How To Install Htop on Fedora 40

In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Htop on Fedora 40. Htop is an interactive process viewer and system monitor that serves as an enhanced alternative to the default top command found in most Linux distributions. With its user-friendly interface and rich set of features, htop provides users with a detailed overview of their system’s resource usage, including CPU, memory, and process management. The tool displays real-time information about running processes, allowing users to easily identify and manage resource-intensive applications. Htop’s interactive nature enables users to perform actions such as sorting processes, filtering results, and even terminating processes directly from the interface, making it a valuable asset for system administrators and power users alike.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the Htop interactive process viewer on a Fedora 40.
Prerequisites
Before we dive into the installation process, ensure that you have the following prerequisites in place:
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Fedora 40.
- It’s highly recommended to update your Fedora system to the latest version before proceeding with the Docker installation.
- You will need access to the terminal to execute commands. Fedora provides the Terminal application for this purpose. It can be found in your Applications menu.
- A stable internet connection to download the necessary packages.
- A non-root sudo user or access to the root user. We recommend acting as a non-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Htop on Fedora 40
Step 1. Update the System.
To begin the installation process, it is crucial to update your Fedora 40 system to ensure that all the necessary packages and dependencies are available. Open a terminal window and execute the following command:
sudo dnf clean all sudo dnf update
This command will synchronize the package repositories and update any outdated packages to their latest versions. Updating your system regularly helps maintain stability, security, and compatibility with new software installations.
Step 2. Enable EPEL Repository.
Htop is not included in the default Fedora repositories, so we need to enable the Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux (EPEL) repository. EPEL is a community-driven repository that provides additional packages for Fedora and other Red Hat-based distributions. To enable EPEL, run the following command:
sudo dnf install epel-release
Step 3. Installing Htop on Fedora 40.
With the EPEL repository enabled, you can now install htop using the following command:
sudo dnf install htop
DNF will resolve any dependencies and prompt you to confirm the installation. Press “y” and hit Enter to proceed. The installation process will download the necessary packages and configure htop on your Fedora 40 system.
Once the installation is complete, you can verify that htop is installed correctly by launching it from the terminal. Simply type:
htop
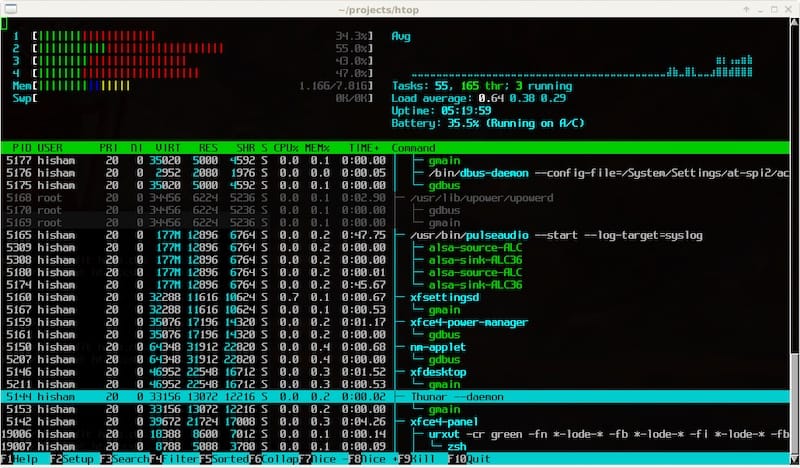
Step 4. Configuring Htop.
After installing htop, you might want to customize its appearance and functionality to better suit your needs:
- Colors and Layout: Access the settings by pressing
F2orSetupin thehtopinterface. Here, you can change colors and choose which columns to display. - Sorting Options: You can sort processes by CPU usage, memory usage, and other criteria by pressing
F6orSortBy.
Step 5. Using Htop to Monitor System Resources.
htop provides a comprehensive view of your system’s operations. Here’s how to interpret the data:
- CPU Usage: Displayed at the top, showing how much CPU power each core is using.
- Memory and Swap Usage: Also at the top, indicating how much RAM and swap space is being used.
- Process List: The main section shows all running processes and their status, CPU, and memory usage.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Htop. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Htop interactive process viewer on your Fedora 40 system. For additional or useful information, we recommend you check the official Htop website.