How To Install Zabbix on Rocky Linux 10

Zabbix stands as one of the most powerful open-source monitoring solutions available today, providing comprehensive infrastructure and application monitoring capabilities for organizations of all sizes. With the recent release of Rocky Linux 10, system administrators now have access to a cutting-edge enterprise platform that perfectly complements Zabbix’s robust monitoring architecture. This comprehensive guide will walk you through every step necessary to successfully install and configure Zabbix 7.4 on Rocky Linux 10, ensuring you have a fully functional monitoring system ready for production use.
System Requirements and Prerequisites
Hardware Requirements for Rocky Linux 10
Rocky Linux 10 introduces specific hardware requirements that differ from previous versions, particularly the mandatory x86-64-v3 architecture support. Your system must meet these essential specifications to ensure optimal performance for both the operating system and Zabbix monitoring platform.
CPU Requirements: Rocky Linux 10 requires processors supporting the x86-64-v3 instruction set, which includes Intel Haswell (2013) or newer processors, and AMD Excavator (2015) or newer architectures. This requirement ensures better performance optimization and security features that benefit Zabbix’s intensive monitoring operations.
Memory Specifications: While Rocky Linux 10 can function with 2GB of RAM, a minimum of 4GB is strongly recommended for Zabbix installations. For production environments monitoring multiple hosts, consider 8GB or more to accommodate database operations, web interface responsiveness, and agent data processing.
Storage Considerations: Allocate at least 20GB of disk space for the base system installation. Zabbix databases can grow significantly depending on your monitoring scope, so plan for additional storage based on your environment’s size and data retention requirements.
Zabbix 7.4 System Requirements
Zabbix 7.4 brings enhanced features and improved performance, but requires specific software components to function correctly. The monitoring platform depends on a properly configured web server, database system, and PHP environment working in harmony.
Database Requirements: Zabbix 7.4 supports multiple database backends including MariaDB 10.5+, MySQL 8.0+, and PostgreSQL 13+. For this installation, we’ll use MariaDB as it provides excellent performance and seamless integration with Rocky Linux 10’s package ecosystem.
PHP Compatibility: PHP versions 8.0 through 8.4 are supported, with PHP 8.2 being the recommended version for optimal performance and security. Essential PHP extensions include mysqlnd, gd, xml, bcmath, ldap, and mbstring for full functionality.
Web Server Support: Both Apache HTTP Server and Nginx are supported, with Apache being the more common choice for Zabbix deployments due to its extensive documentation and community support.
Network and Access Requirements
Before beginning the installation process, ensure your Rocky Linux 10 system has proper network connectivity and administrative access configured. Root or sudo access is mandatory for package installation and system configuration tasks.
Firewall Considerations: Zabbix requires several ports to be accessible for proper operation. Port 80 (HTTP) and 443 (HTTPS) for web interface access, port 10050 for Zabbix agent communication, and port 10051 for active agent connections must be configured in your firewall rules.
Time Synchronization: Accurate timekeeping is crucial for monitoring systems. Ensure your server has NTP or chrony configured to maintain proper time synchronization, as timestamp discrepancies can cause monitoring data inconsistencies.
Step 1: System Preparation and Updates
Initial System Update and Configuration
Begin your Zabbix installation journey by ensuring your Rocky Linux 10 system is fully updated with the latest security patches and package versions. This foundation step prevents compatibility issues and ensures optimal system stability throughout the installation process.
Execute the system update command to refresh all installed packages:
sudo dnf update -yThis command downloads and installs all available updates, including kernel patches, security fixes, and package improvements. The process may take several minutes depending on your internet connection and the number of available updates.
SELinux Configuration: Rocky Linux 10 ships with SELinux enabled by default, which provides an additional security layer. For production environments, maintain SELinux in enforcing mode, but temporarily set it to permissive during installation to avoid configuration conflicts:
sudo setenforce 0
sudo sed -i 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=permissive/' /etc/selinux/configTime Synchronization Setup: Configure chrony for accurate time synchronization, which is essential for monitoring systems:
sudo dnf install chrony -y
sudo systemctl enable chronyd --now
sudo chronyc sources -vFirewall Configuration
Proper firewall configuration ensures Zabbix components can communicate while maintaining system security. Rocky Linux 10 uses firewalld as the default firewall management tool, providing zone-based configuration for different network interfaces.
Configure the necessary firewall rules for Zabbix operation:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=10050/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=10051/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadThese commands open HTTP and HTTPS ports for web interface access, plus Zabbix-specific ports for agent communication. The --permanent flag ensures rules persist across system reboots.
Advanced Firewall Considerations: For enhanced security, consider creating custom firewall zones specifically for Zabbix traffic, limiting source IP addresses to known monitoring networks, and implementing rate limiting to prevent potential DoS attacks.
Repository Management
To avoid package conflicts and ensure you receive official Zabbix packages, configure your system to exclude Zabbix packages from the EPEL repository if it’s installed.
Check if EPEL is installed and configure exclusions:
sudo dnf repolist | grep epelIf EPEL is present, edit the repository configuration:
sudo nano /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repoAdd the following line under the [epel] section:
excludepkgs=zabbix*This configuration prevents potential conflicts between EPEL and official Zabbix repository packages, ensuring consistent package versions and dependencies.
Step 2: Installing LAMP Stack Components
Apache Web Server Installation
Apache HTTP Server forms the foundation of your Zabbix web interface, providing the web service layer that hosts the monitoring interface and handles user authentication. Rocky Linux 10 includes Apache 2.4 in its default repositories, offering excellent performance and security features.
Install Apache using the httpd package group:
sudo dnf install @httpd -yThe @httpd group installation includes the core Apache server along with essential modules and configuration files. This approach ensures all necessary dependencies are resolved automatically.
Start and enable Apache for automatic startup:
sudo systemctl start httpd
sudo systemctl enable httpd
sudo systemctl status httpdApache Configuration Verification: Test Apache installation by accessing your server’s IP address through a web browser. You should see the default Rocky Linux Apache test page, confirming successful installation and proper network connectivity.
Security Hardening: Modify Apache’s default configuration to enhance security by hiding version information and disabling unnecessary modules:
sudo nano /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.confAdd these security directives:
ServerTokens Prod
ServerSignature OffMariaDB Database Server Setup
MariaDB serves as Zabbix’s data storage engine, managing all monitoring data, configuration settings, and user information. Proper database configuration is crucial for optimal Zabbix performance and data integrity.
Install MariaDB server and client packages:
sudo dnf install mariadb-server mariadb -yInitialize and secure the MariaDB installation:
sudo systemctl start mariadb
sudo systemctl enable mariadb
sudo mysql_secure_installationThe mysql_secure_installation script guides you through essential security configurations including root password setup, anonymous user removal, and test database deletion. Follow these recommendations:
- Set a strong root password (minimum 12 characters with mixed case, numbers, and symbols)
- Remove anonymous users (Yes)
- Disallow root login remotely (Yes)
- Remove test database (Yes)
- Reload privilege tables (Yes)
Database Performance Optimization: Configure MariaDB for optimal Zabbix performance by editing the configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/my.cnf.d/mariadb-server.cnfAdd these performance-oriented settings under the [mysqld] section:
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 1G
innodb_log_file_size = 256M
max_connections = 200
query_cache_type = 1
query_cache_size = 64MRestart MariaDB to apply the configuration changes:
sudo systemctl restart mariadbPHP Installation and Configuration
PHP powers Zabbix’s web interface, processing user requests and generating dynamic monitoring pages. Rocky Linux 10 includes PHP 8.2 by default, which provides excellent performance and security features for Zabbix 7.4.
Install PHP and essential extensions for Zabbix:
sudo dnf install php php-mysqlnd php-gd php-xml php-bcmath php-ldap php-mbstring php-json php-fpm -yThese PHP extensions provide:
- php-mysqlnd: Database connectivity for MariaDB/MySQL
- php-gd: Image processing for graphs and charts
- php-xml: XML parsing capabilities
- php-bcmath: Precise mathematical calculations
- php-ldap: LDAP authentication support
- php-mbstring: Multi-byte string handling
- php-json: JSON data processing
PHP Configuration Optimization: Configure PHP settings for optimal Zabbix performance:
sudo nano /etc/php.iniModify these critical settings:
max_execution_time = 300
memory_limit = 256M
post_max_size = 32M
upload_max_filesize = 16M
max_input_time = 300
date.timezone = "Your/Timezone"PHP-FPM Configuration: Configure PHP-FPM for improved performance and resource management:
sudo systemctl start php-fpm
sudo systemctl enable php-fpmEdit the PHP-FPM pool configuration:
sudo nano /etc/php-fpm.d/www.confOptimize these settings for Zabbix workloads:
pm = dynamic
pm.max_children = 50
pm.start_servers = 5
pm.min_spare_servers = 5
pm.max_spare_servers = 35Step 3: Zabbix Repository and Package Installation
Adding Official Zabbix Repository
Installing Zabbix from the official repository ensures you receive the latest stable version with proper package dependencies and security updates. The official Zabbix repository provides packages specifically compiled for Rocky Linux 10.
Install the Zabbix 7.4 repository package:
sudo rpm -Uvh https://repo.zabbix.com/zabbix/7.4/rocky/10/x86_64/zabbix-release-latest-7.4.el10.noarch.rpmThis command downloads and installs the repository configuration, adding the necessary GPG keys and repository definitions to your system. The package includes both stable and testing repositories, with stable enabled by default.
Clear the DNF cache to ensure fresh package metadata:
sudo dnf clean all
sudo dnf makecacheRepository Verification: Confirm the Zabbix repository is properly configured:
sudo dnf repolist | grep zabbixYou should see the Zabbix repository listed, indicating successful configuration.
Installing Zabbix Server Components
Install the complete Zabbix server package set required for a fully functional monitoring system. This installation includes the server daemon, web interface, database scripts, and necessary configuration files.
Execute the comprehensive package installation:
sudo dnf install zabbix-server-mysql zabbix-web-mysql zabbix-apache-conf zabbix-sql-scripts zabbix-selinux-policy zabbix-agent2 -yPackage Component Breakdown:
- zabbix-server-mysql: Core monitoring server with MySQL/MariaDB support
- zabbix-web-mysql: Web interface with database integration
- zabbix-apache-conf: Apache configuration files for Zabbix
- zabbix-sql-scripts: Database schema and initialization scripts
- zabbix-selinux-policy: SELinux policies for proper security integration
- zabbix-agent2: Enhanced monitoring agent for local system monitoring
Installation Verification: Confirm successful package installation by checking installed versions:
rpm -qa | grep zabbix | sortThis command displays all installed Zabbix packages with version numbers, allowing you to verify the installation completed successfully.
Package Verification and Dependency Resolution
After installation, verify that all dependencies are properly resolved and no conflicts exist. Rocky Linux 10’s DNF package manager typically handles dependencies automatically, but manual verification ensures system stability.
Check for any unresolved dependencies:
sudo dnf checkIf any issues are reported, resolve them using:
sudo dnf install --skip-brokenService File Verification: Ensure Zabbix service files are properly installed:
sudo systemctl list-unit-files | grep zabbixYou should see entries for zabbix-server and zabbix-agent2 services, confirming proper package installation.
Step 4: Database Configuration and Schema Import
Creating Zabbix Database and User
Database setup is a critical step that establishes the data storage foundation for your Zabbix monitoring system. Proper database configuration ensures optimal performance and data integrity for all monitoring operations.
Access MariaDB with administrative privileges:
sudo mysql -u root -pCreate the Zabbix database with UTF8MB4 character set for full Unicode support:
CREATE DATABASE zabbix CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_bin;Create a dedicated database user with appropriate privileges:
CREATE USER 'zabbix'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'YourSecurePassword123!';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON zabbix.* TO 'zabbix'@'localhost';Security Best Practices: Choose a strong password containing uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid common dictionary words or predictable patterns.
Configure log_bin_trust_function_creators for schema import:
SET GLOBAL log_bin_trust_function_creators = 1;
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
EXIT;This setting allows the schema import process to create necessary database functions and procedures.
Importing Zabbix Database Schema
The Zabbix database schema contains all necessary tables, indexes, and relationships required for monitoring operations. The import process establishes the complete database structure needed for Zabbix functionality.
Locate and import the Zabbix database schema:
sudo zcat /usr/share/zabbix-sql-scripts/mysql/server.sql.gz | mysql -u zabbix -p zabbixEnter the Zabbix database user password when prompted. The import process may take several minutes to complete, depending on your system’s performance.
Import Progress Monitoring: For large databases or slower systems, monitor the import progress using a separate terminal:
mysql -u zabbix -p -e "SELECT COUNT(*) FROM information_schema.tables WHERE table_schema = 'zabbix';"This command shows the number of tables created during the import process.
Database Optimization Settings
After successful schema import, optimize the database configuration for Zabbix performance. Return to MariaDB and disable the function creator setting:
sudo mysql -u root -pSET GLOBAL log_bin_trust_function_creators = 0;Performance Tuning: Configure additional MariaDB settings for optimal Zabbix performance:
SET GLOBAL innodb_buffer_pool_size = 1073741824;
SET GLOBAL max_connections = 200;
SET GLOBAL query_cache_size = 67108864;These settings optimize memory usage, connection handling, and query caching for typical Zabbix workloads.
Step 5: Zabbix Server Configuration
Configuring zabbix_server.conf
The Zabbix server configuration file contains all operational parameters that control how the monitoring server functions. Proper configuration ensures reliable data collection, processing, and storage across your monitoring infrastructure.
Edit the main server configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/zabbix/zabbix_server.confConfigure essential database connection parameters:
DBHost=localhost
DBName=zabbix
DBUser=zabbix
DBPassword=YourSecurePassword123!Advanced Configuration Options: Optimize server performance by configuring these additional parameters:
StartPollers=30
StartPollersUnreachable=1
StartTrappers=5
StartPingers=1
StartDiscoverers=1
StartHTTPPollers=1
StartTimers=1
HousekeepingFrequency=1
MaxHousekeeperDelete=5000
CacheSize=8M
CacheUpdateFrequency=60
StartDBSyncers=4
HistoryCacheSize=16M
HistoryIndexCacheSize=4M
TrendCacheSize=4M
ValueCacheSize=8M
Timeout=4
TrapperTimeout=300
UnreachablePeriod=45
UnavailableDelay=60
UnreachableDelay=15
LogFile=/var/log/zabbix/zabbix_server.log
LogFileSize=10
DebugLevel=3These settings optimize the server for typical enterprise monitoring environments with multiple hosts and high data volumes.
Starting Zabbix Server Service
With configuration complete, initialize the Zabbix server service and configure it for automatic startup. Proper service management ensures continuous monitoring operation and system reliability.
Start and enable the Zabbix server service:
sudo systemctl start zabbix-server
sudo systemctl enable zabbix-serverVerify service status and troubleshoot any startup issues:
sudo systemctl status zabbix-serverLog File Monitoring: Monitor the Zabbix server log for successful startup confirmation:
sudo tail -f /var/log/zabbix/zabbix_server.logLook for messages indicating successful database connection and server initialization. Common startup messages include:
- “using configuration file: /etc/zabbix/zabbix_server.conf”
- “current database version”
- “server #0 started”
SELinux Policy Configuration
Rocky Linux 10’s SELinux implementation requires specific policies for Zabbix operation. Configure necessary SELinux booleans to allow proper communication between Zabbix components.
Set required SELinux booleans:
sudo setsebool -P httpd_can_connect_zabbix on
sudo setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect_db on
sudo setsebool -P zabbix_can_network on
sudo setsebool -P domain_can_mmap_files on
sudo setsebool -P daemons_enable_cluster_mode onSELinux Context Verification: Verify proper SELinux contexts are applied:
sudo ls -Z /etc/zabbix/
sudo ls -Z /var/log/zabbix/If contexts are incorrect, restore them using:
sudo restorecon -R /etc/zabbix/
sudo restorecon -R /var/log/zabbix/Step 6: Web Server and PHP Configuration
Apache Configuration for Zabbix
Apache configuration for Zabbix involves setting up proper virtual host configurations, directory permissions, and security parameters. The Zabbix Apache configuration file provides optimized settings for the monitoring interface.
Edit the Zabbix Apache configuration:
sudo nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/zabbix.confVerify and optimize these configuration settings:
<Directory "/usr/share/zabbix">
Options FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Order allow,deny
Allow from all
<IfModule mod_php.c>
php_value max_execution_time 300
php_value memory_limit 128M
php_value post_max_size 16M
php_value upload_max_filesize 2M
php_value max_input_time 300
php_value max_input_vars 10000
php_value always_populate_raw_post_data -1
php_value date.timezone Europe/Riga
</IfModule>
</Directory>Time Zone Configuration: Update the date.timezone setting to match your server’s location for accurate timestamp handling.
PHP-FPM Optimization
PHP-FPM provides superior performance and resource management compared to traditional PHP modules. Configure PHP-FPM specifically for Zabbix workloads to ensure optimal response times and resource utilization.
Edit the PHP-FPM pool configuration:
sudo nano /etc/php-fpm.d/www.confOptimize these critical settings:
user = apache
group = apache
listen = /run/php-fpm/www.sock
listen.acl_users = apache,nginx
listen.allowed_clients = 127.0.0.1
pm = dynamic
pm.max_children = 50
pm.start_servers = 5
pm.min_spare_servers = 5
pm.max_spare_servers = 35
pm.process_idle_timeout = 10s
pm.max_requests = 500Memory and Process Optimization: These settings balance performance with resource consumption, ensuring stable operation under varying loads.
Service Management
Restart all web-related services to apply configuration changes and verify proper operation:
sudo systemctl restart httpd
sudo systemctl restart php-fpm
sudo systemctl status httpd php-fpmService Dependencies: Ensure services start in proper order during system boot:
sudo systemctl enable httpd
sudo systemctl enable php-fpmTest web server functionality by accessing your server’s IP address through a web browser. You should see either the Apache test page or be redirected to the Zabbix setup wizard.
Step 7: Zabbix Agent Configuration
Configuring Zabbix Agent 2
Zabbix Agent 2 provides enhanced monitoring capabilities with improved performance and native support for modern monitoring protocols. Proper agent configuration ensures accurate local system monitoring and establishes communication with the Zabbix server.
Edit the Zabbix Agent 2 configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/zabbix/zabbix_agent2.confConfigure essential agent parameters:
PidFile=/var/run/zabbix/zabbix_agent2.pid
LogFile=/var/log/zabbix/zabbix_agent2.log
LogFileSize=10
Server=127.0.0.1
ServerActive=127.0.0.1
Hostname=YourServerName
Include=/etc/zabbix/zabbix_agent2.d/*.confAdvanced Agent Configuration: Enable additional monitoring capabilities:
EnableRemoteCommands=0
LogRemoteCommands=1
UnsafeUserParameters=0
AllowRoot=0
User=zabbix
Timeout=3
Include=/etc/zabbix/zabbix_agent2.d/*.conf
UserParameterDir=/var/lib/zabbix/userparametersSecurity Considerations: The EnableRemoteCommands=0 setting prevents remote command execution for security purposes. Only enable this feature if absolutely necessary and implement proper access controls.
Agent Service Management
Start and configure Zabbix Agent 2 for automatic operation:
sudo systemctl start zabbix-agent2
sudo systemctl enable zabbix-agent2
sudo systemctl status zabbix-agent2Agent Connectivity Testing: Verify agent functionality using the zabbix_get utility:
zabbix_get -s 127.0.0.1 -k agent.pingA successful response returns “1”, indicating proper agent operation and communication.
Log Monitoring: Monitor agent logs for connection status and potential issues:
sudo tail -f /var/log/zabbix/zabbix_agent2.logLook for successful connection messages and absence of error conditions.
Step 8: Web Interface Setup and Initial Configuration
Accessing Zabbix Web Interface
The Zabbix web interface provides the primary management portal for your monitoring system. Proper initial configuration establishes the foundation for all future monitoring operations.
Open your web browser and navigate to:
http://your-server-ip/zabbix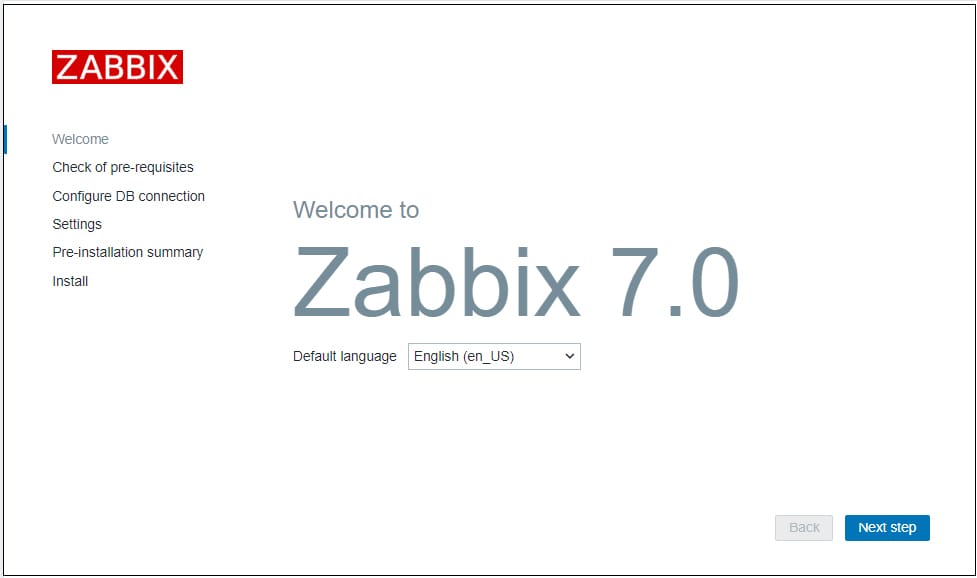
The Zabbix setup wizard guides you through initial configuration steps:
- Welcome Screen: Select your preferred language and click “Next step”
- Prerequisites Check: Verify all system requirements show “OK” status
- Database Configuration: Enter your database connection details
- Server Details: Configure server name and timezone settings
- Pre-installation Summary: Review all settings before proceeding
- Installation Complete: Confirmation of successful setup
Database Connection Parameters:
- Database type: MySQL
- Database host: localhost
- Database port: 0 (default)
- Database name: zabbix
- User: zabbix
- Password: [Your database password]
Initial Login and Security Setup
Complete the initial login process and implement essential security configurations:
Default Credentials:
- Username: Admin
- Password: zabbix
Immediate Security Actions:
- Change the default administrator password to a strong, unique password
- Create additional user accounts with appropriate role assignments
- Disable the default guest account if not needed
- Configure session timeout settings
Access User Management through Administration → Users to implement these security measures.
Password Policy Configuration: Establish strong password requirements:
- Minimum 12 characters
- Mixed case letters, numbers, and symbols
- Regular password rotation schedule
- Account lockout after failed attempts
Dashboard Customization
Configure the Zabbix dashboard to provide immediate visibility into your monitoring environment:
Default Widgets Configuration:
- System information widget showing server status
- Problems widget displaying current issues
- Graph widgets for key performance metrics
- Map widgets for network topology visualization
Custom Dashboard Creation: Create role-specific dashboards for different user groups:
- Executive dashboards with high-level KPIs
- Technical dashboards with detailed metrics
- Service-specific dashboards for application teams
Navigate to Monitoring → Dashboard to access customization options.
Step 9: Testing and Verification
Verifying Zabbix Functionality
Comprehensive testing ensures your Zabbix installation operates correctly and provides reliable monitoring capabilities. Systematic verification identifies potential issues before production deployment.
Server Communication Testing: Verify Zabbix server processes are running correctly:
sudo ps aux | grep zabbix_server
sudo netstat -tlnp | grep :10051These commands confirm the server process is active and listening on the correct port.
Database Connectivity Verification: Test database operations:
mysql -u zabbix -p zabbix -e "SELECT COUNT(*) FROM hosts;"This query should return a count of configured hosts, confirming database connectivity.
Agent Communication Testing: Verify agent-server communication:
zabbix_get -s localhost -k system.uptimeA numeric response indicates successful agent communication and data retrieval.
Performance Monitoring
Monitor system resources during initial operation to establish baseline performance metrics:
System Resource Monitoring:
- CPU utilization during data collection cycles
- Memory consumption by Zabbix processes
- Disk I/O patterns for database operations
- Network traffic for agent communications
Database Performance Analysis:
mysql -u root -p -e "SHOW PROCESSLIST;" | grep zabbix
mysql -u root -p -e "SHOW STATUS LIKE 'Threads_connected';"These queries reveal active database connections and server load.
Basic Troubleshooting
Common installation issues and their solutions:
Service Startup Failures: Check log files for detailed error messages:
sudo journalctl -u zabbix-server -f
sudo tail -f /var/log/zabbix/zabbix_server.logDatabase Connection Issues: Verify user privileges and connection parameters:
mysql -u zabbix -p -e "SHOW GRANTS FOR 'zabbix'@'localhost';"Web Interface Problems: Check Apache error logs:
sudo tail -f /var/log/httpd/error_logFirewall Connectivity Issues: Test port accessibility:
sudo ss -tlnp | grep :10050
sudo ss -tlnp | grep :10051Step 10: Security Hardening and Best Practices
Security Configuration
Implement comprehensive security measures to protect your Zabbix installation from potential threats and unauthorized access:
SSL/TLS Configuration: Secure web interface communications:
sudo dnf install mod_ssl -yConfigure SSL virtual host in /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf:
<VirtualHost *:443>
ServerName your-server-name
DocumentRoot /usr/share/zabbix
SSLEngine on
SSLCertificateFile /etc/ssl/certs/zabbix.crt
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/ssl/private/zabbix.key
<Directory "/usr/share/zabbix">
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>Database Security Hardening: Implement additional database security measures:
-- Remove unnecessary privileges
REVOKE ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* FROM 'zabbix'@'localhost';
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, CREATE, DROP, ALTER, INDEX, REFERENCES ON zabbix.* TO 'zabbix'@'localhost';Performance Optimization
Fine-tune system performance for optimal monitoring efficiency:
Database Optimization: Configure advanced MariaDB settings:
sudo nano /etc/my.cnf.d/zabbix.cnf[mysqld]
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 2G
innodb_log_file_size = 512M
innodb_log_buffer_size = 16M
innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit = 2
innodb_flush_method = O_DIRECT
max_connections = 300
query_cache_type = 1
query_cache_size = 128M
tmp_table_size = 32M
max_heap_table_size = 32MBackup and Maintenance Procedures
Establish comprehensive backup and maintenance procedures to ensure system reliability:
Database Backup Script: Create automated backup solution:
sudo nano /usr/local/bin/zabbix-backup.sh#!/bin/bash
BACKUP_DIR="/backup/zabbix"
DATE=$(date +%Y%m%d_%H%M%S)
DB_NAME="zabbix"
DB_USER="zabbix"
DB_PASS="YourPassword"
mkdir -p $BACKUP_DIR
mysqldump -u$DB_USER -p$DB_PASS $DB_NAME | gzip > $BACKUP_DIR/zabbix_backup_$DATE.sql.gz
# Cleanup old backups (keep 30 days)
find $BACKUP_DIR -name "zabbix_backup_*.sql.gz" -mtime +30 -deleteSystem Maintenance Cron Jobs: Schedule regular maintenance tasks:
sudo crontab -e# Daily database backup at 2 AM
0 2 * * * /usr/local/bin/zabbix-backup.sh
# Weekly log rotation
0 3 * * 0 /usr/sbin/logrotate /etc/logrotate.d/zabbix-server
# Monthly database optimization
0 4 1 * * mysqlcheck -u root -p --optimize zabbixCongratulations! You have successfully installed Zabbix. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Zabbix open-source monitoring software on your Rocky Linux 10 system. For additional or useful information, we recommend you check the official Zabbix website.