
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Nextcloud on Debian 11. For those of you who didn’t know, Nextcloud is a web suite that provides cloud storage over the network, a fork of its ownCloud. It allows you to create your self-hosted services like Dropbox or Google Drive.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of Nextcloud on a Debian 11 (Bullseye).
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Debian 11 (Bullseye).
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Nextcloud on Debian 11 Bullseye
Step 1. Before we install any software, it’s important to make sure your system is up to date by running the following apt commands in the terminal:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
Step 2. Installing the LAMP stack.
A Debian 11 LAMP server is required. If you do not have LAMP installed, Please read our previous tutorial to install LAMP Stack on Debian 11.
Step 3. Installing Nextcloud on Debian 11.
Now we download the latest version of Nextcloud from the official page:
cd /var/www/ curl -o nextcloud.zip https://download.nextcloud.com/server/releases/nextcloud-22.1.1.zip
Next, unzip the Nextcloud zip file:
unzip nextcloud-22.1.0.zip
We will need to change some folders permissions:
chown -R www-data:www-data nextcloud
Step 4. Configuring MariaDB.
By default, MariaDB is not hardened. You can secure MariaDB using the mysql_secure_installation script. You should read and below each step carefully which will set a root password, remove anonymous users, disallow remote root login, and remove the test database and access to secure MariaDB.
mysql_secure_installation
Configure it like this:
- Set root password? [Y/n] y - Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y - Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y - Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y - Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
Next, we will need to log in to the MariaDB console and create a database for Nextcloud. Run the following command:
mysql -u root -p
This will prompt you for a password, so enter your MariaDB root password and hit Enter. Once you are logged in to your database server you need to create a database for Nextcloud installation:
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE nextcloud; MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE USER 'nextclouduser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'your-strong-password'; MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL ON nextcloud.* TO 'nextclouduser'@'localhost'; MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES; MariaDB [(none)]> EXIT;
Step 5. Set up SSL Letsencrypt.
First, we install the Certbot tool for generating SSL Letsencrypt to your system:
sudo apt install certbot
Then, create a new directory for Letsencrypt authorization using the following commands:
mkdir -p /var/lib/letsencrypt/.well-known chgrp www-data /var/lib/letsencrypt chmod g+s /var/lib/letsencrypt
Next, change the directory to the “/etc/apache2/conf-available/” and create a new configuration “well-known.conf” using your favorite text editor:
cd /etc/apache2/conf-available/ nano well-known.conf
Add the following file:
Alias /.well-known/acme-challenge/ "/var/lib/letsencrypt/.well-known/acme-challenge/" <Directory "/var/lib/letsencrypt/"> AllowOverride None Options MultiViews Indexes SymLinksIfOwnerMatch IncludesNoExec Require method GET POST OPTIONS </Directory>
After that, creating a symlink of the ‘well-known.conf‘ file to the directory ‘conf-enabled‘ using the ‘ln’ command below:
ln -s /etc/apache2/conf-available/well-known.conf /etc/apache2/conf-enabled/
Finally, verify the Apache configuration and restart the Apache service:
apachectl configtest sudo systemctl restart apache2
Step 6. Configure Apache.
Now we create a new Apache virtual host configuration for Nextcloud:
cd /etc/apache2/sites-available/ nano nextcloud.conf
Add the following line:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName files.your-domain.com
ServerAlias www.files.your-domain.com
# auto redirect HTTP to HTTPS
Redirect permanent / https://files.your-domain.com/
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost *:443>
ServerName files.your-domain.com
ServerAlias www.files.your-domain.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/nextcloud/
Protocols h2 http/1.1
# auto redirect www to non-www
<If "%{HTTP_HOST} == 'www.files.your-domain.com'">
Redirect permanent / https://files.your-domain.com/
</If>
# log files
ErrorLog /var/log/apache2/files.your-domain.com-error.log
CustomLog /var/log/apache2/files.your-domain.com-access.log combined
SSLEngine On
SSLCertificateFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/files.your-domain.com/fullchain.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/files.your-domain.com/privkey.pem
# HSTS
<IfModule mod_headers.c>
Header always set Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=15552000; includeSubDomains"
</IfModule>
<Directory /var/www/nextcloud/>
Options +FollowSymlinks
AllowOverride All
<IfModule mod_dav.c>
Dav off
</IfModule>
SetEnv HOME /var/www/nextcloud
SetEnv HTTP_HOME /var/www/nextcloud
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
Now, we can restart the Apache webserver so that the changes take place:
sudo a2enmod rewrite sudo a2ensite nextcloud.conf sudo systemctl restart apache2
Step 7. Accessing Nextcloud Web Interface.
Once successfully installed, now open your favorite browser and navigate to http://files.your-domain.com/ and complete the required steps to finish the installation. If you are using a firewall, please open port 80 to enable access to the control panel.
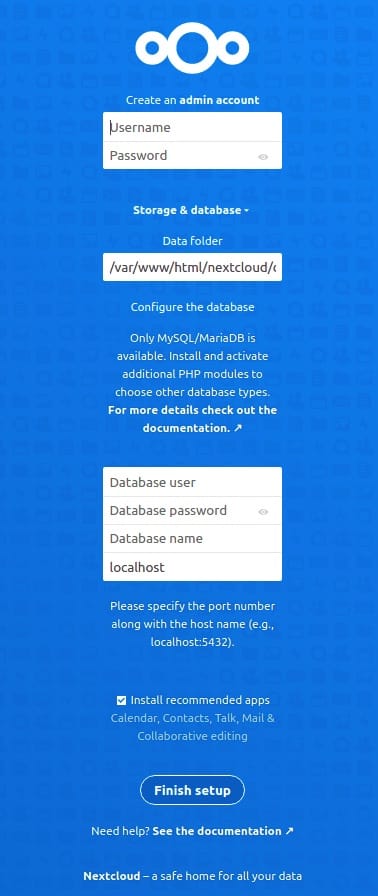
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Nextcloud. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the latest version of the Nextcloud on Debian 11 Bullseye. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Nextcloud website.