How To Install Budgie Desktop on Fedora 41

Fedora 41 stands out as a versatile and robust Linux distribution, favored for its commitment to open-source principles and cutting-edge software. If you’re seeking a seamless blend of modern aesthetics and efficient performance, look no further. Installing the Budgie Desktop environment on Fedora 41 offers a compelling alternative to the default GNOME desktop. This guide provides a detailed walkthrough on how to install Budgie Desktop on Fedora 41.
The Budgie desktop environment is designed with simplicity and elegance in mind. It’s a lightweight, modern desktop environment that’s user-friendly and customizable. Budgie offers a clean, uncluttered interface without sacrificing functionality. Customization is key, and Budgie delivers with a range of themes and applets to personalize the user experience. Budgie is suitable for both new and experienced Linux users.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know to install Budgie Desktop on your Fedora 41 system. We’ll delve into the prerequisites, provide a step-by-step installation process, discuss customization options, and offer troubleshooting tips to ensure a smooth experience. Let’s get started!
Prerequisites for Installing Budgie Desktop on Fedora 41
Before diving into the installation process, it’s essential to ensure your system meets the necessary requirements. Proper preparation can prevent potential issues and streamline the installation. Here’s a breakdown of the prerequisites:
System Requirements
To ensure a smooth experience, consider the minimum and recommended hardware specifications. Fedora 41 and Budgie Desktop have specific demands to run optimally.
- Minimum Hardware Requirements:
- Processor: 2 GHz dual-core processor
- Memory: 2GB RAM (4GB recommended for better performance)
- Storage: 15GB unallocated drive space (25GB recommended)
- Display: VGA capable of 1024×768 screen resolution
- Recommended Hardware:
- Processor: 2 GHz quad-core processor or faster
- Memory: 4GB System Memory
- Storage: 20GB unallocated drive space
Meeting these requirements ensures that your system can handle the Budgie Desktop environment without performance issues. Insufficient hardware may result in lag or instability.
Preparing Your System
Before installing Budgie, ensure your Fedora 41 system is up to date. Updating your system resolves potential conflicts and ensures compatibility with the new desktop environment.
Open your terminal and run the following command:
sudo dnf updateThis command updates all installed packages to their latest versions. It’s a crucial step to avoid dependency issues during the Budgie installation. Next, ensure you have the dnf package manager, which is the default package manager for Fedora. Most Fedora installations include dnf by default, but if you encounter issues, ensure it’s properly installed and configured.
Backup Recommendations
Creating a system backup before making significant changes is always a good practice. Backups safeguard your data and allow you to revert to a stable state if something goes wrong during the installation process.
You can use tools like rsync or graphical utilities like Timeshift to create a backup. Choose the method that best suits your technical expertise and comfort level.
User Account Permissions
Ensure the user account you’re using has administrative privileges. Administrative rights are required to install software and make system-level changes. If you’re unsure whether your account has these privileges, you can check by attempting to run a command with sudo. If prompted for a password, your account has sudo privileges. Otherwise, consult your system administrator.
Step-by-Step Guide to Installing Budgie Desktop Environment on Fedora 41
Now that you’ve prepared your system, let’s proceed with the installation. Follow these steps carefully to install Budgie Desktop on Fedora 41.
1. Adding the Repository for Budgie Desktop
In some cases, the Budgie Desktop environment may not be available in the default Fedora repositories. To address this, you may need to enable a Copr repository. These repositories are community-maintained and can provide access to packages not included in the official Fedora repositorie.
To enable the Copr repository, use the following command:
sudo dnf copr enable cappyishihara/budgieThis command adds the specified Copr repository to your system. Type Y to confirm when prompted.
After enabling the repository, it’s a good idea to verify that it has been added correctly. You can check the available packages using the following command:
dnf repolistThis command lists all enabled repositories. Confirm that the Copr repository you added is among them.
2. Installing Budgie Desktop Environment
With the repository enabled, you can now install the Budgie Desktop environment. Use the following command:
sudo dnf install budgie-desktopThis command downloads and installs the Budgie Desktop environment along with its dependencies. You’ll be prompted to confirm the installation; type Y and press Enter.
During the installation, a number of packages will be installed. These include core components, accessibility tools, fonts, and multimedia support. To enhance your Budgie experience, you can also install recommended packages such as:
sudo dnf install nautilus gnome-terminal gnome-system-monitor arc-theme arc-icon-theme geditnautilus: A popular file manager.gnome-terminal: A terminal emulator.gnome-system-monitor: A system monitoring tool.arc-themeandarc-icon-theme: Themes and icons for visual customization.gedit: A text editor.
3. Setting Budgie as the Default Desktop Environment
After the installation, you need to configure your system to use Budgie as the default desktop environment. This involves setting the graphical login target.
Use the following command:
sudo systemctl set-default graphical.targetThis command sets the default target to graphical, ensuring that the system boots into a graphical interface. Then, reboot your system to apply the changes:
sudo rebootUpon reboot, you’ll be presented with a login screen. Before entering your password, click on the gear icon or session menu and select “Budgie Desktop” from the list of available environments. This ensures that you log into the Budgie session.
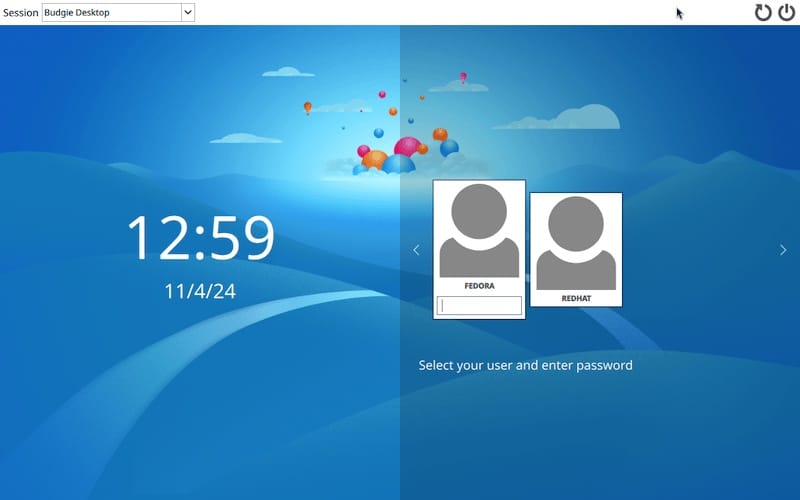
4. Starting Budgie Desktop from Command Line (Optional)
If you’re using Fedora Server or prefer to start Budgie from the command line, follow these steps. This method is useful for users without a graphical login interface.
Open your terminal and run the following commands:
echo "env GNOME_SHELL_SESSION_MODE=Budgie:GNOME /usr/bin/budgie-desktop" >> ~/.xinitrc
startxThe first command adds an environment variable to your .xinitrc file, specifying that the Budgie session should be started using GNOME components. The second command starts the X server, which in turn launches the Budgie Desktop environment.
5. Verifying Installation
To verify that Budgie Desktop is installed correctly, log into the Budgie session and confirm its functionality. Check the version details using the terminal command:
budgie-desktop --versionThis command displays the version of the Budgie Desktop environment that is currently running. If the installation was successful, you should see the version number without any errors.
If the installation fails, double-check each step and ensure you haven’t missed anything. Consult the troubleshooting section for common issues and their solutions.
Customizing Your Budgie Desktop Experience
One of the key advantages of Budgie Desktop is its customizability. You can tailor the environment to suit your preferences with themes, applets, and extensions. Let’s explore some common customization options.
1. Themes and Appearance Settings
Changing the theme can significantly alter the look and feel of your desktop. Budgie supports GTK themes, allowing you to choose from a wide variety of visual styles.
To install additional themes like the Arc Theme, use the following command:
sudo dnf install arc-theme arc-icon-themeAfter installing new themes, navigate to the settings menu to apply them. Open the Budgie Menu and search for “Settings.” From there, go to “Appearance” and select your desired theme and icon set.
2. Adding Applets and Extensions
Applets are small applications that reside in the panel, providing quick access to information and functionality. Extensions can add new features to the desktop environment. The budgie-extras package contains a collection of useful applets.
To install the budgie-extras package, use the following command:
sudo dnf install budgie-extrasSome popular applets include:
- Workspace Switcher: Allows you to quickly switch between workspaces.
- System Monitor: Displays system resource usage.
- Weather Applet: Provides weather information.
To add an applet to the panel, right-click on the panel and select “Add Applets.” Choose the applet you want to add and click “Add.”
3. Keyboard Shortcuts and Panel Customization
Configuring keyboard shortcuts can improve your productivity. Budgie allows you to define custom shortcuts for various actions.
To configure keyboard shortcuts, open the Settings menu and go to “Keyboard.” From there, you can add or modify shortcuts for specific commands and applications.
The panel layout is also customizable. You can move the panel to different edges of the screen, change its size, and adjust the transparency. To customize the panel, right-click on the panel and select “Budgie Settings.” From there, you can modify various panel properties.
Why Choose Budgie Desktop for Fedora?
Budgie Desktop offers several compelling advantages for Fedora users. It strikes a balance between modern aesthetics and efficient performance, making it an excellent choice for a variety of users.
- Lightweight and Resource-Efficient Design: Budgie is designed to be lightweight, making it ideal for older hardware or systems with limited resources. It consumes fewer system resources compared to heavier desktop environments like GNOME or KDE.
- Intuitive User Interface: Budgie provides a clean and intuitive user interface that is easy to navigate. It’s beginner-friendly yet powerful enough for advanced users.
- Seamless Integration with GNOME Applications: Budgie integrates seamlessly with GNOME applications. This means you can use your favorite GNOME apps without compatibility issues.
- Active Development Community: Budgie has an active development community that ensures regular updates and support. This means you can expect bug fixes, new features, and ongoing improvements.
Common Issues During Installation and Their Solutions
While the installation process is generally straightforward, you may encounter some issues. Here are some common problems and their solutions.
- Repository Errors:
- Problem: Unable to add or access the Copr repository.
- Solution: Ensure you have a stable internet connection. Verify the repository URL and try again.
- Dependency Conflicts:
- Problem: Package dependencies conflict with existing software.
- Solution: Use the command
sudo dnf clean allto clear the DNF cache before retrying the installation. This resolves many dependency-related issues.
- Login Screen Not Showing Budgie Option:
- Problem: Budgie Desktop doesn’t appear as an option on the login screen.
- Solution: Reinstall the display manager or manually configure session files. Ensure that the Budgie session file is correctly placed in
/usr/share/xsessions/.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Budgie. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Budgie Desktop environment on your Fedora 41 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Budgie website.