
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Cockpit on CentOS 9 Stream. For those of you who didn’t know, The cockpit is a free remote server manager that is lightweight and easy to use for GNU/Linux servers. It has a pretty web console that allows system administrators to easily perform tasks such as storage administration, network configuration, starting Docker containers, checking out the server performance, start and stop services, and many other administrative operations.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the Cockpit server manager on CentOS 9 Stream.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: CentOS 9 Stream.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Cockpit on CentOS 9 Stream
Step 1. First, let’s start by ensuring your system is up-to-date.
sudo dnf clean all sudo dnf update
Step 2. Installing Cockpit on CentOS 9 Stream.
By default, Cockpit is available on the CentOS 9 Stream base repository. Let’s install the Cockpit server using the following command below:
sudo dnf install cockpit
Once the installation is complete, now enable Cockpit (to start automatically upon system boot), start, and verify the status using the commands below:
sudo systemctl start cockpit sudo systemctl enable cockpit sudo systemctl status cockpit
Step 3. Configure Firewall.
If your server is protected by the firewall and you haven’t opened the Cockpit ports. Enable them with the following command below:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=cockpit sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Step 4. Accessing Cockpit Web Interface.
Once successfully installed, open your web browser and access the Cockpit web interface using the URL http://your-IP-address:9090. You should see the Cockpit containing the login password:
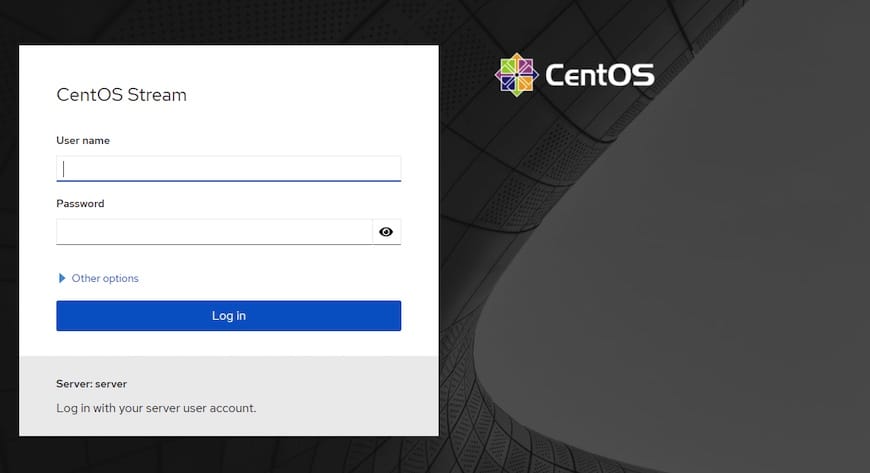
Note: If you are trying for the first time to access the Cockpit service via browser, you will be notified of a warning message as your connection is not secure. This is due to the self-signed certificate used by the Cockpit service. However, you can override this by selecting the ‘Advance’ option and clicking ‘Proceed or Exception’ on the IP address. Once the connection is established without any warning/error message.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Cockpit. Thanks for using this tutorial to install Cockpit server manager on CentOS 9 Stream. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Cockpit website.