How To Install Midnight Commander on Fedora 41

In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Midnight Commander on Fedora 41. Midnight Commander remains one of the most powerful and versatile file managers in the Linux ecosystem, combining efficiency with a nostalgic interface that seasoned Linux users cherish. For Fedora 41 users, this dual-pane file manager offers remarkable capabilities within a text-based environment. Whether you’re managing files on your local system or connecting to remote servers, Midnight Commander provides a consistent, keyboard-driven interface that maximizes productivity.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore multiple methods to install Midnight Commander on Fedora 41, configure it for optimal performance, and leverage its powerful features for efficient file management. By the end of this article, you’ll have a fully functional installation of this classic utility and the knowledge to use it effectively.
What is Midnight Commander and Why Use It?
Midnight Commander (MC) is a feature-rich, text-based file manager that draws inspiration from the classic Norton Commander from the DOS era. Despite the proliferation of graphical file managers, MC maintains its relevance in modern Linux distributions like Fedora 41 due to its efficiency, lightweight nature, and powerful capabilities.
Unlike graphical file managers that require mouse interaction, Midnight Commander provides a fully keyboard-driven interface, allowing experienced users to navigate and manipulate files with remarkable speed. The dual-pane layout presents two directory views simultaneously, making file operations between locations significantly more efficient.
Key features that make Midnight Commander invaluable include:
- Dual-pane interface for easy file comparisons and operations
- Built-in text editor and viewer
- Support for various archive formats (ZIP, TAR, GZ, etc.)
- Virtual filesystem for FTP/SFTP, Samba, and other remote connections
- Syntax highlighting for numerous file types
- Powerful search capabilities
- Minimal resource consumption
- Full functionality over SSH connections
- Customizable appearance and behavior
For system administrators and power users working with Fedora 41, MC transforms terminal-based file management from a necessary task into a streamlined experience. Its text-based interface makes it particularly valuable when working on remote servers or systems without graphical interfaces.
Prerequisites for Installing Midnight Commander
Before proceeding with the installation of Midnight Commander on your Fedora 41 system, ensure you meet the following prerequisites:
- A functioning Fedora 41 installation (desktop or server)
- Sufficient administrative privileges (sudo access) to install packages
- An internet connection to download packages from repositories
- Basic familiarity with terminal commands
- Updated system packages
To update your Fedora 41 system, open a terminal and execute:
sudo dnf updateThis command ensures your system has the latest security patches and package information before proceeding with the installation of Midnight Commander. Depending on your system’s update status, this process might take several minutes to complete.
It’s also recommended to have at least 50MB of free disk space, although Midnight Commander itself has minimal space requirements. The actual space needed will depend on which installation method you choose and what dependencies need to be installed.
Method 1: Installing Midnight Commander via DNF Package Manager
The most straightforward and recommended method to install Midnight Commander on Fedora 41 is through the DNF package manager. DNF (Dandified YUM) is Fedora’s native package management system that handles software installation, updates, and dependency resolution.
Step 1: Update your system repositories
Before installing any package, it’s good practice to ensure your system’s package database is up-to-date:
sudo dnf updateStep 2: Install Midnight Commander
Once your system is updated, install Midnight Commander using the following command:
sudo dnf install mcWhen prompted, press ‘Y’ to confirm the installation. DNF will automatically resolve and install any dependencies required by Midnight Commander.
Step 3: Verify the installation
After the installation completes, verify that Midnight Commander was installed correctly by checking its version:
mc --versionThis command should display information about the installed Midnight Commander version, confirming a successful installation.
Benefits of the DNF method:
- Official package from Fedora repositories
- Automatic dependency resolution
- Easy updates through the standard system update process
- Integration with SELinux policies
- Simpler management of the application lifecycle
The DNF installation method is recommended for most users as it provides the most stable and well-tested version of Midnight Commander for Fedora 41, with proper integration into the system’s package management.
Method 2: Compiling Midnight Commander from Source Code
For users who require the very latest features or specific customizations, compiling Midnight Commander from source code provides the most flexibility. This method is more complex but offers greater control over the installation process.
Step 1: Install required development tools and dependencies
First, install the necessary development packages:
sudo dnf install gcc make autoconf automake libtool glib2-devel slang-devel gettext-devel libssh2-devel e2fsprogs-devel gitThis command installs the essential build tools and libraries needed to compile Midnight Commander from source.
Step 2: Download the source code
You can either download the latest stable release from the official website or clone the Git repository:
git clone https://github.com/MidnightCommander/mc.git
cd mcAlternatively, download the source tarball:
wget https://github.com/MidnightCommander/mc/archive/refs/tags/4.8.29.tar.gz -O mc.tar.gz
tar -xvf mc.tar.gz
cd mc-4.8.29Step 3: Configure the build
Generate the configuration files and set up the build environment:
./autogen.sh
./configureFor customized installations, you can add options to the configure command. For example:
./configure --prefix=/usr/local --with-screen=ncursesStep 4: Compile the source code
Compile Midnight Commander with the make command:
makeThis process may take several minutes depending on your system’s performance.
Step 5: Install the compiled program
Once compilation completes successfully, install Midnight Commander:
sudo make installStep 6: Verify the installation
Confirm the installation by checking the version:
mc --versionAdvantages of compiling from source:
- Access to the latest features and bug fixes
- Ability to customize compilation options
- Optimization for your specific system
- Control over installation paths
- Ability to apply custom patches
While this method requires more technical knowledge, it provides the most customizable installation of Midnight Commander on Fedora 41.
Method 3: Installing via Snap Package Manager
Snap packages provide a universal installation method across Linux distributions, including Fedora 41. This method offers easy installation with automatic updates.
Step 1: Install Snap support on Fedora 41
Fedora doesn’t come with Snap pre-installed, so you’ll need to set it up first:
sudo dnf install snapdStep 2: Enable the systemd unit for Snap
sudo systemctl enable --now snapd.socketStep 3: Create a symbolic link for Snap
sudo ln -s /var/lib/snapd/snap /snapThis step ensures compatibility with snap applications expecting the /snap directory.
Step 4: Install Midnight Commander via Snap
After setting up Snap, install Midnight Commander:
sudo snap install mcStep 5: Verify the installation
Check that Midnight Commander was installed correctly:
snap list | grep mcBenefits of using Snap:
- Automatic updates
- Isolation from system libraries
- Consistent behavior across Linux distributions
- Easy rollback to previous versions
- Self-contained dependencies
The Snap installation method is particularly useful if you work across multiple Linux distributions and want a consistent version of Midnight Commander.
Method 4: Installing via Flatpak
Flatpak provides another distribution-independent method for installing Midnight Commander on Fedora 41. Flatpak packages run in a sandboxed environment and can include all necessary dependencies.
Step 1: Install Flatpak support
Fedora 41 comes with Flatpak pre-installed, but if it’s missing, install it:
sudo dnf install flatpakStep 2: Add the Flathub repository
Flathub is the primary repository for Flatpak applications:
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepoStep 3: Install Midnight Commander
flatpak install flathub org.midnightcommander.mcStep 4: Run Midnight Commander
To run the Flatpak version of Midnight Commander:
flatpak run org.midnightcommander.mcAdvantages of Flatpak installation:
- Sandboxed execution environment
- Independence from system libraries
- Ability to run multiple versions simultaneously
- Consistent runtime environment
- Strong security isolation
Flatpak is ideal if you prefer a containerized application with minimal impact on your base system.
First Launch and Basic Configuration
After installing Midnight Commander, it’s time to configure it for optimal use on your Fedora 41 system.
Step 1: Launch Midnight Commander
Open a terminal and type:
mcThis launches the dual-pane interface of Midnight Commander.
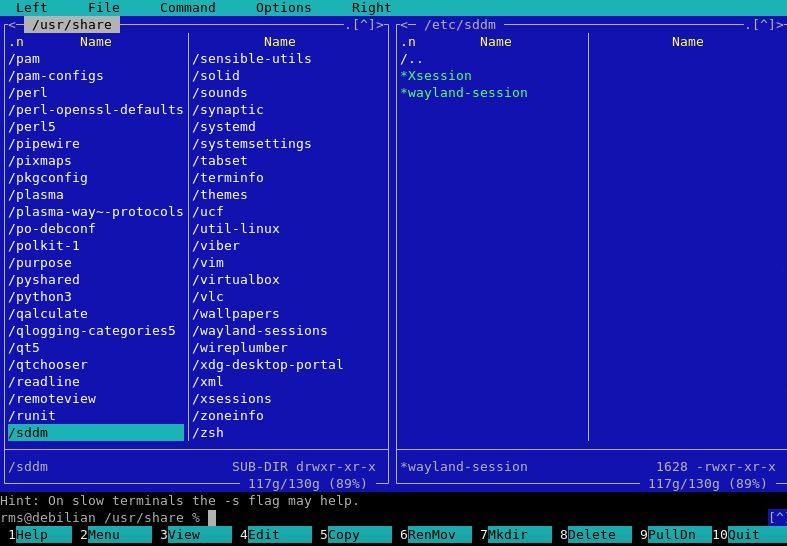
Step 2: Navigate the interface
Midnight Commander presents two panels side by side. The function key mappings are displayed at the bottom of the screen:
- F1: Help
- F2: User menu
- F3: View
- F4: Edit
- F5: Copy
- F6: Move/Rename
- F7: Create directory
- F8: Delete
- F9: Menu bar
- F10: Quit
Step 3: Configure display options
Press F9 to access the menu bar, then select “Options” → “Configuration”. Here you can customize:
- Panel options
- Confirmation settings
- Display settings
- Color schemes
- Virtual file systems
Step 4: Customize panel layout
One of the first configurations many users make is changing the panel display format:
- Press F9 to access the menu
- Select “Left” or “Right” (depending on which panel you want to configure)
- Select “Listing mode”
- Choose “User defined” and enter a format like:
half type name |owner:5|group:5|size|mode:4|mtime
Step 5: Save configuration
After making your preferred changes, save the configuration:
- Press F9
- Select “Options”
- Select “Save setup”
This creates a configuration file at ~/.config/mc/ini that stores your preferences.
Essential Usage Guide for Midnight Commander
Learning to navigate and use Midnight Commander efficiently will significantly improve your file management productivity in Fedora 41.
Basic navigation:
- Use arrow keys to move the cursor
- Tab to switch between panels
- Enter to open directories or files
- Insert to select files
- F5 to copy selected files to the opposite panel
- F6 to move selected files
- F8 to delete selected files
Keyboard shortcuts for efficient operation:
- Ctrl+O: Toggle panels (show/hide to reveal terminal)
- Alt+.: Toggle hidden files
- Ctrl+U: Swap panels
- Alt+,: Switch to previous directory pattern
- Alt+.: Switch to next directory pattern
- Ctrl+\: Show directory hotlist
- Alt+I: Go to the other panel’s directory
- Alt+Y: Go to previous directory
- Alt+S: Quick search within the current panel
Working with files:
- F3: View the contents of a file
- F4: Edit a file using the built-in editor
- Shift+F4: Create a new file and open in editor
- F7: Create a new directory
- Alt+T: Change file attributes
Managing selections:
- Insert: Select/deselect a single file
- *: Select files by pattern
- +: Select files matching a pattern
- -: Unselect files matching a pattern
- Alt+*: Invert selection
These commands and shortcuts make navigating and managing files in Midnight Commander efficient and intuitive, even for complex file operations.
Advanced Features and Customization
Midnight Commander’s power extends far beyond basic file operations. Here are advanced features that can enhance your productivity on Fedora 41.
Panel display customization:
Change how information is displayed in panels by modifying the panel listing format. Press F9, select “Options” → “Panel options” and experiment with different settings like:
- Full file size display
- Permission bits
- Detailed file information
- Custom column layouts
Creating custom color schemes:
- Press F9 and select “Options” → “Colors”
- Customize interface colors to your preference
- Save your custom color scheme
User menu customization:
The user menu (F2) can be customized to add your frequently used commands:
- Edit the file
~/.config/mc/menuor create it if it doesn’t exist - Add entries in the format:
+ "Menu Label" command %f
External tools integration:
Configure MC to use external viewers and editors:
- Press F9, select “Options” → “Configuration”
- Set your preferred editor, viewer, and other external tools
Virtual filesystems:
Midnight Commander supports various virtual filesystems:
- FTP: Access remote FTP servers with
cd ftp://user:pass@hostname - SFTP: Secure file transfers with
cd sftp://user@hostname - Samba: Access Windows shares with
cd smb://server/share - Fish: Connection through SSH with
cd sh://user@hostname
Bookmark management:
Use the directory hotlist for quick access to frequently used locations:
- Navigate to a directory you want to bookmark
- Press Ctrl+\
- Select “Add current” to add the current directory
These advanced features transform Midnight Commander from a simple file manager into a powerful productivity tool customized to your specific needs on Fedora 41.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When using Midnight Commander on Fedora 41, you might encounter some issues. Here are solutions to common problems:
Problem: Terminal display issues (garbled interface)
Solution:
- Check your terminal’s character encoding
- Try launching MC with specific terminal settings:
TERM=xterm-256color mc - Edit
~/.bashrcto include:export TERM=xterm-256color
Problem: Function keys not working
Solution:
- Verify your terminal emulator settings
- Use alternative key combinations (Esc+number instead of function keys)
- Add to
~/.bashrc:export NCURSES_NO_UTF8_ACS=1
Problem: Permission denied errors
Solution:
- Check file ownership with
ls -la - Use sudo to launch MC for administrative tasks:
sudo mc - Be cautious when using MC with elevated privileges
Problem: Editor or viewer not working properly
Solution:
- Check your editor configuration in MC
- Press F9, select “Options” → “Configuration” → “Use internal edit”
- Alternatively, set your preferred external editor
Problem: Slow performance in large directories
Solution:
- Disable file highlighting for large directories
- Turn off file preview
- Consider enabling brief listing mode
Problem: Strange characters in filenames
Solution:
- Check your locale settings with
locale - Ensure UTF-8 is being used:
export LANG=en_US.UTF-8 - Restart MC after changing locale settings
Problem: Installation dependencies
Solution:
- If a dependency is missing during installation, identify it with:
sudo dnf provides */missing-file - Install the required package:
sudo dnf install required-package
For more complex issues, the Midnight Commander community maintains an active mailing list, and the project’s GitHub repository is a valuable resource for troubleshooting and reporting bugs.
Uninstallation Methods
If you need to remove Midnight Commander from your Fedora 41 system, the method depends on how you installed it:
DNF installation:
sudo dnf remove mcSource installation:
Navigate to the source directory and run:
sudo make uninstallSnap package:
sudo snap remove mcFlatpak installation:
flatpak uninstall org.midnightcommander.mcTo completely remove configuration files:
rm -rf ~/.config/mcThese commands ensure a clean removal of Midnight Commander, allowing you to start fresh if needed or free up system resources if the utility is no longer required.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Midnight Commander. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Midnight Commander on Fedora 41 system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Midnight Commander website.