How To Install Cockpit on Fedora 37

In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Cockpit on Fedora 37. For those of you who didn’t know, Cockpit is a web-based graphical user interface (GUI) for Linux servers. It provides a centralized platform for managing various aspects of the server, including system settings, services, and network configuration. Developed by Red Hat, it is designed to be easy to use and accessible for both novice and experienced administrators.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the Cockpit web-based interface manages on a Fedora 37.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Fedora 37.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- An active internet connection. You’ll need an internet connection to download the necessary packages and dependencies for Cockpit.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Cockpit on Fedora 37
Step 1. Before proceeding, update your Fedora operating system to make sure all existing packages are up to date. Use this command to update the server packages:
sudo dnf upgrade sudo dnf update
Step 2. Installing Cockpit on Fedora 37.
By default, the Cockpit package comes in the default repository of Fedora 37. Now run the following command below to install the latest version of Cockpit to your Fedora system:
sudo dnf install cockpit
After the installation is complete, start the Cockpit service and enable it to start at boot time by running the following commands:
sudo systemctl start cockpit sudo systemctl enable cockpit
Step 3. Configure Firewall for Cockpit.
By default, Cockpit listens on port 9090, so you need to allow incoming traffic on this port in your system firewall. Follow the steps below to allow incoming traffic on port 9090:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=cockpit sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Step 4. Accessing Cockpit Web Interface.
Once successfully installed, open your web browser and access Cockpit using the URL http://your-IP-address:9090. You will be prompted to enter the username and password of a user account. After entering the credentials, you will be redirected to the Cockpit web interface:
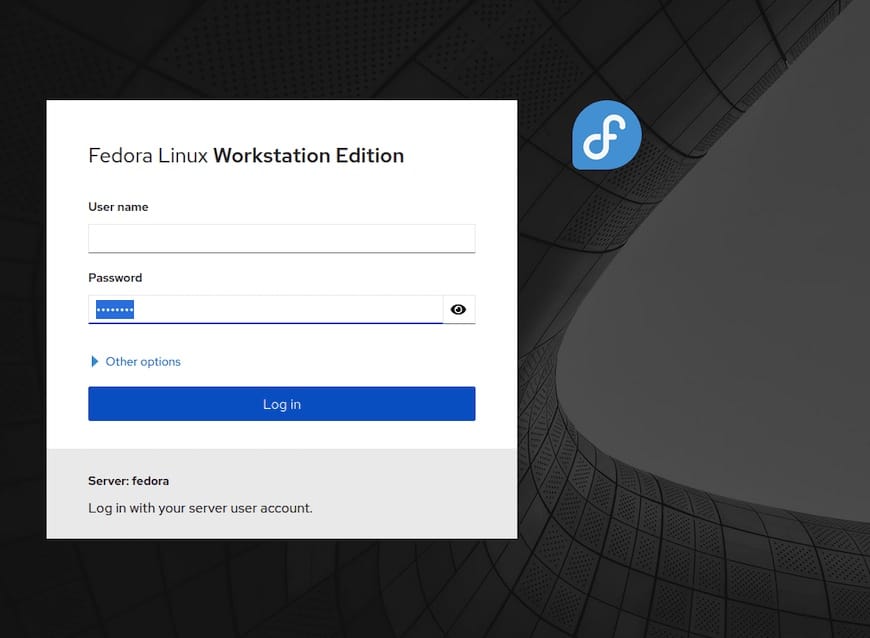
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Cockpit. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Cockpit on your Fedora 37 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Cockpit website.