How To Install ERPNext on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS

In this tutorial, we will show you how to install ERPNext on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS. For those of you who didn’t know, ERPNext is an open-source enterprise resource planning (ERP) software that is built using the Frappé framework, which is written in Python. It is a web-based application that can be used to manage various business operations, including financial accounting, inventory management, and customer relationship management. ERPNext is designed to be easy to use and highly customizable, making it a popular choice for businesses of all sizes.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the ERPNext on Ubuntu 22.04 (Jammy Jellyfish). You can follow the same instructions for Ubuntu 22.04 and any other Debian-based distribution like Linux Mint, Elementary OS, Pop!_OS, and more as well.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Ubuntu 22.04, 20.04, and any other Debian-based distribution like Linux Mint.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install ERPNext on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS Jammy Jellyfish
Step 1. First, make sure that all your system packages are up-to-date by running the following apt commands in the terminal.
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade sudo apt install python3-dev libffi-dev git python3-pip python3-testresources libssl-dev wkhtmltopdf gcc g++ make python3.10-venv -y
Step 2. Installing Node.js.
By default, Node.js is not available on Ubuntu 22.04 base repository. Now run the following command below to add the NodeSource repository to your Ubuntu system:
wget -qO- https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_16.x | sudo -E bash
After adding the NodeSource repository to your system, install the Node.js and Redis using the Apt package manager:
sudo apt install nodejs redis-server -y
Confirm the latest LTS version has been installed and run the command:
node -v
Additionally, you can check the version of NPM using the following command below:
npm -v
Once both packages are installed, install the Yarn package by running the following command:
npm install -g yarn
For additional resources on installing Node.js, read the post below:
Step 3. Installing MariaDB.
By default, the MariaDB is available on Ubuntu 22.04 base repository. Now run the following command below to install the latest version of MariaDB to your Ubuntu system:
sudo apt install mariadb-server mariadb-client
After successfully installing, enable MariaDB (to start automatically upon system boot), start, and verify the status using the commands below:
sudo systemctl enable mariadb sudo systemctl start mariadb sudo systemctl status mariadb
Confirm the installation and check the installed build version of MariaDB:
mariadb --version
By default, MariaDB is not hardened. You can secure MariaDB using the mysql_secure_installation script. you should read and below each step carefully which will set a root password, remove anonymous users, disallow remote root login, and remove the test database and access to secure MariaDB:
mysql_secure_installation
Configure it like this:
- Set root password? [Y/n] y - Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y - Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y - Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y - Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
You can now connect to the MariaDB server using the new password:
mysql -u root -p
Next, you will need to change the MariaDB InnoDB file format to Barracuda. You can do it by editing the file /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnf:
nano /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnf
Add the following lines:
[mysqld] innodb-file-format=barracuda innodb-file-per-table=1 innodb-large-prefix=1 character-set-client-handshake = FALSE character-set-server = utf8mb4 collation-server = utf8mb4_unicode_ci
Save and close the file, then restart the MariaDB service to implement the changes:
sudo systemctl restart mariadb
For additional resources on installing MariaDB, read the post below:
Step 4. Installing ERPNext on Ubuntu 22.04.
Before installing, now we create a new user to run the ERPNext using the following command:
useradd -m -s /bin/bash erpnext
Next, set the password for ERPNext with the following command:
passwd erpnext usermod -aG sudo erpnext
After that, log in to the ERPNext user and setup the environment variable with the following command:
su - erpnext nano ~/.bashrc
Add the following line:
PATH=$PATH:~/.local/bin/
Save the file, then activate the environment variable with the following command below:
source ~/.bashrc
Next, create a directory for ERPNext with the following command:
sudo mkdir /opt/bench
Next, set the ownership to the erpnext user:
sudo chown -R erpnext:erpnext /opt/bench
Next, change the directory to /opt/bench and clone the bench repository from GitHub:
cd /opt/bench git clone https://github.com/frappe/bench bench-repo
Next, install the bench repo using the pip3 command:
pip3 install -e bench-repo
Once installed, initialize the bench directory with the frappe framework using the following command:
bench init erpnext
Next, change the directory to erpnext and create a new ERPNext site with the following command:
cd /opt/bench/erpnext bench new-site your-domain.com
You will be asked to provide your MariaDB root password and Administrator password as shown below:
MySQL root password: Installing frappe... Updating DocTypes for frappe : [========================================] 100% Updating country info : [========================================] 100% Set Administrator password: Re-enter Administrator password: *** Scheduler is disabled *** Current Site set to your-domain.com
Step 5. Configure ERPNext.
Now we manage the ERPNext process and configure Nginx as a reverse proxy:
su - erpnext sudo apt-get install supervisor nginx -y
Next, install the frappe-bench with the following command:
sudo pip3 install frappe-bench
Next, change the directory to /opt/bench/erpnext and setup ERPNext for the production environment with the following command:
cd /opt/bench/erpnext sudo /home/erpnext/.local/bin/bench setup production erpnext
Output:
PLAY RECAP ************************************************************************************************************************************ localhost : ok=8 changed=4 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=1 rescued=0 ignored=0 $ sudo systemctl restart supervisor Port configuration list: Site your-domain.com assigned port: 80 $ /usr/bin/supervisorctl reread No config updates to processes $ /usr/bin/supervisorctl update $ sudo /usr/sbin/nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful $ sudo systemctl reload nginx
Step 6. Configure Firewall.
Now we set up an Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW) with ERPNext to allow public access on default web ports 80:
sudo ufw allow OpenSSH sudo ufw allow 'Nginx Full' sudo ufw enable
Step 7. Accessing ERPNext Web Interface.
Once successfully installed, open your web browser and access the ERPNext Web UI using the URL http://your-domain.com. You will be redirected to the following page:
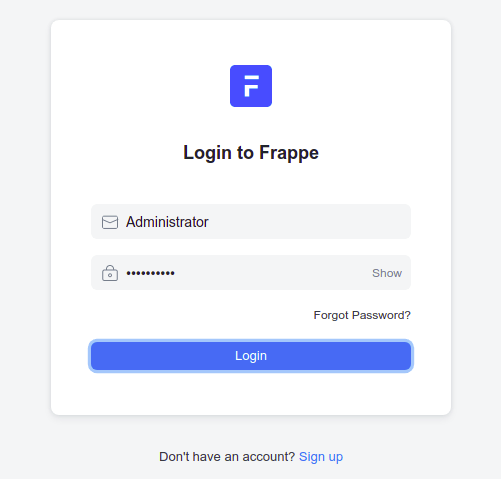
Congratulations! You have successfully installed ERPNext. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing ERPNext on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS Jammy Jellyfish system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official ERPNext website.