
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Odoo on Debian 11. For those of you who didn’t know, Odoo is an integrated ERP (Enterprise Resources Planning) application. That is to say, it works by installable modules that make the application have many functionalities. It includes a wide range of applications such as CRM, e-commerce, website builder, billing, accounting, manufacturing, warehouse, project management, inventory, and much more, all seamlessly integrated. Odoo currently has two versions, one of them is the community that is free and completely open-source, and another version Enterprise for professional corporate support. This post focuses on the community version.
This article assumes you have at least basic knowledge of Linux, know how to use the shell, and most importantly, you host your site on your own VPS. The installation is quite simple and assumes you are running in the root account, if not you may need to add ‘sudo‘ to the commands to get root privileges. I will show you the step-by-step installation of the Odoo 15 on a Debian 11 (Bullseye).
Prerequisites
- A server running one of the following operating systems: Debian 11 (Bullseye).
- It’s recommended that you use a fresh OS install to prevent any potential issues.
- An active internet connection. You’ll need an internet connection to download the necessary packages and dependencies for Odoo.
- A
non-root sudo useror access to theroot user. We recommend acting as anon-root sudo user, however, as you can harm your system if you’re not careful when acting as the root.
Install Odoo on Debian 11 Bullseye
Step 1. Before we install any software, it’s important to make sure your system is up to date by running the following apt commands in the terminal:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
Step 2. Installing PostgreSQL on Debian 11.
By default, PostgreSQL is not available to install directly from the Debian 11 base repository. Now we add the official PostgreSQL repository to your system:
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/postgresql-keyring.gpg] http://apt.postgresql.org/pub/repos/apt/ bullseye-pgdg main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/postgresql.list
Next, import the PostgreSQL signing key:
curl -fsSL https://www.postgresql.org/media/keys/ACCC4CF8.asc | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/postgresql-keyring.gpg
Finally, run the following command below to install PostgreSQL:
sudo apt update sudo apt install postgresql-13
After installing PostgreSQL, start the PostgreSQL service and enable it to start at system reboot:
sudo systemctl start postgresql sudo systemctl enable postgresql sudo systemctl status postgresql
Next, we create a PostgreSQL user with the same name as the previously created system user:
sudo su - postgres -c "createuser -s odoo15"
For additional resources on installing PostgreSQL, read the post below:
Step 3. Installing Wkhtmltopdf.
Run the following command below to download and install the Wkhtmltopdf package from Github:
sudo wget https://github.com/wkhtmltopdf/wkhtmltopdf/releases/download/0.12.5/wkhtmltox_0.12.5-1.bionic_amd64.deb sudo apt install ./wkhtmltox_0.12.5-1.bionic_amd64.deb
Step 4. Installing Odoo on Ubuntu 20.04.
Now we clone the Odoo source code from GitHub:
sudo su - odoo15 git clone https://www.github.com/odoo/odoo --depth 1 --branch 15.0 /opt/odoo
Next, create a new Python virtual environment for Odoo:
cd /opt/odoo15 python3 -m venv odoo-venv
Activate the virtual environment:
source odoo-venv/bin/activate
After that, install all required Python modules with pip3:
(venv) $ pip3 install wheel (venv) $ pip3 install -r odoo/requirements.txt
Once done, deactivate the environment using the following command:
(venv) $ deactivate
Step 5. Configure Odoo.
Now we create a configuration file with the following content:
sudo nano /etc/odoo15.conf
Add the following configuration:
[options] ; This is the password that allows database operations: admin_passwd = admin-passwd db_host = False db_port = False db_user = odoo15 db_password = False addons_path = /opt/odoo15/odoo/addons,/opt/odoo15/odoo-custom-addons
Step 6. Creating Systemd Unit for Odoo.
First, create a file named odoo15.service with the following content:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/odoo15.service
Add the following file:
[Unit] Description=Odoo15 Requires=postgresql.service After=network.target postgresql.service [Service] Type=simple SyslogIdentifier=odoo15 PermissionsStartOnly=true User=odoo15 Group=odoo15 ExecStart=/opt/odoo15/odoo-venv/bin/python3 /opt/odoo15/odoo/odoo-bin -c /etc/odoo15.conf StandardOutput=journal+console [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save and close the file, then start the Odoo service and enable it to start on boot by running:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl enable --now odoo15 sudo systemctl status odoo15
Step 7. Accessing Odoo Web Interface.
Once successfully installed, open your web browser and access the Odoo using the URL http://your-ip-address:8069. You will be redirected to the Odoo interface page:
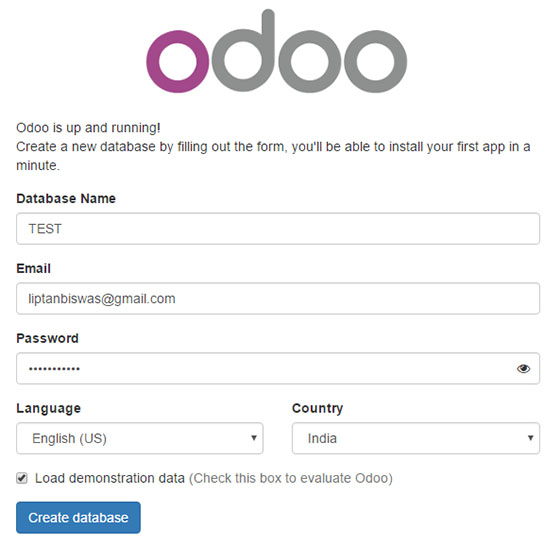
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Odoo. Thanks for using this tutorial for installing the latest version of Odoo on the Debian system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Odoo website.