How To Install Apache Tomcat on Linux Mint 21

In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Apache Tomcat on Linux Mint 21. For those of you who didn’t know, Apache Tomcat is a widely used open-source web server software that plays a crucial role in web development, particularly in the Java ecosystem. It is known for its reliability, scalability, and flexibility, making it a popular choice among developers and system administrators.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of an Apache Tomcat on Linux Mint 21 (Vanessa).
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Linux Mint 21.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Apache Tomcat on Linux Mint 21 Vanessa
Step 1. Before running the tutorial below, it’s important to make sure your system is up to date by running the following apt commands in the terminal:
sudo apt update sudo apt install software-properties-common apt-transport-https wget ca-certificates gnupg2
Step 2. Installing Java.
Apache Tomcat required Java installation. Now run the following command to install Java to your system using the following command:
sudo apt install default-jdk
Check the currently installed version by simply running the command below:
java --version
For additional resources on installing Java, read the post below:
Step 3. Installing Apache Tomcat on Linux Mint 21.
To download Apache Tomcat, navigate to the official Apache Tomcat website and click on the “Download” button. Select the Linux package that matches your system architecture (64-bit or 32-bit). Once the download is complete, you can proceed with the installation.
wget https://dlcdn.apache.org/tomcat/tomcat-10/v10.1.24/bin/apache-tomcat-10.1.24.tar.gz
Next, extract the downloaded archive:
tar xvf apache-tomcat-10.1.24.tar.gz
Then, move it to the /usr directory using the following command:
sudo mv apache-tomcat-10.1.24 /usr/share/apache-tomcat
Next, create a user for Apache Tomcat and give ownership:
sudo useradd -M -d /usr/share/apache-tomcat tomcat sudo chown -R tomcat /usr/share/apache-tomcat
Step 4. Configure Apache Tomcat
Now allow access to Apache Tomcat UI from your IP address:
sudo nano /usr/share/apache-tomcat/webapps/manager/META-INF/context.xml
Allow specific IP address by adding it to the line:
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.RemoteAddrValve" allow="127\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+|::1|0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1|192.168.0.1" />
Do the same with the following file:
sudo nano /usr/share/apache-tomcat/webapps/host-manager/META-INF/context.xml
To allow any IP address to access remove the added IP above:
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.RemoteAddrValve" allow="127\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+|::1|0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1" />
Next, we set up a secure Apache Tomcat dashboard:
sudo nano /usr/share/apache-tomcat/conf/tomcat-users.xml
Add the following file above <tomcat-users xm..:
<!-- manager section user role --> <role rolename="manager-gui" /> <user username="manager" password="Your-Strong-Passwd" roles="manager-gui" /> <!-- admin section user role --> <role rolename="admin-gui" /> <user username="admin" password="Your-Strong-Passwd" roles="manager-gui,admin-gui" />
Step 5. Create Systemd for Apache Tomcat
Now we create systemd unit for tomcat to start/stop and restart service:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/tomcat.service
Add the following file:
[Unit] Description=Tomcat After=syslog.target network.target [Service] Type=forking User=tomcat Group=tomcat Environment=JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/default-java Environment='JAVA_OPTS=-Djava.awt.headless=true' Environment=CATALINA_HOME=/usr/share/apache-tomcat Environment=CATALINA_BASE=/usr/share/apache-tomcat Environment=CATALINA_PID=/usr/share/apache-tomcat/temp/tomcat.pid ExecStart=/usr/share/apache-tomcat/bin/catalina.sh start ExecStop=/usr/share/apache-tomcat/bin/catalina.sh stop [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save and close the file, then reload systemd daemon:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl enable tomcat sudo systemctl status tomcat
Step 6. Configure Firewall.
Now we set up an Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW) with Tomcat to allow public access on default web port 8080:
sudo ufw allow OpenSSH sudo ufw allow 8080 sudo ufw enable
Step 7. Accessing Apache Tomcat Web Interface.
Once successfully installed, open your web browser and access the OwnCloud installation wizard using the URL http://your-IP-address:8080. You will be redirected to the following page:
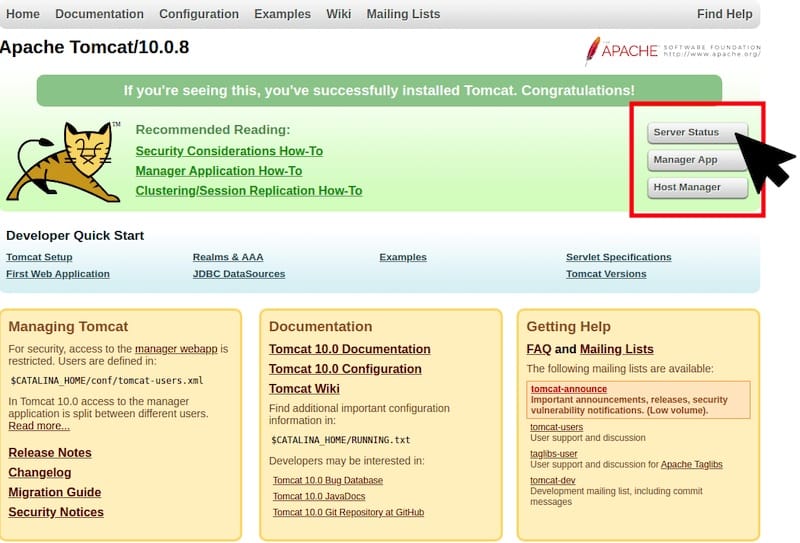
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Apache Tomcat. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the latest version of Apache Tomcat on the Linux Mint system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Apache website.