How To Install DirectAdmin on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS

DirectAdmin stands as one of the most efficient web hosting control panels available for Linux servers today. This powerful tool transforms complex server administration tasks into manageable operations through an intuitive graphical interface. Whether managing multiple websites, configuring email accounts, or handling databases, DirectAdmin streamlines these processes significantly. This comprehensive guide walks through every step needed to successfully install DirectAdmin on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS, ensuring a secure and optimized server environment ready for production use.
What is DirectAdmin?
DirectAdmin represents a commercial web hosting control panel designed to simplify server management through automation and user-friendly interfaces. The platform excels at centralizing domain management, email configuration, database administration, and web application deployment into a single dashboard. Unlike resource-intensive alternatives, DirectAdmin maintains minimal system overhead while delivering comprehensive functionality. The control panel supports multiple user levels including administrators, resellers, and end users, each with appropriate permission sets. Features include Apache configuration management, DNS zone editing, FTP account creation, file management, backup automation, and detailed usage statistics. This control panel proves particularly valuable for hosting providers and system administrators managing multiple client accounts or domains from a unified interface.
Prerequisites Before Installation
System Requirements
DirectAdmin installation demands specific hardware and software conditions for optimal performance. The minimum hardware specifications include 4 GB of RAM and 2 GB of available disk space, though production environments benefit from significantly higher allocations. The platform supports both amd64 and arm64 architectures on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS systems. DirectAdmin requires a completely clean server installation without pre-existing web services, control panels, or conflicting software packages. The presence of Apache, MySQL, or PHP installations from other sources will cause installation failures. Ubuntu 24.04 LTS enjoys full DirectAdmin support with an extended End of Life date through July 2029, ensuring long-term stability and security updates. Fresh server deployments eliminate compatibility issues and dependency conflicts that plague installations on previously configured systems.
DirectAdmin License Requirements
Obtaining a valid DirectAdmin license represents a mandatory prerequisite for installation. License acquisition occurs through the official DirectAdmin website where various pricing tiers accommodate different server configurations and user requirements. After purchase completion, users receive a Client ID, License ID, and a license.dat file containing authorization credentials. The license undergoes verification through DirectAdmin’s licensing servers during installation, confirming active status before proceeding. License types vary based on server specifications, including options for internal usage, external hosting, and datacenter-level deployments. Proper license documentation must remain accessible throughout the installation process to avoid interruptions.
Server Preparation Checklist
Successful DirectAdmin deployment requires thorough server preparation. Root access or sudo privileges with administrative capabilities are essential for executing installation commands and modifying system configurations. A fully qualified domain name (FQDN) must be configured and properly resolving through DNS before beginning installation. Network connectivity verification ensures the server can reach DirectAdmin’s download servers and licensing systems without firewall interference. Port availability checks confirm that ports 2222 (DirectAdmin), 80 (HTTP), and 443 (HTTPS) remain unblocked and unused by other services. Verifying these elements prevents common installation failures and reduces troubleshooting time significantly.
Step 1: Update and Upgrade System Packages
Beginning with a fully updated system foundation ensures compatibility and security. Execute the following command to refresh package repositories and upgrade all installed packages to their latest versions:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -yThis command performs two critical operations simultaneously. The apt update component refreshes the local package index with the newest versions available from Ubuntu repositories. The apt upgrade portion installs updated versions of all currently installed packages. The -y flag automatically confirms installation prompts, streamlining the process. This step eliminates potential conflicts arising from outdated libraries or deprecated package versions. System updates also patch known security vulnerabilities that could compromise server integrity. Allow sufficient time for this process to complete, as it may download substantial data depending on system age and previous maintenance schedules.
Step 2: Install Required Dependencies
Understanding DirectAdmin Dependencies
DirectAdmin’s operation relies on numerous system libraries and development tools that must be present before installation begins. These dependencies encompass web server components, database systems, programming language interpreters, and development libraries necessary for compiling certain DirectAdmin modules. Each package serves specific functions within the DirectAdmin ecosystem. Web server packages enable HTTP request handling and content delivery. Database components provide data storage and retrieval capabilities for hosted applications. PHP modules support server-side scripting for dynamic content generation. Development libraries supply the building blocks for compiling additional software components during DirectAdmin’s automated setup process. SSL libraries enable encrypted communication channels protecting sensitive data transmission. Understanding these dependencies helps troubleshoot installation issues when specific packages fail to install correctly.
Installing Dependencies Command
The comprehensive dependency installation for DirectAdmin requires executing the following command:
sudo apt-get install wget gcc g++ make flex bison openssl libssl-dev perl perl-base perl-modules libperl-dev libperl4-corelibs-perl libwww-perl libaio1 libaio-dev zlib1g zlib1g-dev libcap-dev cron bzip2 zip automake autoconf libtool cmake pkg-config python3 libdb-dev libsasl2-dev libncurses5 libncurses5-dev libsystemd-dev bind9 dnsutils quota patch logrotate rsyslog libc6-dev libexpat1-dev libcrypt-openssl-rsa-perl curl libnuma-dev libnuma1 -yThis command installs essential compilation tools like gcc, g++, and make for building software from source code. Development libraries including libssl-dev enable SSL/TLS encryption implementation. Perl modules support DirectAdmin’s internal scripting operations. Database libraries facilitate MySQL connectivity and operations. The bind9 package provides DNS server functionality for domain name resolution. Compression utilities like bzip2 and zip handle file archival operations. Each package contributes specific functionality required for DirectAdmin’s comprehensive feature set. Installation typically completes within several minutes depending on network speed and system performance. Monitor the output for any package installation failures requiring resolution before proceeding.
Step 3: Configure System Hostname
Proper hostname configuration ensures DirectAdmin identifies the server correctly and generates appropriate SSL certificates. Execute the following command to set a fully qualified domain name:
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname server.yourdomain.comReplace “server.yourdomain.com” with the actual FQDN designated for this server. The hostname should resolve to the server’s public IP address through DNS records. Verify hostname configuration with the command:
hostnamectl statusThis displays current hostname settings and system information. Additionally, edit the /etc/hosts file to ensure proper hostname resolution locally. Add an entry mapping the server’s IP address to the FQDN. Correct hostname configuration prevents SSL certificate generation errors and email delivery issues that arise from hostname mismatches. Many server applications rely on proper hostname resolution for security certificate validation and authentication processes.
Step 4: Download DirectAdmin Installation Script
Accessing the Official Installation Script
DirectAdmin provides an automated installation script streamlining the deployment process. Download this script directly from DirectAdmin’s official repository using wget:
wget https://download.directadmin.com/setup.shAlternatively, use curl to download and execute in a single operation:
sh <(curl -fsSL https://download.directadmin.com/setup.sh)The wget method downloads the script to the current directory for review before execution. The curl method retrieves and executes immediately, suitable for experienced administrators. Both approaches access the same official installation script maintained by DirectAdmin developers. This script contains logic for detecting the operating system version, validating system requirements, and guiding users through the installation process. Always download installation scripts from official sources to avoid malicious modifications or outdated versions causing installation failures.
Making the Script Executable
After downloading the setup.sh file, modify its permissions to enable execution:
chmod +x setup.shAlternatively, use numeric permission notation:
chmod 755 setup.shThe chmod command modifies file access permissions in Linux systems. The +x flag adds execute permissions for the file owner. The numeric 755 notation grants read, write, and execute permissions to the owner while providing read and execute permissions to group members and others. Verify permission changes with:
ls -l setup.shThe output should display executable permissions indicated by an “x” character in the permissions string. Proper permissions ensure the installation script can execute without permission denied errors that halt the installation process.
Step 5: Execute DirectAdmin Installation
Running the Installation Script
Launch the DirectAdmin installation process by executing the setup script with root privileges:
sudo ./setup.shFor users operating as root directly:
./setup.shThe script initiates system environment checks, verifying operating system compatibility and available resources. Initial setup performs preliminary configuration and downloads additional components required for the web-based installer. This process generates a unique access URL containing a security token for continuing installation through a web browser. The URL follows the format:
http://192.168.0.1:35222/?key=DAdYbfkB5JIAQmCqYtziZ9vyTaCucbeiCopy this URL exactly as displayed, including the security key parameter. The installation script must run as root; using sudo with non-root shells often causes complications. If working from a non-root account, first obtain a root shell with sudo -s before executing the installation command.
Installation Prompts and Configuration
Access the provided URL in a web browser to continue with DirectAdmin’s web-based installation interface. The installation wizard presents several configuration prompts requiring specific information:
Client ID and License ID: Enter the credentials received upon license purchase. These authenticate your installation and activate the DirectAdmin software.
Hostname Confirmation: Verify the system hostname matches the intended FQDN. The installer pre-fills this field based on system configuration.
Server Type Selection: Choose “Admin setup” for standard DirectAdmin control panel installations. Alternative options accommodate specific deployment scenarios.
Terms of Service Agreement: Review and accept DirectAdmin’s terms of service to proceed with installation.
Administrator Account Creation: Set a username and secure password for the primary admin account. This account grants full system access and control.
The web-based installer downloads required packages, configures services, compiles software components, and establishes the DirectAdmin environment. Progress indicators display current operations and completion percentages. Avoid interrupting the installation process as this may result in incomplete or corrupted installations requiring server rebuilding.
Installation Process Duration
DirectAdmin installation typically requires 15 to 45 minutes depending on server hardware specifications, network bandwidth, and selected installation options. Faster processors and solid-state drives significantly reduce compilation times. Network latency affects package download durations. The installation process compiles several software packages from source code, an operation consuming substantial CPU resources. Modern servers with multiple processor cores complete installations faster than single-core configurations. During installation, DirectAdmin configures Apache web server, PHP interpreter, MySQL/MariaDB database server, email services including Exim and Dovecot, FTP server, and various supporting utilities. Each component undergoes configuration optimization for DirectAdmin integration. Monitor installation output for error messages indicating problems requiring intervention.
Step 6: Post-Installation Configuration
Configuring Firewall Rules (UFW)
Securing the DirectAdmin installation begins with proper firewall configuration. Ubuntu 24.04 LTS commonly utilizes UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) for managing iptables rules:
sudo ufw allow 22/tcp
sudo ufw allow 80/tcp
sudo ufw allow 443/tcp
sudo ufw allow 2222/tcp
sudo ufw enableThese commands open essential ports for server operation. Port 22 enables SSH remote administration access. Port 80 allows standard HTTP web traffic for hosted websites. Port 443 facilitates HTTPS encrypted web connections. Port 2222 provides access to the DirectAdmin control panel interface. The ufw enable command activates the firewall with configured rules. Verify firewall status with:
sudo ufw status verboseThis displays all active firewall rules and their configurations. Additional ports may require opening based on specific service needs such as SMTP (25, 587), IMAP (143, 993), POP3 (110, 995), and FTP (21, passive ports).
Alternative Firewall Configuration (firewalld)
Systems utilizing firewalld instead of UFW require different command syntax:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=ssh
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=2222/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadThe --permanent flag ensures rules persist across system reboots. The --reload command applies configuration changes immediately. Query active firewall rules with:
sudo firewall-cmd --list-allChoose the firewall management tool matching the system’s installed configuration. Mixing firewall tools causes conflicts and unpredictable security policies.
Setting Up SSL/TLS Certificates
Implementing SSL/TLS encryption protects administrative access and hosted website traffic. Install Certbot for automated Let’s Encrypt certificate management:
sudo apt install certbot python3-certbot-apache -yGenerate SSL certificates for the DirectAdmin panel:
sudo certbot --apache -d server.yourdomain.comReplace “server.yourdomain.com” with the actual server hostname. Certbot automatically configures Apache to use generated certificates and enables HTTPS redirection. The interactive prompts request an email address for renewal notifications and agreement to terms of service. Let’s Encrypt certificates expire after 90 days, requiring periodic renewal. Configure automatic renewal with:
sudo certbot renew --dry-runThis tests the renewal process without generating new certificates. Set up a cron job for automatic renewal checks:
echo "0 3 * * * root certbot renew --quiet" | sudo tee -a /etc/crontabThis schedules daily renewal checks at 3:00 AM. Certbot only renews certificates approaching expiration, minimizing unnecessary operations.
Initial Admin Account Configuration
Access DirectAdmin immediately after installation to configure the primary administrator account. Strong password policies enhance security significantly. Navigate to:
https://your-server-ip:2222Log in using the administrator credentials established during installation. Navigate through the initial setup wizard completing basic configuration options. Set administrative email addresses for system notifications. Configure default resource limits for user accounts. Review and adjust global server settings according to organizational requirements. The initial configuration establishes baseline settings affecting all subsequently created accounts and hosted services.
Step 7: Accessing DirectAdmin Control Panel
Web Interface Access
DirectAdmin’s web-based control panel provides centralized management capabilities accessible through standard web browsers:
http://your-server-ip:2222Replace “your-server-ip” with the server’s actual IP address or configured hostname. Modern browsers may display security warnings when accessing HTTPS sites with self-signed certificates initially. Proceed past these warnings during initial configuration, then implement valid SSL certificates as described previously. The login screen requests username and password credentials. Enter the administrator account information configured during installation. Successful authentication presents the main DirectAdmin dashboard displaying server status information, quick access shortcuts, and navigation menus. Bookmark this URL for convenient future access. Consider restricting DirectAdmin access to specific IP addresses for enhanced security in production environments.
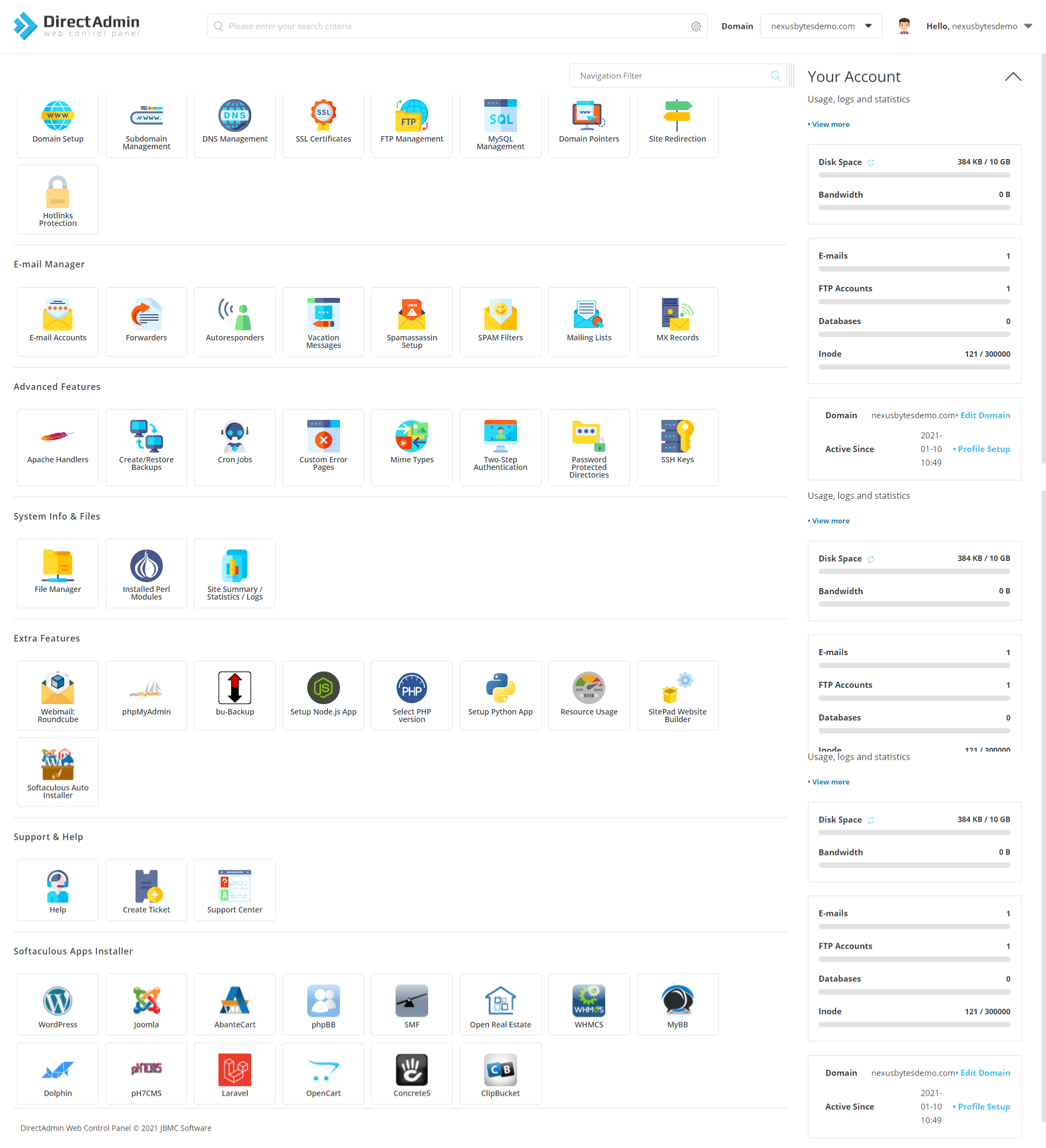
DirectAdmin Dashboard Overview
The DirectAdmin dashboard organizes functionality into logical sections accessible through the main navigation menu. The Account Manager section handles user account creation, modification, and deletion. The Email Manager configures email accounts, forwarders, autoresponders, and spam filters. The DNS Management section edits zone files, manages DNS records, and configures nameservers. The System Info & Files area displays server statistics, allows file management, and provides backup restoration capabilities. The Extra Features menu accesses additional modules, plugins, and advanced configuration options. The dashboard’s visual design emphasizes usability with clear labeling and intuitive organization. Status indicators display service health, resource utilization, and system alerts requiring attention. Familiarizing oneself with dashboard layout accelerates administrative task completion and improves operational efficiency.
Step 8: Essential Security Hardening
Configuring DirectAdmin Brute Force Protection
Implementing brute force attack protection safeguards administrative access from unauthorized login attempts. Navigate to DirectAdmin’s security settings to enable automated detection and response mechanisms:
cd /usr/local/directadmin/conf
sudo nano directadmin.confAdd or modify these configuration directives:
brute_force_protection=1
brute_force_log_scanner=1
unblock_brute_force_ip_time=3600These settings activate brute force monitoring, enable log scanning for suspicious activity, and automatically unblock IP addresses after one hour. Configure maximum login attempt thresholds:
login_tries=5
clear_brute_attempts_after=1440This allows five login attempts before triggering blocks and clears attempt counters after 24 hours. Restart DirectAdmin to apply configuration changes:
sudo systemctl restart directadminReview blocked IP addresses in DirectAdmin’s security logs. Whitelist trusted IP addresses to prevent accidental administrative lockouts during legitimate access attempts.
SSH Security Configuration
Securing SSH access prevents unauthorized server entry through compromised credentials or automated attacks. Modify SSH daemon configuration:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_configImplement these security enhancements:
Change Default SSH Port:
Port 2222Relocating SSH from port 22 to an alternative port reduces automated attack exposure significantly.
Disable Root Login:
PermitRootLogin noThis forces attackers to know both username and password combinations rather than targeting the known root account.
Enable Key-Based Authentication:
PubkeyAuthentication yes
PasswordAuthentication noSSH key authentication provides superior security compared to password-based access. Generate SSH keys before disabling password authentication to avoid lockout situations.
Restrict User Access:
AllowUsers admin_usernameReplace “admin_username” with legitimate administrator account names. This explicitly permits only specified users SSH access.
Restart SSH service to activate changes:
sudo systemctl restart sshdTest new SSH configuration from a separate terminal session before closing existing connections to prevent accidental lockouts.
Implementing Additional Security Measures
Comprehensive server security extends beyond basic access controls. Mount temporary directories with restrictive options preventing execution of malicious scripts:
sudo mount -o remount,noexec,nosuid /tmpMake this permanent by editing /etc/fstab. Disable dangerous PHP functions in php.ini:
disable_functions = exec,passthru,shell_exec,system,proc_open,popen,curl_exec,curl_multi_exec,parse_ini_file,show_sourceInstall and configure ModSecurity web application firewall:
sudo apt install libapache2-mod-security2 -y
sudo systemctl restart apache2ModSecurity provides real-time application-layer attack detection and prevention. Implement regular security audits reviewing log files, user activities, and system modifications. Install automated security scanning tools like Lynis or rkhunter identifying potential vulnerabilities. Maintain regular backup schedules ensuring data recovery capabilities following security incidents. Security represents an ongoing process requiring continuous monitoring and adjustment rather than one-time configuration.
Step 9: Initial Server Configuration
Setting Up Email Services
DirectAdmin includes comprehensive email service management capabilities supporting SMTP, IMAP, and POP3 protocols. Access the Email Manager section from the main dashboard. Configure basic email settings including mail server hostname, default mailbox quota, and spam filtering preferences. Create email accounts by specifying username, password, and quota limits. Configure DNS MX records pointing to the server’s mail exchanger. Test email functionality by sending test messages to external addresses and verifying successful delivery. Implement SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records enhancing email authentication and deliverability. These DNS records verify legitimate sending sources reducing spam classification likelihood. Review email logs regularly monitoring for delivery issues or suspicious activity patterns.
Configuring DNS Settings
Proper DNS configuration ensures hosted domains resolve correctly to the server’s IP addresses. DirectAdmin provides DNS zone management tools within the DNS Management section. Create DNS zones for each hosted domain specifying primary nameservers. Add A records mapping domain names to IP addresses. Configure CNAME records for subdomain aliases. Set MX records directing email traffic to appropriate mail servers. Add TXT records containing SPF, DKIM, and DMARC policies. DirectAdmin generates basic DNS templates automatically, requiring only IP address and nameserver adjustments. Verify DNS propagation using external lookup tools ensuring changes replicate across global DNS infrastructure. DNS modifications require 24-48 hours for complete worldwide propagation.
Creating First User Account
User account creation establishes hosting environments for individual clients or websites. Navigate to Account Manager and select Create User Account. Specify username, password, email address, and domain name. Allocate resources including disk space quota, bandwidth allowance, database limits, and email account restrictions. Choose package templates applying predefined resource allocations consistently across multiple accounts. User accounts receive isolated environments preventing interference between different hosted sites. Each user accesses a limited control panel view managing only their assigned resources. Monitor resource utilization preventing individual accounts from consuming excessive system resources. Adjust allocations based on actual usage patterns and performance requirements.
Common Troubleshooting Issues
DirectAdmin Service Not Starting
Service startup failures typically indicate configuration errors or missing dependencies. Check DirectAdmin service status:
sudo systemctl status directadminThis displays current service state and recent log entries. Review detailed error logs:
sudo tail -f /var/log/directadmin/error.logCommon causes include port conflicts, permission issues, or corrupt configuration files. Verify port 2222 availability:
sudo netstat -tulpn | grep 2222No output indicates the port remains available for DirectAdmin use. Conflicting services must be stopped or reconfigured using alternative ports. Restart DirectAdmin service after resolving issues:
sudo systemctl restart directadminEnable automatic startup on system boot:
sudo systemctl enable directadminCheck file permissions on DirectAdmin directories ensuring proper ownership and access rights.
Port 2222 Not Accessible
Inability to access DirectAdmin’s web interface through port 2222 stems from firewall restrictions, licensing problems, or service configuration errors. Verify firewall rules permit traffic on port 2222:
sudo ufw status | grep 2222Add missing rules as described in the firewall configuration section. Test port accessibility from external locations using online port checking tools. Examine DirectAdmin configuration files for incorrect network interface bindings:
grep "ethernet_dev" /usr/local/directadmin/conf/directadmin.confThe ethernet_dev setting must specify the correct network interface name. Modern systems typically use names like “eth0” or “ens3” rather than legacy conventions. License verification failures prevent service operation. Confirm license status through the DirectAdmin client portal ensuring active and verified status. Contact DirectAdmin support for licensing issues requiring administrative intervention.
Login Failures and Access Issues
Authentication problems prevent legitimate administrator access to the control panel. Perform password resets through command line tools:
cd /usr/local/directadmin/scripts
sudo ./resetpass.sh admin new_secure_passwordReplace “admin” with the actual username and specify the desired password. Check IP blacklist status potentially blocking legitimate access attempts:
sudo cat /usr/local/directadmin/data/admin/ip_blacklistRemove incorrectly blocked addresses by editing this file directly. Clear browser cache and cookies eliminating stored credential conflicts causing repeated authentication failures. Review DirectAdmin security logs identifying specific error messages:
sudo tail -100 /var/log/directadmin/security.logThese logs detail authentication attempts, failures, and security-related events. Verify system time accuracy as significant clock drift causes SSL certificate validation failures preventing secure connections.
Installation Fails on Ubuntu 24.04
Installation failures on Ubuntu 24.04 occasionally occur due to dependency conflicts or version-specific issues. Verify using a completely clean Ubuntu 24.04 installation without pre-existing web services. Check DirectAdmin’s official forum for Ubuntu 24.04-specific compatibility notes and workarounds. Ensure the DirectAdmin license supports Ubuntu 24.04 as legacy licenses may lack compatibility with newer operating system versions. Review installation logs for specific error messages:
cat /var/log/directadmin/install.logThese logs contain detailed information about failed operations and error conditions. Dependency resolution errors require manual package installation or repository configuration adjustments. Contact DirectAdmin technical support providing detailed error logs and system information for troubleshooting assistance. Consider testing installation on a virtual machine before deploying to production environments.
Best Practices for DirectAdmin Management
Regular Updates and Maintenance
Maintaining current software versions ensures security patch application and feature improvements. DirectAdmin includes built-in update mechanisms accessible through the control panel. Navigate to System Info & Files, then select DirectAdmin Updates. Schedule regular update checks ensuring timely security patch deployment. Update system packages independently through Ubuntu’s package management:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -yPerform updates during maintenance windows minimizing disruption to hosted services. Test updates in staging environments before applying to production systems. Review DirectAdmin’s changelog noting new features, bug fixes, and potential compatibility issues. Backup configurations before major updates enabling rapid rollback if problems emerge.
Backup Configuration
Implementing comprehensive backup strategies protects against data loss from hardware failures, security breaches, or operational errors. DirectAdmin provides integrated backup functionality creating full account backups. Configure automated backup schedules within DirectAdmin’s backup settings. Store backups on external storage systems preventing data loss from server failures. Implement backup rotation policies retaining multiple historical versions. Test backup restoration procedures regularly verifying data integrity and recovery capabilities. Document backup procedures ensuring consistency across administrative team members. Consider offsite backup replication protecting against physical disasters affecting primary data center locations. Maintain backup encryption protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access during storage or transmission.
Performance Optimization Tips
Optimizing DirectAdmin performance improves user experience and system efficiency. Allocate adequate system resources based on expected hosting load. Monitor resource utilization identifying bottlenecks limiting performance. Enable opcode caching for PHP applications reducing processing overhead. Implement content delivery networks distributing static content across geographic locations. Configure Apache’s MPM settings matching server hardware specifications and traffic patterns. Optimize MySQL/MariaDB configuration files improving database query performance. Enable compression reducing bandwidth consumption and accelerating page load times. Implement caching mechanisms at multiple levels including browser, application, and database layers. Regularly review and optimize hosted websites identifying resource-intensive applications requiring attention.
Monitoring and Logging
Comprehensive monitoring provides visibility into system health and operational status. DirectAdmin includes built-in monitoring displaying resource usage statistics. Implement external monitoring solutions checking service availability from multiple geographic locations. Configure automated alerting notifying administrators of critical issues requiring immediate attention. Review log files regularly identifying patterns indicating potential problems. Analyze access logs detecting security threats or abuse patterns. Monitor disk space consumption preventing service disruptions from full filesystems. Track bandwidth utilization ensuring compliance with hosting terms and identifying traffic anomalies. Establish baseline performance metrics enabling comparison during troubleshooting. Document monitoring procedures and escalation paths ensuring consistent incident response.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed DirectAdmin. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the DirectAdmin control panel on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official DirectAdmin website.