
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Drupal on Debian 11. For those of you who didn’t know, Drupal is a free and open-source content management system based on the LAMP stack. It has great standard features, like easy content authoring, reliable performance, and excellent security. Flexibility and modularity are some of the core principles that set it apart from the rest.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of Drupal CMS on a Debian 11 (Bullseye).
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Debian 11 (Bullseye).
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Drupal on Debian 11 Bullseye
Step 1. Before we install any software, it’s important to make sure your system is up to date by running the following apt commands in the terminal:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
Step 2. Installing the LAMP stack.
A Debian 11 LAMP server is required. If you do not have LAMP installed, Please read our previous tutorial to install LAMP Server on Debian 11.
Step 3. Installing Drupal on Debian 11.
Now we download the latest version of Drupal from the official page:
wget https://www.drupal.org/download-latest/tar.gz -O drupal.tar.gz
Next, extract the downloaded file, use the below command:
tar -xvf drupal.tar.gz mv drupal-* /var/www/html/drupal
We will need to change some folder permissions:
chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/drupal/ chmod -R 755 /var/www/html/drupal/
Step 4. Configuring MariaDB.
By default, MariaDB is not hardened. You can secure MariaDB using the mysql_secure_installation script. You should read and below each step carefully which will set the root password, remove anonymous users, disallow remote root login, and remove the test database and access to secure MariaDB:
mysql_secure_installation
Configure it like this:
- Set root password? [Y/n] y - Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y - Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y - Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y - Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
Next, we will need to log in to the MariaDB console and create a database for WordPress. Run the following command:
mysql -u root -p
This will prompt you for a password, so enter your MariaDB root password and hit Enter. Once you are logged in to your database server, you need to create a database for WordPress installation:
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE drupal_db; MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE USER 'drupal_user'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'your-strong-password'; MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON drupal_db.* to drupal_user@'localhost'; MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES; MariaDB [(none)]> exit
Step 5. Configuring Apache.
Now, let’s configure Apache to create a new server block to use with our Drupal website:
nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/drupal.conf
Add the following file:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin admin@your-domain.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/drupal/
ServerName drupal.example.com
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
<Directory /var/www/html/drupal/>
Options FollowSymlinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
<Directory /var/www/html/>
RewriteEngine on
RewriteBase /
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ index.php?q=$1 [L,QSA]
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
Save and close, then restart the Apache webserver so that the changes take place:
sudo a2enmod rewrite sudo a2ensite drupal.conf sudo systemctl restart apache2
Step 6. Installing the Let’s Encrypt Certificates.
First, you will need to install the Certbot client to install and manage the SSL on your Debian system:
sudo apt install python3-certbot-apache
After Certbot is installed, run the following command below to secure your website with Let’s Encrypt SSL:
certbot --apache -d drupal.your-domain.com
You will then be prompted to enter an email address for the certificate. After you have entered that you must agree to the term of service and decide if you want to share your email address with the Electronic Frontier Foundation.
Step 7. Accessing Drupal Web Interface.
Once successfully installed, open a web browser and go to https://drupal.your-domain.com and you will see the following screen starting the installer:
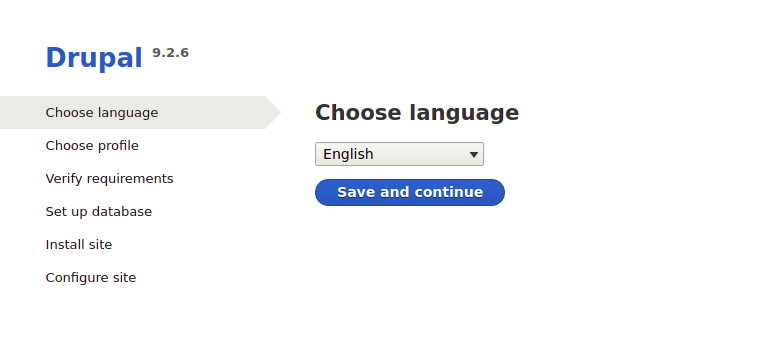
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Drupal. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the latest version of Drupal CMS on Debian 11 Bullseye. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Drupal website.