How To Check MySQL Version on Linux

In this tutorial, we will show you how to check the MySQL version on Linux. For those of you who didn’t know, MySQL is a widely used open-source relational database management system. It powers a significant portion of the web, including many popular websites and applications. Knowing your MySQL version is crucial for several reasons, including compatibility with other software, applying security updates, and taking advantage of new features.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step checking of the MySQL/MariaDB version on Linux.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Linux.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- Before proceeding, ensure you have basic knowledge of Linux command line operations. You should also have SSH access to your server and appropriate user permissions to execute the necessary commands.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Check MySQL Version on Linux
Simply follow the below steps to check the MySQL version in Linux:
-
Check MySQL Version From the Command Line
The MySQL server binary is named mysqld. To get the server version run the binary using the --version or -V option:
mysqld --version
Output:
mysqld Ver 8.0.25-0ubuntu0.18.04.1 for Linux on x86_64 ((Ubuntu))
You can also check the MySQL or MariaDB database server version using the below command:
mysqladmin -V
The output will be slightly different from the previous command:
MySQL output: mysqladmin Ver 8.0.26-0ubuntu0.20.04 for Linux on x86_64 ((Ubuntu)) MariaDB output: mysqladmin Ver 9.1 Distrib 10.3.28-MariaDB, for Debian-linux-gnu on x86_64
-
Check MySQL Version Using Linux Package Manager
You can also check your MySQL version through your Linux distribution’s package manager. The exact command will depend on your distribution:
Debian and Ubuntu √
On Debian, Ubuntu, and their derivatives, use the dpkg command:
dpkg -s mysql-server | grep Version
This command will output the installed MySQL server version, like this:
Version: 8.0.28-1ubuntu20.04
RHEL, CentOS, and Fedora √
On RHEL, CentOS, Fedora, and similar distributions, use the rpm command:
rpm -qa | grep mysql-community-server
The output will display the installed MySQL server package and its version:
mysql-community-server-8.0.28-1.el8.x86_64
-
Check MySQL Version From the MySQL Shell
In this method, you can use MySQL Client Tools to find version details:
sudo mysql
Output:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MySQL connection id is 4 Server version: 8.0.28-0ubuntu0.20.04 (Ubuntu)
To get the information about the MySQL version and other components, query the version variables:
mysql> SHOW VARIABLES LIKE "%version%";
Output:
+-------------------------+-------------------------+ | Variable_name | Value | +-------------------------+-------------------------+ | innodb_version | 5.8.14 | | protocol_version | 10 | | slave_type_conversions | | | tls_version | TLSv1,TLSv1.1 | | version | 8.0.28-0ubuntu0.20.04 | | version_comment | (Ubuntu) | | version_compile_machine | x86_64 | | version_compile_os | Linux | +-------------------------+-------------------------+
-
Check MySQL Version Using the PHPMyAdmin Interface
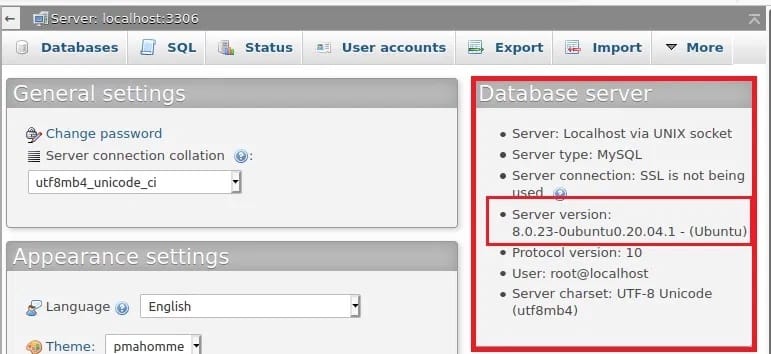
If you aren’t familiar with running commands through SSH, you may have access to PHPMyAdmin on the server which gives a nice graphical interface for managing the databases. Login into your hosting account, open up the PHP Admin, and look at the right side of the phpMyAdmin dashboard, you can see a box named Database server:
MySQL Version Naming Scheme
Understanding MySQL version numbers is crucial for ensuring compatibility and staying informed about new features and bug fixes. MySQL follows a versioning scheme that consists of three numbers: major, minor, and release. For example, in version 8.0.28:
- 8 is the major version, indicating significant changes and new features.
- 0 is the minor version, representing smaller enhancements and bug fixes.
- 28 is the release version, denoting incremental updates and patches.
Additionally, MySQL version numbers may include suffixes like “dmr” (development milestone release) or “rc” (release candidate) for pre-release versions. It’s generally recommended to avoid using non-GA (General Availability) releases in production environments to ensure stability and reliability.
Congratulations! You have successfully checked the MySQL version. Thanks for using this tutorial to Check the MySQL Version of a server. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official MySQL website.