
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Jenkins on CentOS 8. For those of you who didn’t know, Jenkins is an open-source continuous integration tool written in Java. Jenkins provides continuous integration services for software development. It is a server-based system running in a servlet container such as Apache Tomcat. It supports SCM tools including AccuRev, CVS, Subversion, Git, Mercurial, Perforce, Clearcase, and RTC, and can execute Apache Ant and Apache Maven-based projects as well as arbitrary shell scripts and Windows batch commands.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of Jenkins on CentOS 8.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: CentOS 8.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- A network connection or internet access.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Jenkins on CentOS 8
Step 1. First, let’s start by ensuring your system is up-to-date.
sudo dnf update
Step 2. Installing Java.
Install JAVA on the server so we can use Jenkins properly:
sudo dnf install java-1.8.0-openjdk
Verify the Java version by running the following command:
java -version
Step 3. Installing Jenkins on CentOS 8.
First, download and enable Jenkins Repository:
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/jenkins.repo https://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat-stable/jenkins.repo
Now, import Jenkins GPG Key:
rpm --import https://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat-stable/jenkins.io.key
Then, start to proceed with the installation of Jenkins:
sudo dnf install jenkins
Now you have to start the Jenkins service so we can use it and enable it on boot so if the system reboots Jenkins will start automatically:
systemctl start jenkins systemctl enable jenkins systemctl status jenkins
Step 4. Configure Firewall.
You know Jenkins is working on port 8080 so we need to allow connection on that port by adding it to the firewall:
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=8080/tcp sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Step 5. Accessing Jenkins Web Interface.
Jenkins will be available on HTTP port 8080 by default. Open your favorite browser and navigate to http://your-domain.com:8080 or http://server-ip:8080 and complete the required steps to finish the installation.
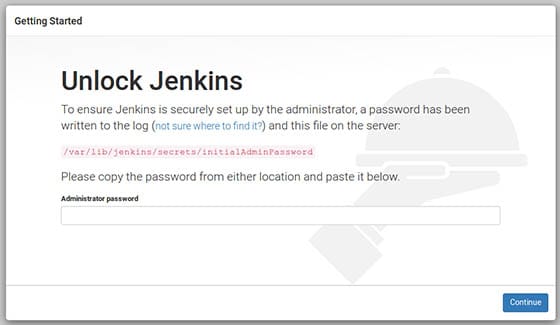
The default installation password can be found at /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword as shown in the below image.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Jenkins. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Jenkins on the CentOS 8 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Jenkins website.