
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install and configuration of Gitlab on your Debian 9. For those of you who didn’t know, Gitlab is a graphical implementation of git, it is open-source repository management and version control system. GitLab is developed on Ruby on Rails. Using GitLab you can host your source code on your own server. This ensures the security of the code and gives you total freedom on the number of users as well as the number of repositories and the number of files. GitLab provides you with a platform to collaborate on projects and to keep track of changes in code. GitLab has widely used for software development and version control-related tasks. In many ways, it is similar to GitHub, except you can install it on your own server.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of Gitlab on a Ubuntu Debian 9 (Stretch) server.
GitLab Features
- GitLab provides you a web interface to edit files, directories and create merge requests.
- It is self-hosted, hence you have full control over your server and the source code hosted inside.
- It provides LDAP user authentication and has a two-factor authentication system which makes the application very secure.
- You can insert your own branding on the login page and it also supports project import from GitHub and other sources to GitLab.
- It has lots of features like code reviews, issue tracking, activity feeds, and an inbuilt wiki.
- It provides fine workflow management which gives you the ability to create groups for a project, the ability to fork a repository as well as it provides the ability to manage large binaries with git LFS.
- GitLab comes with GitLab CI for continuous integration. You can also Docker with GitLab CI.
- It’s free and open sources hence you won’t have to deal with any licensing issues.
Install Gitlab on Debian 9 Stretch
Step 1. Before we install any software, it’s important to make sure your system is up to date by running the following apt-get commands in the terminal:
apt-get update apt-get upgrade apt-get install curl openssh-server ca-certificates postfix
Step 2. Installing GitLab.
Use the following command to install GitLab packages on the server:
curl -sS https://packages.gitlab.com/install/repositories/gitlab/gitlab-ce/script.deb.sh | sudo bash
The script will set up your server to use the GitLab maintained repositories. This lets you manage GitLab with the same package management tools you use for your other system packages. Once this is complete, you can install the actual GitLab application with apt:
sudo bash script.deb.sh
If you are not comfortable installing the repository through a piped script, you can find the entire script here. After adding the repository, run the following command to install GitLab Community Edition on Debian 9:
sudo apt install gitlab-ce
Step 3. Configure GitLab on Server.
Run this command on the shell to configure and start Gitlab. The gitlab-ctl the command uses a set of chef scripts to setup the Gitlab system components:
sudo nano /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure
Step 4. Accessing Gitlab.
Gitlab will be available on HTTP port 80 by default. Open your favorite browser and navigate to http://your-domain.com/ or http://your-server-ip. If you are using a firewall, please open port 80 to enable access to the control panel.
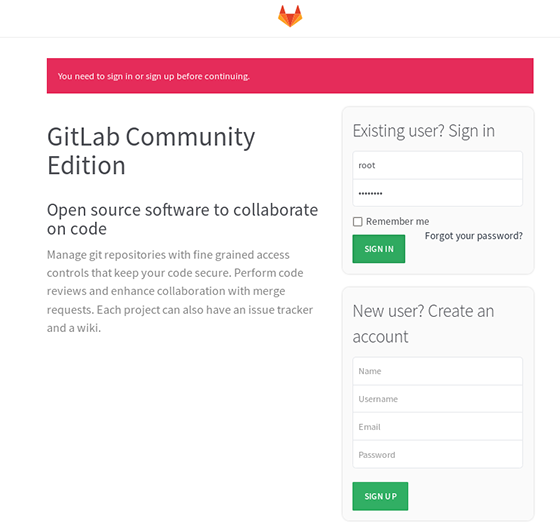
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Gitlab. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Gitlab on Debian 9 (Stretch) system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you to check the official Gitlab website.