How To Setup UFW Firewall on Linux Mint 22

In this tutorial, we will show you how to setup UFW Firewall on Linux Mint 22. In today’s digital landscape, securing your Linux system is paramount. One of the most effective ways to protect your Linux Mint 22 installation from unauthorized access and malicious attacks is by configuring a firewall. Among the various firewall options available, the Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW) stands out due to its simplicity and ease of use. This article will guide you through setting up UFW on Linux Mint 22, ensuring your system remains secure and robust.
Introduction to UFW Firewall
UFW is a user-friendly interface for managing firewall rules on Linux systems. It acts as a front-end for the iptables framework, making it easier for users to configure and manage their firewall settings without delving into complex command-line syntax. UFW’s key features include its ability to allow or deny incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined rules, support for IPv6, and the option to limit connection rates to prevent brute-force attacks.
Benefits of Using UFW
- Simplicity: UFW simplifies firewall management with straightforward commands.
- Flexibility: It supports both IPv4 and IPv6 protocols.
- Security: UFW helps protect against unauthorized access by controlling network traffic.
Preparing Your Linux Mint 22 System
Before configuring UFW, ensure your Linux Mint 22 system is up-to-date and properly configured.
Update Your System
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade -yThis step ensures you have the latest security patches and software versions.
Backup Your System
It’s always a good practice to create a backup of your system before making significant changes. You can use tools like `rsync` or `Timeshift` for this purpose.
Verify Network Interfaces
ip addrThis command helps in identifying the interfaces you might need to configure later.
Installation of UFW on Linux Mint 22
UFW is often pre-installed on many Linux distributions, but if it’s not available on your system, you can easily install it.
Check if UFW is Installed
sudo ufw statusIf UFW is installed, this command will show its current status.
Install UFW
sudo apt install ufwThis command downloads and installs UFW on your system.
Verify Installation
sudo systemctl status ufwAfter installation, check the UFW service status to ensure it’s running properly.
Basic Configuration of UFW Firewall
Configuring UFW involves setting default policies and enabling the firewall.
Setting Default Policies
By default, UFW denies incoming traffic and allows outgoing traffic. You can explicitly set these policies using the following commands:
sudo ufw default deny incoming
sudo ufw default allow outgoingEnabling UFW
sudo ufw enableTo activate the firewall, run this command. You will be prompted to confirm that you want to proceed, as enabling the firewall might disrupt existing connections.
Checking Firewall Status
sudo ufw status verboseThis command displays detailed information about the firewall’s status, including all active rules.
Managing Firewall Rules with UFW
UFW allows you to manage network traffic by creating rules for specific ports or services.
Allowing Specific Ports and Services
- Allowing SSH Connections:
sudo ufw allow sshAlternatively, you can specify the port directly:
sudo ufw allow 22/tcp- Allowing HTTP/HTTPS Traffic:
sudo ufw allow http
sudo ufw allow httpsDenying Specific Ports
To block traffic on a specific port, use the `deny` command:
sudo ufw deny 80/tcpThis command blocks incoming traffic on port 80 (HTTP).
Deleting Rules
If you need to remove a rule, use the `delete` command followed by the rule you want to remove:
sudo ufw delete allow 80/tcpResetting Firewall Rules
To revert to UFW’s default settings, you can reset all rules:
sudo ufw resetThis command removes all user-defined rules and resets UFW to its default state.
Advanced Configuration Techniques
UFW offers several advanced features to enhance your firewall setup.
Configuring IPv6 Support
By default, UFW supports IPv6 rules. To ensure IPv6 is enabled, check the `/etc/default/ufw` file:
sudo nano /etc/default/ufwLook for the line `IPV6=yes` and ensure it is uncommented.
Allowing IP Ranges and Subnets
You can allow traffic from specific IP addresses or subnets using the `from` option:
sudo ufw allow from 192.168.1.100 to any port 22This command allows SSH access from the IP address `192.168.1.100`.
Limiting Connections
To prevent brute-force attacks, you can limit the number of connections from a single IP address:
sudo ufw limit sshThis command limits SSH connections to prevent excessive login attempts.
Enabling Logging for Security Auditing
UFW provides logging capabilities to monitor firewall activity:
sudo ufw logging onLogs are stored in `/var/log/ufw.log`, which can be reviewed for security auditing purposes.
Port Forwarding and NAT Configuration
While UFW itself does not handle port forwarding directly, you can configure it by editing the `/etc/ufw/before.rules` file. This involves setting up NAT rules using iptables, which UFW integrates with. Here’s a basic example of how to forward traffic from one port to another:
1. Open the `/etc/ufw/before.rules` file:
sudo nano /etc/ufw/before.rules2. Add the following lines at the top of the file (before any existing rules):
# NAT table rules
*nat
:POSTROUTING ACCEPT [0:0]
# Forward traffic from port 80 to port 8080
-A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-port 8080
COMMIT3. Save and close the file, then reload UFW:
sudo ufw reloadThis setup redirects incoming traffic on port 80 to port 8080.
Graphical User Interface (GUI) Management with GUFW
For users who prefer a graphical interface, GUFW provides an intuitive way to manage UFW settings.
Install GUFW
sudo apt install gufwLaunch GUFW
You can find GUFW in the Linux Mint menu. Once launched, it displays a simple interface where you can enable/disable the firewall, add/remove rules, and view current settings.
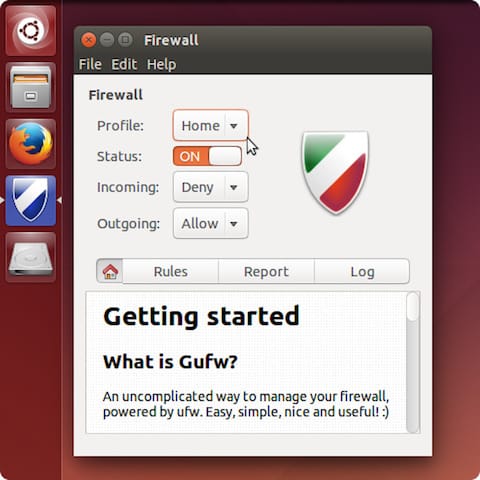
Troubleshooting Common Issues with UFW
Diagnosing Blocked Traffic
If legitimate traffic is being blocked, check the UFW logs for clues:
sudo tail -f /var/log/ufw.logThis command displays recent log entries, helping you identify which rules might be causing issues.
Resolving SSH Connection Disruptions
After enabling UFW, ensure that SSH connections are allowed to prevent being locked out of your server. If you’re having trouble connecting via SSH, verify that the SSH rule is in place:
sudo ufw allow sshCommon Error Messages and Solutions
- “Connection Refused” Errors: Ensure that the service you’re trying to connect to is running and that UFW rules allow the necessary traffic.
- “No Route to Host” Errors: Check network connectivity and ensure that UFW rules are not blocking necessary traffic.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed and set up UFW. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing UFW Firewall on your Linux Mint 22 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official UFW Firewall website.