
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Ajenti Control Panel on CentOS 7. For those of you who didn’t know, Ajenti is a hosting control panel that allows you to set up a website very easily. It comes with a clean and modern interface, so setting up application servers, databases and routing should not be difficult at all. Moreover, it comes with great language support. Using Ajenti, you can set up applications written in PHP (PHP-FPM), Python (WSGI), Ruby, and Node.js in no time. Exim 4 and Courier IMAP are automatically configured so you can use virtual e-mails, DKIM, DMARC, and SPF. This control panel is written in Python and runs on multiple Linux distributions.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS or dedicated server. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation Ajenti control panel on a CentOS 7 server.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: CentOS 7.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Ajenti Control Panel on CentOS 7
Step 1. First, you need to enable the EPEL repository on your system.
## RHEL/CentOS 7 64-Bit ## # wget http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/e/epel-release-7-8.noarch.rpm # rpm -ivh epel-release-7-8.noarch.rpm
Download and install Ajenti’s official repository by using the following commands:
wget http://repo.ajenti.org/ajenti-repo-1.0-1.noarch.rpm rpm -i ajenti-repo-1.0-1.noarch.rpm
Step 2. Installing Ajenti.
Install Ajenti using YUM the command:
yum install ajenti
Now, we’ll gonna start the Anjeti daemon as it’s installed successfully. To do so, we’ll gonna run the following command:
systemctl start ajenti
Step 3. Configure firewall for the Anjeti control panel.
If we have firewalld firewall solution running in our Linux machine, we’ll need to run firewall-cmd command in the root or sudo access to open port 8000 as follows:
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=8000/tcp firewall-cmd --reload
Step 4. Accessing Anjeti control panel.
Anjeti will be available on HTTP port 8000 by default. Open your favorite browser and navigate to http://your-domain.com:8000 or http://your-server-ip:8000 and enter the default username “admin” or “root” and the password is “admin“.
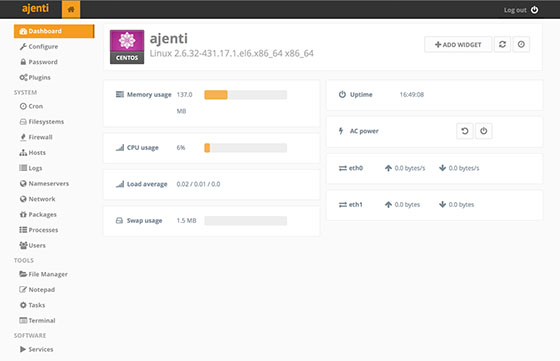
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Ajenti. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Ajenti control panel on your CentOS 7 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Ajenti website.