IP address:
sudo ufw allow 3389While convenient, this configuration increases security risks by exposing the RDP service to the entire network or internet. Use this approach only on trusted private networks behind additional firewall protection.
After adding firewall rules, reload UFW to activate changes:
sudo ufw reloadVerify the rule was added successfully by checking the status again:
sudo ufw status numberedThe output lists all active firewall rules including the newly added RDP permission.
Step 6: Configure Desktop Environment
Ubuntu 24.04’s default GNOME desktop sometimes requires additional configuration for optimal Xrdp compatibility. Create a session configuration file in the home directory:
echo "gnome-session" > ~/.xsessionThis file instructs Xrdp which desktop environment to launch when establishing remote connections. The command creates the .xsession file and populates it with the GNOME session directive.
GNOME on Ubuntu 24.04 occasionally triggers authentication prompts related to color management and other system policies. Resolve these issues by configuring Polkit rules. Create a new configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/polkit-1/localauthority.conf.d/02-allow-colord.confAdd the following content to the file:
polkit.addRule(function(action, subject) {
if ((action.id == "org.freedesktop.color-manager.create-device" ||
action.id == "org.freedesktop.color-manager.create-profile" ||
action.id == "org.freedesktop.color-manager.delete-device" ||
action.id == "org.freedesktop.color-manager.delete-profile" ||
action.id == "org.freedesktop.color-manager.modify-device" ||
action.id == "org.freedesktop.color-manager.modify-profile") &&
subject.isInGroup("{users}")) {
return polkit.Result.YES;
}
});Save and close the file. This configuration prevents repeated authentication prompts during remote sessions, improving the user experience significantly. Restart the Xrdp service once more to apply all desktop environment configurations.
Step 7: Connect from Windows Client
With Xrdp configured, establish a remote connection from a Windows computer. First, determine the Ubuntu system’s IP address by running:
ip addr showAlternatively, use the shorter command:
hostname -IBoth commands display network interface information. Identify the IP address assigned to the primary network interface, typically starting with 192.168 for local networks or 10.0 for certain configurations.
On the Windows computer, open the Remote Desktop Connection application by searching for “Remote Desktop” in the Start menu. Enter the Ubuntu system’s IP address in the “Computer” field. Click “Connect” to initiate the connection.
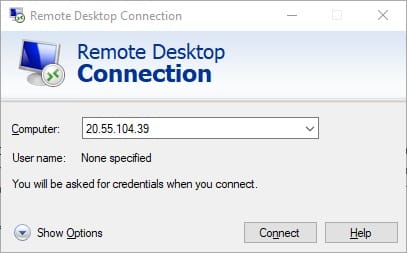
An important consideration: users must log out of the Ubuntu desktop session before connecting remotely. Linux typically prevents the same user from maintaining simultaneous local and remote graphical sessions, causing connection failures if already logged in locally.
The Xrdp login screen appears after successful connection. Enter the Ubuntu username and password. Select “Xorg” as the session type from the dropdown menu if multiple options appear. Click “OK” to proceed with authentication.
After successful authentication, the Ubuntu desktop environment loads within the Remote Desktop window. The remote session provides full graphical access to applications, files, and system settings just as if working locally.
Step 8: Connect from Other Operating Systems
Xrdp’s compatibility extends beyond Windows to support RDP clients on various platforms. macOS users can install Microsoft Remote Desktop from the App Store, which provides native RDP functionality. Launch the application, add a new connection, and enter the Ubuntu server’s IP address along with authentication credentials.
Linux users have multiple RDP client options available. Remmina is a popular choice pre-installed on many distributions. Open Remmina, create a new connection profile, select RDP as the protocol, and configure the connection details. Other alternatives include FreeRDP command-line tools and xfreerdp for scripted connections.
Mobile devices also support remote desktop access through dedicated apps. Both iOS and Android offer official Microsoft Remote Desktop applications. Install the app, configure a new connection with the server IP address, and connect using standard authentication procedures. Mobile connections work best over WiFi networks for optimal performance and responsiveness.
Configuring Alternative Desktop Environments
While GNOME functions well with Xrdp, lighter desktop environments often deliver better remote performance, especially over slower network connections. LXDE provides a minimal yet functional desktop ideal for remote access scenarios.
LXDE Installation and Configuration
Install LXDE with the following command:
sudo apt install lxde -yThe installation includes core desktop components without heavy resource requirements. LXDE’s lightweight nature significantly reduces bandwidth consumption and improves responsiveness during remote sessions.
Configure Xrdp to launch LXDE by editing the session startup file:
sudo nano /etc/xrdp/startwm.shAdd the following line before the last line that starts test and exec commands:
startlxdeSave the file and restart Xrdp. New remote connections will now launch the LXDE desktop environment instead of GNOME.
Xfce Installation and Configuration
Xfce strikes a balance between features and performance, offering more functionality than LXDE while remaining resource-efficient. Install Xfce with this command:
sudo apt install xfce4 xfce4-goodies -yThe xfce4-goodies package includes useful plugins and enhancements for improved functionality. After installation, configure Xrdp to use Xfce by creating a session file:
echo "xfce4-session" > ~/.xsessionRestart the Xrdp service to apply changes. The next remote connection will present the Xfce desktop, providing a smoother experience compared to GNOME while maintaining comprehensive desktop features.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Despite straightforward installation, users occasionally encounter issues requiring troubleshooting. Understanding common problems and their solutions ensures quick resolution.
Black Screen After Connection
Black screens represent one of the most frequently reported issues with Ubuntu 24.04 and GNOME. The problem often stems from session initialization failures or compatibility issues between Xrdp and GNOME’s Wayland display server.
A temporary workaround involves using the xmessage command to display a basic window, preventing the session from immediately terminating. Create an autostart entry that launches a simple application during login.
Alternatively, ensure necessary X server components are installed:
sudo apt install xserver-xorg-core xserver-xorg-input-allMissing packages can prevent proper session initialization. After installing these components, restart Xrdp and attempt reconnection.
Connection Disconnects Immediately
Immediate disconnections typically occur when attempting to connect while already logged into the system locally. Ubuntu’s session manager prevents duplicate graphical sessions for the same user. Log out of the local desktop session before initiating remote connections.
Review Xrdp logs for additional diagnostic information:
sudo cat /var/log/xrdp.logThe log file contains detailed connection attempts, authentication results, and error messages. Look for entries corresponding to the connection timestamp to identify specific failure causes.
Another common cause involves incorrect session configuration. Verify the .xsession file exists and contains valid desktop environment commands. Incorrect or missing session files cause immediate disconnection after authentication.
Authentication Failures
Repeated password prompts during remote sessions indicate Polkit configuration issues. The Ubuntu desktop requests authentication for various system operations like mounting drives or accessing network resources. Without proper Polkit rules, these prompts interrupt workflow and diminish usability.
Verify Polkit configuration files were created correctly as described in the desktop environment configuration section. Check file permissions and ensure the xrdp user has appropriate group memberships:
groups xrdpThe output should include ssl-cert among other groups. Missing group memberships prevent proper service operation and authentication handling.
Performance Issues
Slow or laggy remote desktop sessions stem from various factors including network latency, insufficient bandwidth, or excessive resource consumption. Adjust compression settings in the Xrdp configuration file to optimize performance:
sudo nano /etc/xrdp/xrdp.iniLocate the compression-related settings and modify values to balance quality and speed. Reducing color depth from 24-bit to 16-bit significantly improves performance with minimal visual impact.
Desktop environment optimization also helps. Disable visual effects, animations, and unnecessary background services. Consider switching to lighter desktop environments like Xfce or LXDE for bandwidth-constrained connections.
Security Best Practices
Remote desktop access creates potential security vulnerabilities requiring proactive protection measures. Implementing comprehensive security practices safeguards systems against unauthorized access and attacks.
Limiting Access by IP Address
Restricting connections to known IP addresses provides the most effective security layer. Configure UFW to accept connections only from trusted sources as demonstrated in the firewall configuration section. Regularly review and update allowed IP addresses as requirements change.
For dynamic IP scenarios, consider implementing VPN access to create a secure tunnel before allowing RDP connections. This approach maintains security even when client IP addresses change frequently.
Implementing Strong Authentication
Strong passwords are essential for protecting remote access. Enforce password complexity requirements through PAM (Pluggable Authentication Modules) configuration. Passwords should include uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters with minimum lengths of 12 characters or more.
Consider implementing SSH key authentication combined with SSH tunneling for enhanced security. This approach encrypts RDP traffic within an SSH tunnel, adding an additional security layer beyond RDP’s native encryption.
Configuring SSL/TLS Certificates
Xrdp supports SSL/TLS encryption for securing data transmission. Generate self-signed certificates or obtain certificates from trusted authorities. Edit the Xrdp configuration to enable stronger encryption:
sudo nano /etc/xrdp/xrdp.iniLocate the security layer settings and configure them for maximum protection:
security_layer=tls
crypt_level=highSpecify strong TLS protocols and cipher suites. Disable older protocols like SSL 3.0 and TLS 1.0 that contain known vulnerabilities. Save the configuration and restart Xrdp to apply security enhancements.
Regular Updates and Monitoring
Maintaining current software versions protects against known vulnerabilities. Enable automatic security updates or establish regular update schedules. Monitor security advisories related to Xrdp and Ubuntu to quickly address discovered issues.
Implement log monitoring to detect suspicious connection attempts:
sudo tail -f /var/log/xrdp.logWatch for repeated failed authentication attempts indicating brute force attacks. Consider installing fail2ban to automatically block IP addresses after multiple failed login attempts.
Advanced Configuration Options
Xrdp’s flexibility allows extensive customization through its configuration files. The primary configuration file located at /etc/xrdp/xrdp.ini controls numerous operational parameters.
Customizing Connection Parameters
Edit the configuration file to adjust session behavior:
sudo nano /etc/xrdp/xrdp.iniModify the port number if the default 3389 conflicts with other services or security requirements dictate non-standard ports. Change the port= directive to the desired port number.
Configure connection types and session parameters including bitmap caching, which improves performance by storing frequently accessed graphics locally. Enable or disable various features based on specific requirements and security policies.
Managing Multiple Sessions
Xrdp supports multiple concurrent connections from different users. Configure session limits and resource allocation to prevent system overload. The max_bpp setting controls color depth, affecting both visual quality and bandwidth consumption.
Set up different connection profiles for various use cases. Create separate configurations for high-bandwidth LAN connections versus bandwidth-limited remote connections, optimizing each for its environment.
Performance Optimization Tips
Maximizing remote desktop performance enhances user experience and productivity. Several optimization strategies reduce latency and improve responsiveness.
Adjusting Visual Settings
Reduce color depth to 16-bit for faster screen updates:
sudo nano /etc/xrdp/xrdp.iniLocate the max_bpp= parameter and set it to 16. Lower color depth significantly reduces data transmission requirements while maintaining acceptable visual quality for most tasks.
Disable desktop composition and effects within the desktop environment settings. Visual effects like transparency, shadows, and animations consume resources and bandwidth without improving functionality during remote sessions.
Network Optimization
Enable bitmap compression in Xrdp configuration to reduce bandwidth consumption. Compression algorithms balance processing overhead against transmission savings, generally providing net performance improvements.
Adjust bitmap cache settings to store frequently accessed graphics locally on the client. This reduces redundant data transmission, particularly beneficial for applications with static interface elements.
Consider network bandwidth when planning remote desktop usage. LAN connections easily handle full desktop sessions, while WAN connections may require additional optimization. Test performance under actual usage conditions and adjust settings accordingly.
Verifying Successful Installation
After completing installation and configuration, verify everything functions correctly. Run comprehensive tests to confirm proper operation before relying on remote access for production work.
Check that the Xrdp service runs without errors:
sudo systemctl status xrdpVerify the service listens on the correct port:
sudo netstat -plnt | grep xrdpThe output should show Xrdp listening on port 3389. If the port differs, review configuration files for custom port assignments.
Test local connections before attempting remote access from other networks. This isolates network-related issues from service configuration problems. Use an RDP client on the same network to connect using the localhost or local IP address.
Confirm firewall rules allow connections:
sudo ufw status numberedVerify the appropriate rule exists permitting traffic on port 3389. Missing or incorrect firewall rules prevent remote connections even when the service functions properly.
Create a verification checklist documenting successful completion of each installation step. This documentation aids troubleshooting if issues arise later and serves as reference for future installations.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Xrdp. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Xrdp remote desktop protocol (RDP) server on the Ubuntu 24.04 LTS system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Xrdp website.