
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Jenkins on Fedora 35. For those of you who didn’t know, Jenkins is a popular and open source automation server written in Java, which helps automate the non-human part of the whole software development process. Jenkins allows executing a predefined list of steps, for example: to compile Golang source code to build a binary file.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you through the step-by-step installation of the Jenkins open source automation server on a Fedora 35.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Fedora 35 or Fedora 34.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Jenkins on Fedora 35
Step 1. Before proceeding, update your Fedora operating system to make sure all existing packages are up to date. Use this command to update the server packages:
sudo dnf upgrade sudo dnf update
Step 2. Installing Java.
Jenkins requires Java installed on the server in order to run, now we install Java using the following command below:
sudo dnf install java-11-openjdk
Step 3. Installing Jenkins on Fedora 35.
By default, Jenkins is not available on Fedora 35 base repository. Then we can add the Jenkins repository to your Fedora with the following command:
sudo wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/jenkins.repo https://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat/jenkins.repo
Next, import the GPG key:
sudo rpm --import https://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat/jenkins.io.key
Finally, install Jenkins with dnf command:
sudo dnf update sudo dnf install jenkins
After installation is complete we need to start the Jenkins server to start operating. We do that with the following command below:
sudo systemctl start jenkins sudo systemctl enable jenkins sudo systemctl status jenkins
Step 4. Configure Firewall.
Configure the FirewallD to allow external machines to access the Jenkins:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=8080/tcp sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Step 5. Accessing Jenkins Web Interface.
Once successfully installed, open your web browser and access the Jenkins using the URL http://your-IP-address:8080. You will be redirected to the Jenkins page:
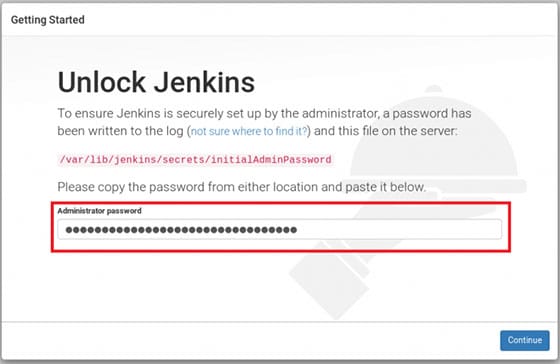
You will be asked to provide an initial password found in this location /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword. Get it by running this command on the server:
[root@idroot.us ~]# cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword 29cuan444aebmwe469db69f5efast509c0
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Jenkins. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the Jenkins open-source automation tool on your Fedora 35 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Jenkins website.