
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Observium on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS. For those of you who didn’t know, Observium is a Network Management and Monitoring System that collects data from multiple devices using SNMP and allows you to monitor all of the network’s devices via an easy-to-use interface. It is PHP-based and uses a MySQL database to store data.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of Observium on the Ubuntu 18.04 server.
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Ubuntu 18.04.
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- SSH access to the server (or just open Terminal if you’re on a desktop).
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Observium on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS
Step 1. First, make sure that all your system packages are up-to-date by running the following apt-get commands in the terminal.
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
Step 2. Installing required packages dependency.
Install packages required by Observium:
sudo apt install rrdtool whois fping imagemagick graphviz \ mtr-tiny nmap python-mysqldb snmp snmpd python-memcache mtr-tiny acl
Step 3. Install LEMP (Linux, Nginx, MariaDB, and PHP) server.
A Ubuntu 18.04 LEMP server is required. If you do not have LEMP installed, you can follow our guide here.
Step 4. Configuring MariaDB for Observium.
By default, MariaDB is not hardened. You can secure MariaDB using the mysql_secure_installation script. you should read and below each step carefully which will set a root password, remove anonymous users, disallow remote root login, and remove the test database and access to secure MariaDB:
mysql_secure_installation
Configure it like this:
- Set root password? [Y/n] y - Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y - Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y - Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y - Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
Next, we will need to log in to the MariaDB console and create a database for the Observium. Run the following command:
mysql -u root -p
This will prompt you for a password, so enter your MariaDB root password and hit Enter. Once you are logged in to your database server you need to create a database for Observium installation:
create database observium; grant all privileges on observium.* to observium@localhost IDENTIFIED by "Your-Strong-Password"; flush privileges; quit
Step 5. Installing Observium on CentOS 8.
First, add the Observium system user:
sudo useradd -r -M -d /opt/observium observium
Now add this user to the web user group www-data:
sudo usermod -a -G observium www-data
Download the latest Observium Community edition:
cd /opt wget http://www.observium.org/observium-community-latest.tar.gz tar xvf observium-community-latest.tar.gz rm observium-community-latest.tar.gz
Next, change to the Observium directory and create a config file:
sudo cp /opt/observium/config.php.default /opt/observium/config.php
Edit the file to set database connection:
sudo nano /opt/observium/config.php
/ Database config --- This MUST be configured $config['db_extension'] = 'mysqli'; $config['db_host'] = 'localhost'; $config['db_user'] = 'observium'; $config['db_pass'] = 'Your-Strong-Password'; $config['db_name'] = 'observium';
Create rrd and logs directory:
sudo mkdir /opt/observium/{rrd,logs}
Change permission of the directory:
sudo chown -R observium:observium /opt/observium/ sudo chmod -R 775 /opt/observium/
Configure snmpd:
sudo cp /opt/observium/snmpd.conf.example /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf
Configure String:
sudo nano /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf com2sec readonly default 0bservium
Then, restart snmpd:
sudo systemctl restart snmpd
Step 6. Configure Nginx.
Now, we create the VirtualHost definition for Nginx to load the Observium web interface:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/observium.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name observium.example.com;
root /opt/observium/html;
index index.php;
charset utf-8;
gzip on;
gzip_types text/css application/javascript text/javascript application/x-javascript image/svg+xml text/plain text/xsd text/xsl text/xml image/x-icon;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$query_string;
}
location /api/v0 {
try_files $uri $uri/ /api_v0.php?$query_string;
}
location ~ \.php {
include fastcgi.conf;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.2-fpm.sock;
}
location ~ /\.ht {
deny all;
}
}
Now restart Nginx for affect changes configuration:
sudo systemctl restart nginx
Step 7. Configure Observium Web Interface.
Import MySQL scheme:
cd /opt/observium ./discovery.php -u
Then, add a user for accessing the Observium portal:
# cd /opt/observium # ./adduser.php admin AdminPass 10 Observium CE 17.9.0 Add User User admin added successfully. # ./adduser.php godetz password 10 Observium CE 17.9.0 Add User User godetz added successfully.
Step 8. Accessing Observium.
Observium will be available on HTTP port 80 by default. Open your favorite browser and navigate to http://observium.example.com or http://observium.server-ip-address.
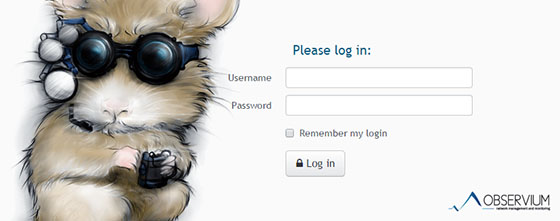
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Observium. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing Observium on your Ubuntu 18.04 LTS system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you to check the official Observium website.