How To Install Htop on Fedora 39

In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Htop on Fedora 39. Htop isn’t just another monitoring tool; it’s a command-line powerhouse with real-time system metrics, an intuitive interface, and robust process management capabilities. In comparison to traditional tools, Htop provides a more insightful and interactive approach to system monitoring, making it an invaluable asset for both novices and seasoned Linux users alike.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the Htop monitoring system on a Fedora 39.
Prerequisites
Before diving into the installation process, let’s ensure that you have everything you need:
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Fedora 39.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- You will need access to the terminal to execute commands. Fedora 39 provides the Terminal application for this purpose. It can be found in your Applications menu.
- You’ll need an active internet connection to download Htop and its dependencies.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Htop on Fedora 39
Step 1. Before diving into the installation process, ensure your Fedora 39 system is up to date. Open the terminal and execute the following commands to update your repositories and upgrade installed packages:
sudo dnf clean all sudo dnf update
These commands will fetch the latest updates for your system, providing a stable foundation for the upcoming installation.
Step 2. Installing Htop on Fedora 39.
Now, let’s proceed with the installation of Htop. Open the terminal and enter the following command:
sudo dnf install htop
This command fetches the latest Htop package from the Fedora repositories, ensuring you have the most up-to-date version installed.
Step 3. Accessing Htop on Fedora.
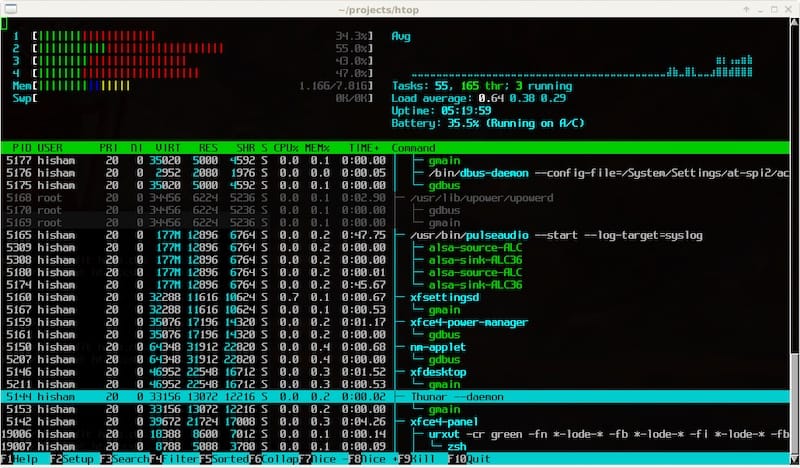
With Htop installed, it’s time to explore its interface. Launch Htop by typing htop in the terminal. Take a moment to absorb the wealth of information presented on your screen:
- CPU and Memory Meters: Located at the top, these meters provide real-time usage statistics.
- Process List and Details: The heart of Htop, displays all running processes along with their resource usage.
-
Interactive Process Management: Use your keyboard to interact with processes, kill or renice them on the fly.
Step 4. Best Practices for System Monitoring with Htop
Monitoring isn’t a one-time task; it’s a commitment. Adopt these best practices to make the most of Htop:
- Regular Checks: Establish a routine for checking system resource usage.
- Diagnostic Power: Htop’s real-time insights are invaluable for diagnosing and resolving performance issues.
-
Stay Informed: Keep abreast of updates and new features in the Htop universe.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Htop. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Htop interactive process viewer on your Fedora 39 system. For additional Apache or useful information, we recommend you check the official Htop website.