How To Install Htop on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS

In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Htop on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS. Htop is an interactive process viewer and system monitor for Linux. It provides a real-time view of the system’s processes, resource usage, and overall performance. Compared to the top command, htop offers a more intuitive and visually appealing interface, making it easier to navigate and interpret system information.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the Htop interactive process viewer on Ubuntu 24.04 (Noble Numbat). You can follow the same instructions for Ubuntu 22.04 and any other Debian-based distribution like Linux Mint, Elementary OS, Pop!_OS, and more as well.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Ubuntu and any other Debian-based distribution like Linux Mint.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- An active internet connection. You’ll need an internet connection to download the necessary packages and dependencies.
- An Ubuntu 24.04 system with root access or a user with sudo privileges.
Install Htop on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS Noble Numbat
Step 1. Updating the Package Repository.
To begin the Htop installation process, it’s crucial to start with an up-to-date Ubuntu system. Updating your system ensures that you have the latest security patches, bug fixes, and compatible libraries. Open your terminal and run the following command to update the package indexes:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
This command will fetch the latest package information from the Ubuntu repositories, allowing you to install the most recent version of htop and its dependencies. Updating the package repository is crucial to maintaining the security and stability of your system.
Step 2. Installing Htop on Ubuntu 24.04.
There are multiple ways to install htop on Ubuntu 24.04, catering to different user preferences and requirements. Let’s explore each method in detail.
- Method 1: Installing Htop from the Ubuntu Repository
The simplest and most straightforward method to install htop is using the apt package manager, which retrieves the package from the official Ubuntu repository. To install htop using apt, follow these steps:
sudo apt install htop
The apt package manager will handle the download and installation of htop and its dependencies. This method is recommended for most users, as it ensures a stable and tested version of htop is installed.
- Method 2: Installing Htop Using Snap
Snap is a universal package manager developed by Canonical, the company behind Ubuntu. It allows for easy installation and management of applications across different Linux distributions. To install htop using Snap, follow these steps:
sudo snap install htop
Using Snap provides benefits such as automatic updates and the ability to install applications in isolated environments, ensuring better security and compatibility.
- Method 3: Compiling from Source
For advanced users who require the latest features or specific customizations, compiling htop from source may be necessary. To compile and install htop from the source, follow these steps:
sudo apt install build-essential git libncursesw5-dev
Clone the htop repository from GitHub:
git clone https://github.com/htop-dev/htop.git
Navigate to the cloned directory:
cd htop
Configure the build:
./autogen.sh ./configure
Compile the source code:
make
Install the compiled binary:
sudo make install
Compiling from source allows for greater flexibility and access to the latest features, but it requires more technical knowledge and may not be necessary for most users.
After completing the installation process, it’s essential to verify that htop is correctly installed and accessible. To check the installation, run the following command in the terminal:
htop --version
Step 3. Configuring Htop.
Once htop is installed, you can launch it by simply typing htop in the terminal and pressing Enter. The htop interface will appear, displaying real-time system information and a list of running processes. To navigate the htop interface, use the following keys:
- Arrow keys: Move the selection cursor up, down, left, or right
- F1: Access the help menu
- F2: Open the setup menu for configuration options
- F3: Search for a process
- F4: Filter processes
- F5: Toggle tree view
- F6: Sort processes
- F9: Kill a selected process
- F10 or q: Quit
htop
In the setup menu (F2), you can customize various aspects of htop‘s display, such as the color scheme, columns, and meters. Experiment with different settings to tailor htop to your preferences and requirements.
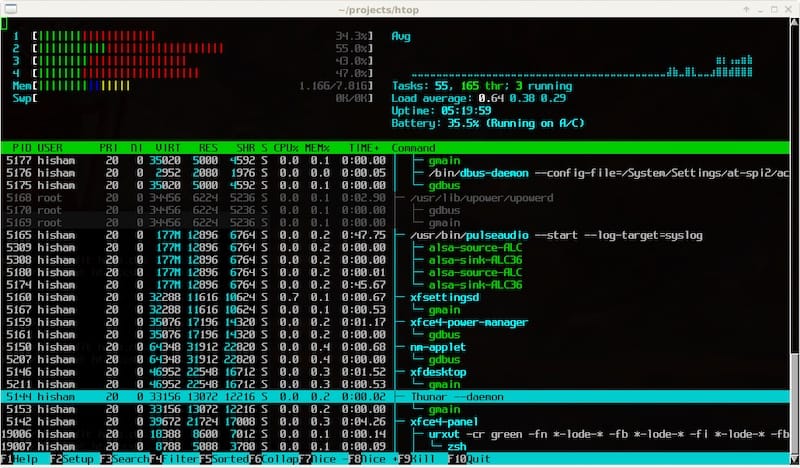
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Htop. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Htop interactive process viewer on the Ubuntu 24.04 LTS system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the Htop website.