How To Install Angular on Linux Mint 22

Angular has emerged as one of the most powerful and widely-used JavaScript frameworks for building dynamic web applications. Developed by Google, this robust framework enables developers to create scalable, maintainable single-page applications with ease. Linux Mint 22, based on Ubuntu’s latest LTS release, provides an excellent development environment for Angular applications with its stability, user-friendly interface, and comprehensive package management system.
Installing Angular on Linux Mint 22 requires careful attention to prerequisites, proper Node.js setup, and Angular CLI configuration. This comprehensive guide walks you through every step of the installation process, from system preparation to creating your first Angular project. Whether you’re a seasoned developer transitioning to Linux or a beginner exploring modern web development frameworks, this tutorial provides detailed instructions, troubleshooting solutions, and best practices to ensure a smooth installation experience.
The installation process involves several key components: updating your Linux Mint system, installing Node.js and npm (Node Package Manager), setting up Angular CLI globally, and verifying your installation by creating a test project. Each step includes multiple approaches to accommodate different preferences and system configurations, ensuring compatibility across various development scenarios.
Understanding Angular and Its Requirements
What is Angular?
Angular represents a complete rewrite of AngularJS, offering a component-based architecture that promotes code reusability and maintainability. This TypeScript-based frontend framework excels at creating responsive web applications, progressive web apps (PWAs), and enterprise-level solutions. Angular’s powerful features include two-way data binding, dependency injection, routing capabilities, and comprehensive testing tools that streamline the development workflow.
The framework follows a regular release cycle with major versions appearing approximately every six months. Angular’s ecosystem includes Angular CLI for project scaffolding, Angular Universal for server-side rendering, and Angular Material for UI components. These tools collectively create a comprehensive development environment that enhances productivity and code quality.
Current Angular versions maintain backward compatibility while introducing performance improvements and new features. The framework’s popularity stems from its ability to handle complex application states, provide excellent developer tools, and offer extensive documentation with community support.
System Requirements for Linux Mint 22
Linux Mint 22 “Wilma” provides excellent compatibility for Angular development environments. The operating system requires minimal hardware specifications: at least 4GB RAM for comfortable development (8GB recommended for larger projects), 20GB available disk space for Angular projects and dependencies, and a modern 64-bit processor supporting current Node.js versions.
Angular development demands Node.js version 18.19.1 or higher, with the latest LTS (Long Term Support) versions recommended for production environments. The framework supports all modern browsers including Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge, ensuring broad compatibility for developed applications.
Development environments benefit from additional tools like Git for version control, a capable text editor or IDE, and sufficient network bandwidth for downloading packages and dependencies. Linux Mint’s built-in package manager simplifies installing these prerequisites.
Prerequisites and System Preparation
Updating Linux Mint 22
System updates ensure compatibility with the latest packages and security patches. Begin by opening the terminal application using Ctrl+Alt+T or accessing it through the applications menu. Execute the following commands to refresh package repositories and install available updates:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade -yThe update process downloads package information from configured repositories, while upgrade installs newer versions of installed packages. The -y flag automatically confirms installation prompts, streamlining the update process. This procedure typically requires several minutes depending on available updates and internet connection speed.
Verify successful updates by checking the system version and ensuring no error messages appeared during the upgrade process. Restart your system if kernel updates were installed, as indicated by update manager notifications or terminal messages.
Installing Essential Build Tools
Development environments require compilation tools and utilities for building native modules and dependencies. Install essential build tools using the following command:
sudo apt install curl build-essential git -yThe curl utility enables downloading files from URLs, essential for installing Node.js and other development tools. Build-essential provides GCC compiler, make utility, and development libraries required for compiling native Node.js modules. Git version control system manages source code, tracks changes, and facilitates collaboration in Angular projects.
Consider installing additional text editors for development work. Visual Studio Code offers excellent Angular support with extensions, while traditional editors like nano and vim provide lightweight alternatives for configuration file editing:
sudo snap install code --classicCreate a dedicated development directory structure to organize Angular projects effectively:
mkdir -p ~/Development/Angular
cd ~/Development/AngularInstalling Node.js and npm
Method 1: Installing via NodeSource Repository
NodeSource repository provides the most current Node.js versions with regular updates and security patches. This method offers greater control over Node.js versions compared to default Ubuntu repositories. Begin by adding the NodeSource repository to your system:
curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_lts.x | sudo -E bash -This command downloads and executes the NodeSource setup script, which configures package repositories and GPG keys for secure package installation. The LTS (Long Term Support) version ensures stability and long-term maintenance for production environments.
Install Node.js and npm using the configured repository:
sudo apt-get install nodejs -yVerify the installation by checking installed versions:
node --version
npm --versionNodeSource installations typically provide the latest stable versions with automatic security updates through the standard package management system. This method integrates seamlessly with Linux Mint’s update manager, ensuring consistent maintenance alongside system updates.
The NodeSource approach offers several advantages: regular updates, security patches, consistent versioning, and integration with system package management. These benefits make it the preferred installation method for most development environments.
Method 2: Using Ubuntu Default Repository
Linux Mint’s default repositories include Node.js packages suitable for basic development needs. While these versions may lag behind the latest releases, they provide stable, tested packages that integrate well with the operating system. Install Node.js and npm using the default package manager:
sudo apt install nodejs npm -yDefault repository installations often include older Node.js versions that may not support the latest Angular features. Check the installed versions to ensure compatibility with Angular requirements:
nodejs --version
npm --versionNote that default installations may create the nodejs command instead of node. Create a symbolic link for compatibility with Angular CLI and other tools:
sudo ln -s /usr/bin/nodejs /usr/bin/nodeThis method suits environments prioritizing system stability over cutting-edge features. Default repository packages receive security updates through regular system maintenance cycles, providing reliable long-term support.
Method 3: Using Node Version Manager (NVM)
Node Version Manager (NVM) enables installing and managing multiple Node.js versions simultaneously. This approach proves invaluable for developers working on projects requiring different Node.js versions or testing compatibility across versions.
Install NVM using the official installation script:
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.4/install.sh | bashReload your shell configuration to activate NVM:
source ~/.bashrcVerify NVM installation:
nvm --versionInstall the latest LTS Node.js version:
nvm install --lts
nvm use --ltsList available Node.js versions:
nvm list-remoteSwitch between installed versions as needed:
nvm use 18.17.0
nvm use 20.5.1NVM provides unparalleled flexibility for managing Node.js environments, particularly beneficial for developers maintaining multiple projects with varying requirements. The tool integrates project-specific version files (.nvmrc) for automatic version switching.
Installing Angular CLI
Global Angular CLI Installation
Angular Command Line Interface (CLI) streamlines project creation, development server management, and build processes. The CLI provides scaffolding capabilities, testing utilities, and deployment tools essential for Angular development workflows.
Install Angular CLI globally using npm:
npm install -g @angular/cliGlobal installation makes the ng command available system-wide, enabling project creation from any directory location. The installation process downloads Angular CLI and its dependencies, creating executable commands for development tasks.
Verify successful installation by checking the Angular CLI version:
ng versionThis command displays Angular CLI version information, Node.js version, package manager details, and installed Angular packages. The output confirms proper installation and provides environment details useful for troubleshooting.
Global installations place Angular CLI in npm’s global packages directory, typically /usr/local/lib/node_modules or similar paths depending on Node.js installation method. The npm package manager automatically configures PATH variables for global command access.
Installing Specific Angular Versions
Development projects may require specific Angular versions for compatibility with existing codebases or libraries. Install particular Angular CLI versions to match project requirements:
npm install -g @angular/cli@17
npm install -g @angular/cli@16
npm install -g @angular/cli@15Multiple Angular CLI versions can coexist through npm’s versioning system. Specify exact versions when creating projects to ensure consistency across development environments:
npx @angular/cli@17 new my-angular-17-project
npx @angular/cli@16 new my-angular-16-projectVersion-specific installations provide precise control over Angular features and compatibility requirements. This approach proves essential for maintaining legacy projects or ensuring consistency in team development environments.
Check available Angular CLI versions before installation:
npm view @angular/cli versions --jsonTroubleshooting Angular CLI Installation
Permission errors commonly occur during global package installations. Resolve npm permission issues by configuring npm to use a different directory for global packages:
mkdir ~/.npm-global
npm config set prefix '~/.npm-global'Add the new directory to your PATH by editing ~/.bashrc:
echo 'export PATH=~/.npm-global/bin:$PATH' >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrcClear npm cache to resolve installation conflicts:
npm cache clean --force
npm cache verifyPATH configuration issues prevent the ng command from being recognized. Verify PATH settings include npm’s global binary directory:
echo $PATH
which ngReinstall Angular CLI if persistent issues occur:
npm uninstall -g @angular/cli
npm install -g @angular/cliNetwork connectivity problems during installation require proxy configuration or alternative registry settings. Configure npm for corporate networks or restricted environments:
npm config set proxy http://proxy.company.com:8080
npm config set https-proxy http://proxy.company.com:8080Creating Your First Angular Project
Project Creation Process
Angular CLI simplifies project scaffolding through the ng new command, which creates a complete project structure with configuration files, dependencies, and sample components. Navigate to your development directory and create a new Angular project:
cd ~/Development/Angular
ng new my-first-angular-appThe project creation wizard prompts for several configuration options. Choose whether to add Angular routing for single-page application navigation:
? Would you like to add Angular routing? (y/N)Select a stylesheet format for component styling. Options include CSS, SCSS, Sass, Less, and Stylus:
? Which stylesheet format would you like to use?
❯ CSS
SCSS [ https://sass-lang.com/documentation/syntax#scss ]
Sass [ https://sass-lang.com/documentation/syntax#the-indented-syntax ]
Less [ http://lesscss.org ]Angular CLI downloads project dependencies, creates directory structure, and initializes git repository automatically. The process typically requires several minutes depending on internet connection speed and system performance.
Project naming conventions follow standard JavaScript practices: use lowercase letters, hyphens for word separation, and avoid special characters or spaces. Examples include my-angular-app, company-dashboard, or user-management-system.
Navigating Project Directory
Angular projects follow a standardized directory structure promoting code organization and maintainability. Explore the generated project structure:
cd my-first-angular-app
ls -laKey directories and files include:
src/: Application source code including components, services, and assetssrc/app/: Main application module and component filessrc/environments/: Environment-specific configuration filesangular.json: Angular workspace configuration and build settingspackage.json: Project dependencies and npm scriptstsconfig.json: TypeScript compiler configurationkarma.conf.js: Unit testing configuratione2e/: End-to-end testing files and configuration
The src/app directory contains the root application component, module definitions, and initial application structure. This directory serves as the primary location for application development and feature implementation.
Understanding project structure accelerates development workflow and helps locate specific functionality during debugging or enhancement tasks. Angular’s opinionated structure promotes consistency across projects and development teams.
Installing Project Dependencies
Project dependencies install automatically during project creation, but understanding the process helps with troubleshooting and maintenance. Navigate to the project directory and install dependencies manually if needed:
npm installThe node_modules directory contains all project dependencies, including Angular framework packages, development tools, and third-party libraries. This directory can grow quite large and should be excluded from version control systems.
Package-lock.json ensures consistent dependency versions across different environments and development machines. This file locks specific package versions and their dependency trees, preventing version conflicts during team development.
Monitor dependency installation for warnings or errors that might indicate compatibility issues or network problems. Address warnings promptly to maintain project stability and security.
Testing Your Angular Installation
Starting the Development Server
Angular CLI includes a development server with live reload capabilities for efficient development workflows. Start the development server from your project directory:
ng serveThe development server compiles the application, watches for file changes, and automatically reloads the browser when modifications occur. Default server configuration binds to localhost port 4200, accessible at http://localhost:4200.
Customize server settings using command-line options:
ng serve --port 3000 --host 0.0.0.0 --openThe --port option specifies alternative ports, --host configures network binding for external access, and --open automatically launches the default browser. These options prove useful for development environments with specific networking requirements or port conflicts.
Development server output provides compilation status, error messages, and performance metrics. Monitor console output for warnings or errors that require attention during development.
Verifying Installation Success
Navigate to http://localhost:4200 in your web browser to view the default Angular welcome page. The page displays Angular logo, CLI version information, and links to documentation and resources.
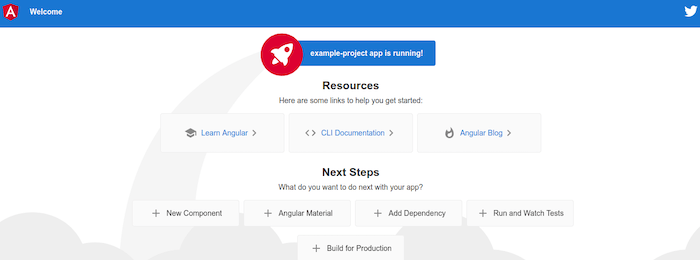
Browser developer tools provide additional verification of successful installation. Open developer tools (F12) and examine the console for error messages or warnings. The network tab shows resource loading and potential connectivity issues.
Successful installations display the Angular welcome page without console errors, demonstrate responsive design across different screen sizes, and show proper asset loading including images and stylesheets. Page source code reveals Angular framework integration and component rendering.
Performance considerations for development servers include compilation time, memory usage, and live reload responsiveness. Optimize development experience by closing unnecessary applications and ensuring adequate system resources for Angular development.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Node.js and npm Issues
Version compatibility problems arise when Angular CLI requires newer Node.js versions than installed. Update Node.js using your chosen installation method or install compatible versions using NVM. Check Angular CLI documentation for supported Node.js versions before upgrading.
npm permission errors prevent global package installations and updates. Configure npm to use user-specific directories rather than system-wide locations requiring administrative privileges:
mkdir ~/.npm-global
npm config set prefix '~/.npm-global'
export PATH=~/.npm-global/bin:$PATHCache corruption causes installation failures and inconsistent behavior. Clear npm cache using force options:
npm cache clean --force
npm cache verifyNetwork connectivity issues during package downloads require alternative registries or proxy configuration. Configure npm for restricted network environments:
npm config set registry https://registry.npmjs.org/
npm config set strict-ssl falseAngular CLI Problems
“ng command not found” errors indicate PATH configuration issues or incomplete installations. Verify global npm packages directory appears in PATH environment variable:
echo $PATH
npm config get prefixAdd npm global directory to PATH if missing:
echo 'export PATH=$(npm config get prefix)/bin:$PATH' >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrcCLI version conflicts between projects cause compatibility issues with dependencies and features. Use npx to run specific Angular CLI versions without global installation conflicts:
npx @angular/cli@17 new project-name
npx @angular/cli@16 generate component exampleGlobal package installation issues require cleaning npm cache and reinstalling Angular CLI:
npm uninstall -g @angular/cli
npm cache clean --force
npm install -g @angular/cli@latestProject Creation and Serving Issues
Port conflicts prevent development server startup when other applications use port 4200. Specify alternative ports or terminate conflicting processes:
ng serve --port 3000
lsof -ti:4200 | xargs kill -9File permission problems cause compilation errors and prevent file modifications. Ensure proper ownership of project directories:
sudo chown -R $USER:$USER ~/Development/Angular
chmod -R 755 ~/Development/AngularMemory issues during compilation manifest as slow performance or out-of-memory errors. Increase Node.js memory limits for large projects:
node --max-old-space-size=8192 ./node_modules/@angular/cli/bin/ng serveBuild errors require examining console output for specific error messages and stack traces. Common issues include TypeScript compilation errors, missing dependencies, and configuration problems.
Development Environment Optimization
Code Editor Setup
Visual Studio Code offers comprehensive Angular development support through extensions and integrated features. Install VS Code using snap package manager:
sudo snap install code --classicEssential Angular extensions enhance development productivity:
- Angular Language Service: Provides IntelliSense, error checking, and navigation for Angular templates
- Angular Snippets: Offers code snippets for common Angular patterns and components
- TypeScript Hero: Organizes imports and provides advanced TypeScript features
- Prettier: Formats code consistently across project files
- GitLens: Enhances Git integration with blame annotations and repository insights
Configure VS Code settings for optimal Angular development experience:
{
"typescript.preferences.importModuleSpecifier": "relative",
"editor.formatOnSave": true,
"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {
"source.organizeImports": true
}
}Alternative editors include WebStorm with built-in Angular support, Atom with community packages, and Vim with TypeScript plugins for terminal-based development workflows.
Additional Development Tools
Angular DevTools browser extension provides debugging capabilities and performance analysis for Angular applications. Install the extension from Chrome Web Store or Firefox Add-ons marketplace for enhanced development workflows.
Git configuration ensures proper version control integration with Angular projects. Configure user information and preferences:
git config --global user.name "Your Name"
git config --global user.email "your.email@example.com"
git config --global init.defaultBranch mainPackage manager alternatives to npm include Yarn and pnpm, offering different performance characteristics and feature sets. Install Yarn for faster dependency resolution:
npm install -g yarn
yarn --versionDebugging tools include Chrome DevTools for runtime debugging, Angular DevTools for component inspection, and VS Code debugging configuration for breakpoint debugging in development environments.
Best Practices and Next Steps
Angular Development Best Practices
Project structure organization promotes maintainability and scalability as applications grow. Follow Angular style guide recommendations for file naming, directory structure, and component organization. Create feature modules for related functionality and shared modules for common components.
Coding standards ensure consistency across development teams and improve code quality. Implement ESLint and Prettier for automated code formatting and linting. Configure pre-commit hooks to enforce standards:
npm install --save-dev @angular-eslint/builder @angular-eslint/eslint-plugin @angular-eslint/eslint-plugin-template @angular-eslint/template-parser
ng add @angular-eslint/schematicsVersion control best practices include meaningful commit messages, feature branch workflows, and regular integration with main development branches. Use conventional commit format for automated changelog generation and semantic versioning.
Testing setup recommendations include unit tests for components and services, integration tests for component interactions, and end-to-end tests for user workflows. Angular CLI generates test files automatically and configures Karma and Jasmine for testing frameworks.
Learning Path and Resources
Official Angular documentation provides comprehensive guides, API references, and tutorials for framework features. The documentation includes getting started tutorials, advanced concepts, and best practices for production applications.
Recommended learning resources include Angular University courses, Pluralsight tutorials, and freeCodeCamp interactive lessons. These resources cover beginner to advanced topics with hands-on exercises and real-world examples.
Community forums and support channels include Angular Discord server, Stack Overflow angular tag, and Reddit r/Angular community. These platforms provide peer support, problem-solving assistance, and discussions about Angular development practices.
Advanced topics for continued learning include component architecture patterns, services and dependency injection, routing and navigation strategies, state management with NgRx, performance optimization techniques, and Progressive Web App (PWA) development with Angular.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Angular. Thanks for using this tutorial to install the latest version of Angular on Linux Mint 22 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Angular website.