How To Install DokuWiki on AlmaLinux 10

DokuWiki stands out as one of the most versatile wiki platforms available today, offering a lightweight, file-based content management system that requires no database. This comprehensive guide walks you through installing DokuWiki on AlmaLinux 10, a powerful enterprise-grade Linux distribution that provides stability and security for your documentation needs.
Whether you’re building an internal knowledge base, creating technical documentation, or establishing a collaborative workspace, DokuWiki delivers exceptional performance with minimal resource overhead. Its simplicity combined with AlmaLinux 10’s robust infrastructure creates an ideal environment for hosting wiki solutions.
What is DokuWiki?
DokuWiki represents a paradigm shift in wiki software design. Unlike traditional wiki platforms that rely on database backends, DokuWiki stores content in plain text files, making backups incredibly straightforward and reducing system complexity. This file-based architecture ensures your data remains accessible even without sophisticated database management tools.
The platform excels in various scenarios: software documentation, project collaboration, intranet knowledge bases, and personal note-taking systems. Its clean syntax resembles markdown, enabling rapid content creation without steep learning curves. DokuWiki supports extensive customization through plugins and templates while maintaining excellent performance characteristics.
Released under the GPL license, DokuWiki benefits from active community development and regular security updates. The current stable versions support PHP 7.4 and newer, with PHP 8.x providing optimal performance. Organizations worldwide trust DokuWiki for mission-critical documentation needs.
Prerequisites
Before diving into the installation process, ensure your system meets these essential requirements. You’ll need a fresh AlmaLinux 10 installation with root or sudo privileges to execute administrative commands. Minimum hardware specifications include 1.5GB RAM and 10GB available disk space, though 2GB RAM is recommended for optimal performance.
Having a registered domain name or subdomain proves beneficial for production deployments, though you can test locally using your server’s IP address. Basic familiarity with Linux command-line operations will streamline the installation process. Ensure SSH access is configured and functioning properly.
Your firewall should permit traffic on ports 80 (HTTP) and 443 (HTTPS). Familiarity with text editors like vim or nano will help when editing configuration files. Finally, stable internet connectivity is essential for downloading packages and dependencies throughout this tutorial.
Step 1: Update System Packages
Maintaining current system packages provides crucial security patches and compatibility improvements. Begin by connecting to your AlmaLinux 10 server via SSH. Once logged in, update the package repository cache and upgrade existing packages:
sudo dnf update -yThis command refreshes repository metadata and applies available updates. The -y flag automatically confirms installation prompts, streamlining the process. After updates complete, install essential utilities that facilitate the installation workflow:
sudo dnf install wget tar unzip curl vim -yThese tools enable file downloading, archive extraction, and text editing capabilities. Verify successful installation by checking version information for installed packages. Keeping your system updated establishes a solid foundation for the DokuWiki deployment.
Step 2: Install and Configure PHP
DokuWiki relies heavily on PHP for dynamic content generation and processing. AlmaLinux 10 typically includes PHP 8.3 in its default repositories, which aligns perfectly with DokuWiki’s requirements. install PHP along with necessary extensions:
sudo dnf install php php-cli php-fpm php-gd php-xml php-zip php-json php-mbstring -yEach extension serves specific purposes: php-gd handles image manipulation, php-xml processes XML data structures, php-zip manages compressed archives, while php-json and php-mbstring provide JSON parsing and multibyte string handling respectively.
After installation completes, configure PHP-FPM for optimal performance. Edit the PHP-FPM pool configuration:
sudo nano /etc/php-fpm.d/www.confLocate and modify the following directives to match your web server user. For Nginx deployments, change:
user = nginx
group = nginxAdditionally, adjust performance parameters based on your server resources:
pm = dynamic
pm.max_children = 25
pm.start_servers = 5
pm.min_spare_servers = 5
pm.max_spare_servers = 10These settings balance resource utilization with request handling capacity. Save changes and enable PHP-FPM to start automatically:
sudo systemctl start php-fpm
sudo systemctl enable php-fpm
sudo systemctl status php-fpmVerify PHP installation by checking the version:
php --versionYou should see PHP 8.3 or later displayed, confirming successful installation.
Step 3: Install and Configure Nginx Web Server
Nginx provides superior performance for serving DokuWiki’s file-based architecture. Its lightweight footprint and efficient request handling make it the preferred choice for wiki deployments. Install Nginx using the package manager:
sudo dnf install nginx -yOnce installation completes, start the Nginx service and configure it to launch automatically at boot:
sudo systemctl start nginx
sudo systemctl enable nginx
sudo systemctl status nginxThe status command confirms Nginx is running properly. You can verify functionality by accessing your server’s IP address through a web browser—you should see the default Nginx welcome page. This confirms the web server is operational and ready for DokuWiki configuration.
Step 4: Download DokuWiki
Navigate to the web server’s document root where DokuWiki files will reside. Create a dedicated directory for the wiki installation:
cd /var/www/html
sudo mkdir dokuwiki
cd dokuwikiDownload the latest stable DokuWiki release directly from the official website. Using wget ensures a reliable download:
sudo wget https://download.dokuwiki.org/src/dokuwiki/dokuwiki-stable.tgzThis command retrieves the current stable version packaged as a compressed tarball. Verify the download completed successfully by checking file size. Extract the archive contents:
sudo tar -xzf dokuwiki-stable.tgz --strip-components=1The --strip-components=1 flag removes the top-level directory from the archive, placing files directly in the current location. Once extraction finishes, remove the tarball to conserve disk space:
sudo rm dokuwiki-stable.tgzList directory contents to confirm DokuWiki files extracted properly:
ls -laYou should see directories like bin, conf, data, inc, and lib among others. These comprise DokuWiki’s core structure.
Step 5: Set Proper File Permissions
Correct permissions ensure the web server can read and modify DokuWiki files while maintaining security. Assign ownership to the Nginx user:
sudo chown -R nginx:nginx /var/www/html/dokuwikiThis recursive operation applies nginx user ownership throughout the DokuWiki directory tree. Next, set appropriate permission levels:
sudo find /var/www/html/dokuwiki -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;
sudo find /var/www/html/dokuwiki -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;These commands set directories to 755 (rwxr-xr-x) and files to 644 (rw-r–r–), balancing accessibility with security. Certain directories require write permissions for DokuWiki functionality:
sudo chmod -R 775 /var/www/html/dokuwiki/data
sudo chmod -R 775 /var/www/html/dokuwiki/confThe data directory stores wiki pages and media, while conf contains configuration files that DokuWiki modifies during operation. Proper permissions prevent common “permission denied” errors while protecting sensitive information.
Step 6: Configure Nginx for DokuWiki
Creating a dedicated Nginx server block provides fine-grained control over how the web server handles DokuWiki requests. Generate a new configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/dokuwiki.confInsert the following comprehensive configuration, replacing dokuwiki.example.com with your actual domain:
server {
listen 80;
server_name dokuwiki.example.com;
root /var/www/html/dokuwiki;
index doku.php;
client_max_body_size 50M;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ @dokuwiki;
}
location @dokuwiki {
rewrite ^/_media/(.*) /lib/exe/fetch.php?media=$1 last;
rewrite ^/_detail/(.*) /lib/exe/detail.php?media=$1 last;
rewrite ^/_export/([^/]+)/(.*) /doku.php?do=export_$1&id=$2 last;
rewrite ^/(.*) /doku.php?id=$1&$args last;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
try_files $uri =404;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php-fpm/www.sock;
fastcgi_index doku.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
location ~ /(data|conf|bin|inc|vendor)/ {
deny all;
}
location ~ /\.ht {
deny all;
}
}This configuration implements several critical features. The client_max_body_size directive permits file uploads up to 50MB. URL rewriting rules create clean, user-friendly addresses for wiki pages. Security directives block direct access to sensitive directories like data and conf.
The PHP-FPM integration uses Unix sockets for optimal performance. Save the file and test Nginx configuration syntax:
sudo nginx -tA successful test displays “syntax is ok” and “test is successful” messages. Apply the new configuration by reloading Nginx:
sudo systemctl reload nginxYour web server now routes requests appropriately for DokuWiki functionality.
Step 7: Configure Firewall Rules
AlmaLinux 10 uses firewalld for network security management. Permit HTTP and HTTPS traffic through the firewall:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=httpsThe --permanent flag ensures rules persist across system reboots. Reload firewall configuration to activate changes:
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadVerify active services:
sudo firewall-cmd --list-servicesYou should see http and https among allowed services. These rules enable external access to your DokuWiki installation while maintaining security. For enhanced security in restricted environments, consider limiting access to specific IP addresses or subnets.
Step 8: Install SSL Certificate with Let’s Encrypt
Implementing HTTPS encryption protects data transmitted between users and your wiki. Let’s Encrypt provides free, automated SSL certificates. Install Certbot and the Nginx plugin:
sudo dnf install certbot python3-certbot-nginx -yCertbot automates certificate issuance and renewal processes. Obtain an SSL certificate for your domain:
sudo certbot --nginx -d dokuwiki.example.comReplace dokuwiki.example.com with your actual domain name. Certbot prompts for your email address and agreement to terms of service. It automatically configures Nginx to use the new certificate and redirects HTTP traffic to HTTPS.
Verify automatic renewal functionality:
sudo certbot renew --dry-runThis test ensures certificates will renew automatically before expiration. Let’s Encrypt certificates remain valid for 90 days, with Certbot handling renewals automatically. Your DokuWiki installation now benefits from encrypted connections, building user trust and protecting sensitive information.
Step 9: Complete Web-Based Installation
With server configuration complete, finalize DokuWiki setup through the web interface. Open your browser and navigate to:
https://dokuwiki.example.com/install.phpThe DokuWiki installer presents a configuration form requiring several inputs. Provide a descriptive wiki name that reflects its purpose. Create administrative credentials by entering a username, full name, email address, and secure password.
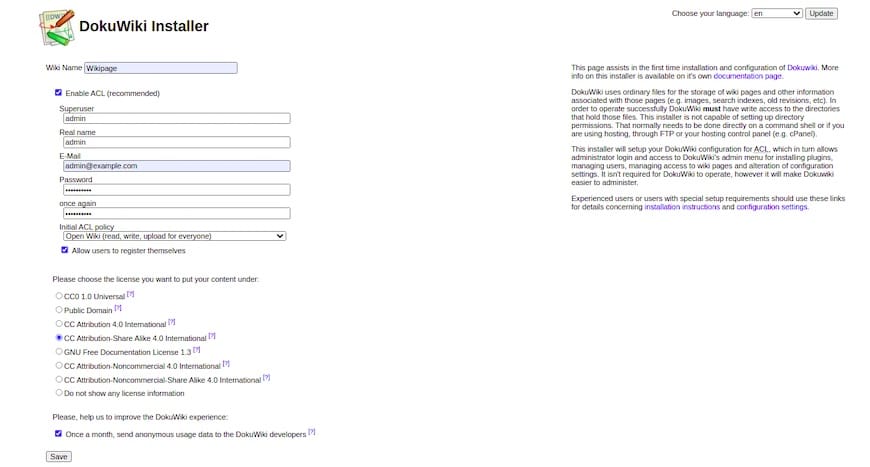
The ACL (Access Control List) policy determines wiki accessibility. Select from three primary options: “Open Wiki” allows anonymous editing, “Public Wiki” permits reading but requires login for editing, while “Closed Wiki” restricts all access to registered users. Choose the policy aligning with your security requirements.
Select an appropriate license for your wiki content—options include Creative Commons variants or proprietary licenses. Review all entries carefully before clicking the “Save” button. DokuWiki processes your configuration and displays a success message upon completion.
Critical security step: Immediately delete the installation file after successful setup:
sudo rm /var/www/html/dokuwiki/install.phpLeaving this file accessible creates a significant security vulnerability, potentially allowing unauthorized users to reconfigure your wiki. This deletion completes the installation process.
Step 10: Security Hardening and Best Practices
Beyond basic installation, implementing additional security measures protects your DokuWiki deployment. First, verify the install.php file was removed as described above. Review your Nginx configuration to confirm sensitive directories remain blocked from web access.
Configure regular automated backups of critical directories:
sudo tar -czf dokuwiki-backup-$(date +%Y%m%d).tar.gz /var/www/html/dokuwiki/data /var/www/html/dokuwiki/confSchedule this command via cron for daily execution. Store backups in a separate location or remote server for disaster recovery purposes. Consider implementing fail2ban to detect and block brute-force login attempts targeting your wiki.
Review PHP security settings in /etc/php.ini. Disable potentially dangerous functions and ensure expose_php is set to Off to reduce information disclosure. Keep DokuWiki, PHP, and Nginx updated regularly to patch security vulnerabilities:
sudo dnf update -yEnable DokuWiki’s built-in security features through the configuration manager. Restrict user registration if operating a private wiki. Monitor access logs periodically for suspicious activity patterns.
Testing Your DokuWiki Installation
Navigate to your DokuWiki homepage using your configured domain. The default start page welcomes new installations with basic usage instructions. Log in using the administrative credentials created during installation.
Test core functionality by creating a new page. Click “Create this page” on any non-existent page link, add content using DokuWiki syntax, and save your changes. The wiki should display formatted content correctly. Upload an image through the Media Manager to verify file handling capabilities work properly.
Test the search functionality by entering keywords in the search box. Results should appear promptly, demonstrating proper indexing. Access your wiki from mobile devices to confirm responsive design functions across different screen sizes. Try different web browsers to ensure cross-platform compatibility.
Verify URL rewriting by examining page addresses—they should appear clean without query strings like ?id=. If URLs contain parameters, review your Nginx configuration for proper rewrite rules.
Customizing Your DokuWiki
Access the Configuration Manager by navigating to Admin → Configuration Settings. This interface provides extensive customization options without directly editing configuration files. Modify your wiki’s title, tagline, and copyright information to reflect your organization’s branding.
Choose from numerous templates that alter visual appearance. The default template works well, but alternatives offer different aesthetics and functionality. Install templates through Admin → Extension Manager → Templates tab. Preview templates before applying them permanently.
Extend functionality through plugins. Popular choices include the “Wrap” plugin for advanced formatting, “Gallery” for image collections, and “Discussion” for page comments. Access plugins through Admin → Extension Manager → Plugins tab. Search the extensive plugin directory for tools matching your specific requirements.
Configure notification settings to receive emails when pages change. Set your preferred date format, timezone, and language options. Adjust editor preferences including toolbar visibility and automatic saving intervals. Each modification enhances user experience while maintaining DokuWiki’s simplicity.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Permission Problems
If DokuWiki displays errors about writing files, verify ownership and permissions. Re-run permission commands from Step 5, ensuring the nginx user owns all DokuWiki files. Check SELinux status if problems persist:
sudo getenforceIf SELinux is enforcing policies, configure appropriate contexts for DokuWiki directories.
PHP-FPM Connection Failures
When pages display “502 Bad Gateway” errors, PHP-FPM likely isn’t running or Nginx can’t connect. Verify PHP-FPM status:
sudo systemctl status php-fpmCheck that the socket path in your Nginx configuration matches the actual PHP-FPM socket location. Look in /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf for the listen directive value.
URL Rewriting Issues
If links generate 404 errors or display PHP code, rewrite rules aren’t functioning properly. Verify your Nginx configuration includes all rewrite directives from Step 6. Test Nginx configuration syntax and reload if changes were made. As a temporary workaround, DokuWiki can operate without URL rewriting, though links will be less elegant.
Slow Performance
If pages load slowly, review PHP-FPM pool settings in /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf. Increase pm.max_children to handle more concurrent requests. Monitor system resources using htop to identify bottlenecks. Consider enabling DokuWiki’s built-in caching mechanisms through the Configuration Manager.
Maintaining Your DokuWiki Installation
Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance and security. Monitor available updates for DokuWiki through Admin → Extension Manager. The update manager displays when new versions become available and facilitates upgrading through the web interface.
Periodically review installed plugins and remove unused extensions. Each plugin introduces potential security vulnerabilities and performance overhead. Prune old wiki pages that no longer serve purposes, improving search relevance and reducing backup sizes.
Analyze access logs to understand usage patterns:
sudo tail -f /var/log/nginx/access.logMonitor error logs for issues requiring attention:
sudo tail -f /var/log/nginx/error.logImplement log rotation to prevent log files from consuming excessive disk space. Review disk usage regularly, especially if your wiki contains substantial media files. Consider implementing quota limits for user uploads if necessary.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed DokuWiki. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing DokuWiki open source wiki software on your AlmaLinux OS 10 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official DokuWiki website.