How To Install Pinta on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS

Pinta stands as one of the most accessible image editing tools available for Linux users, offering a streamlined alternative to more complex software like GIMP. Whether you need to make quick edits, create simple graphics, or annotate screenshots, Pinta provides the perfect balance of functionality and simplicity. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore multiple methods to install Pinta on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS (Noble Numbat), ensuring you can choose the approach that best suits your needs and technical comfort level.
What is Pinta?
Pinta is an open-source, cross-platform drawing and image editing application designed to provide a simpler alternative to more complex image editors. Initially developed as a Linux alternative to Windows’ Paint.NET, Pinta has evolved into a versatile tool that maintains simplicity while offering powerful features.
History and Development
Developed using the Mono framework (an open-source implementation of Microsoft’s .NET Framework), Pinta first appeared in 2010 and has been maintained by community contributors since then. The project aims to strike a balance between ease of use and functionality, making image editing accessible to users of all skill levels.
Key Features and Capabilities
Pinta offers numerous features that make it valuable for everyday image editing tasks:
- Intuitive layer support for advanced editing techniques
- Extensive selection of drawing tools and brushes
- Multiple adjustment tools for color, brightness, and contrast
- Over 35 effects for image enhancement
- Text tools for adding and manipulating text
- Shape tools for creating geometric objects
- Support for common image formats including PNG, JPEG, TIFF, and BMP
- Unlimited history for undoing and redoing actions
Advantages of Pinta on Ubuntu
Compared to other image editing options on Ubuntu, Pinta offers several advantages:
- Significantly lighter resource usage than GIMP
- Familiar interface for users transitioning from Windows
- Quick startup time for rapid edits
- Cross-platform compatibility
- No steep learning curve
Use Cases for Pinta
Pinta excels in numerous everyday scenarios:
- Quick photo cropping and resizing
- Simple graphic design for social media
- Screenshot annotation for documentation
- Basic photo correction and enhancement
- Creating diagrams and simple illustrations
- Minor touch-ups and adjustments to images
Prerequisites for Installation
Before proceeding with Pinta installation on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS, ensure your system meets the necessary requirements and preparations for a smooth installation process.
System Requirements
Pinta’s lightweight nature means it runs well even on modest hardware:
- Ubuntu 24.04 LTS (Noble Numbat) or compatible derivative
- 1 GHz processor (or better)
- 512 MB RAM (1 GB recommended)
- 100 MB available disk space
- Display capable of 1024×768 resolution or higher
Preparation Steps
To ensure a successful installation, complete these preliminary tasks:
- Update your system’s package repositories:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade - Ensure you have administrative privileges (sudo access) to install software
- Verify internet connectivity for downloading packages
- If planning to use the PPA method, ensure you have the
software-properties-commonpackage:sudo apt install software-properties-common
Different Installation Approaches
Pinta can be installed through various methods on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS, each with its own advantages:
- Ubuntu Software Center: Graphical, beginner-friendly approach
- APT Package Manager: Command-line installation using standard repositories
- Snap: Universal packaging system integrated with Ubuntu
- Flatpak: Alternative universal packaging system
- PPA Repository: Access to more recent versions
- Source Installation: Maximum control and customization
It’s important to note that as of Ubuntu 24.04’s release, Pinta may not be available in the standard repositories as it was removed during the Ubuntu 23.10 development cycle. This makes alternative installation methods particularly important.
Method 1: Installing Pinta Using Ubuntu Software Center
The Ubuntu Software Center provides the most user-friendly approach for installing applications, perfect for beginners or those preferring a graphical interface over command-line operations.
Benefits of GUI Installation
Using the Software Center offers several advantages:
- Visual interface requiring no command-line knowledge
- Simplified browsing and searching capabilities
- Easy-to-understand installation progress
- Integrated reviews and ratings system
- Seamless update management through the same interface
Step-by-Step Process
Follow these steps to install Pinta through the Ubuntu Software Center:
- Click on the Ubuntu Software Center icon in the Dock or find it in the Applications menu
- Once opened, click on the search icon in the top-right corner
- Type “Pinta” in the search box and press Enter
- From the search results, select Pinta (usually showing the paintbrush icon)
- Click the “Install” button to begin the installation process
- If prompted, enter your user password to authorize the installation
- Wait for the installation to complete, which typically takes less than a minute depending on your internet speed
Verification and First Launch
After installation completes:
- Search for “Pinta” in the Applications menu or overview
- Click on the Pinta icon to launch the application
- Verify that the program opens correctly and the interface appears
Limitations of This Method
While convenient, the Software Center installation has some considerations:
- The version available may not be the latest release
- In Ubuntu 24.04, Pinta might be available only as a Snap package through the Software Center
- Limited configuration options during installation
- Dependency management happens automatically, with no manual control
Note that if Pinta doesn’t appear in search results, it might be because it’s not available in the standard repositories for Ubuntu 24.04, as indicated by bug reports. In that case, proceed to one of the alternative installation methods.
Method 2: Installing Pinta via APT Package Manager
The APT (Advanced Package Tool) package manager offers a straightforward command-line approach to installing software on Ubuntu systems.
Understanding APT Installation
APT provides several benefits for software installation:
- Efficient management of dependencies
- Access to the official Ubuntu repositories
- Simple command syntax
- Integration with system updates
- Scriptable for automation
Preparation Commands
Before installation, ensure your system’s package information is current:
sudo apt updateThis command refreshes your system’s package index files, ensuring you’re installing the most up-to-date available version of Pinta.
Installation Process
To install Pinta using APT, execute the following command:
sudo apt install pintaDuring the installation process, you might see output similar to:
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
Reading state information... Done
The following additional packages will be installed:
[list of dependencies]
Do you want to continue? [Y/n]Press Y and Enter to confirm the installation.
Important Note: As mentioned in search result, Pinta may not be available in the standard Ubuntu 24.04 repositories. If you encounter an error message like:
Package pinta is not available, but is referred to by another package.
This may mean that the package is missing, has been obsoleted, or is only available from another sourceThen you’ll need to use one of the alternative installation methods described later.
Verification Steps
After installation completes, verify that Pinta installed correctly:
- Check the installed version:
pinta --version - Launch the application from the terminal:
pinta - Alternatively, find and launch Pinta from the Applications menu
Advantages and Disadvantages
The APT installation method offers:
Advantages:
- Fast and efficient installation
- Minimal resource usage
- Full integration with the system package management
Disadvantages:
- May provide an older version of Pinta
- Limited to what’s available in official repositories
- Might not be available in Ubuntu 24.04’s standard repositories
Method 3: Installing Pinta Using Snap
Snap packages offer a modern solution for software distribution on Linux, providing isolated, self-contained applications with their dependencies included.
Introduction to Snap Packages
Snap is Ubuntu’s preferred universal package system with several distinctive features:
- Self-contained applications with bundled dependencies
- Automatic background updates
- Sandboxed for improved security
- Cross-distribution compatibility
- Direct from developer to user delivery
Preparing for Snap Installation
Ubuntu 24.04 LTS comes with Snap pre-installed and configured. To verify this, run:
snap versionIf for some reason Snap is not installed, you can add it with:
sudo apt install snapdInstallation Commands and Process
Installing Pinta using Snap is straightforward:
sudo snap install pintaThe terminal will display progress information as the Snap package downloads and installs:
pinta x.x.x from Pinta Project installedSnap automatically handles all dependencies, and the installation typically completes in under a minute depending on your internet connection speed.
Post-Installation Verification
To ensure Pinta installed correctly:
- Launch Pinta from the Applications menu
- Alternatively, run it from the terminal:
pinta - Check the Snap installation status:
snap list | grep pinta
Managing Snap Packages
Once installed, you can manage your Snap installation of Pinta:
To check for updates:
sudo snap refresh --listTo update Pinta specifically:
sudo snap refresh pintaTo remove Pinta if needed:
sudo snap remove pintaSnap Benefits and Limitations
Snap installation offers particular advantages:
Benefits:
- Always provides the latest stable version
- Automatic background updates
- Works consistently across Ubuntu versions
- Isolated from system libraries
Limitations:
- Larger disk space usage due to bundled dependencies
- Slightly slower first-launch time
- Limited integration with system themes
- Confined access to system resources
Method 4: Installing Pinta Using Flatpak
Flatpak provides another universal package management solution that focuses on sandboxed applications and is gaining popularity across many Linux distributions.
Introduction to Flatpak
Flatpak differs from Snap in several ways:
- Community-driven rather than Canonical-backed
- Decentralized repository structure
- Strong focus on sandboxing for security
- Runtime sharing between applications
- Broad adoption across Linux distributions
Setting Up Flatpak on Ubuntu 24.04
Unlike Snap, Flatpak is not installed by default on Ubuntu. To set it up:
- Install Flatpak:
sudo apt install flatpak - Add the Flathub repository, which hosts most Flatpak applications:
sudo flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo - Restart your system to ensure Flatpak is properly integrated:
sudo reboot
Pinta Installation Process
After your system restarts, install Pinta using Flatpak:
flatpak install flathub com.github.PintaProject.PintaDuring the installation, Flatpak will prompt you to confirm the installation of Pinta along with any required runtimes and dependencies. Type ‘y’ to proceed when prompted.
Post-Installation Steps
After installation:
- Launch Pinta using the applications menu
- Alternatively, run it from the terminal with:
flatpak run com.github.PintaProject.Pinta - Verify the installation:
flatpak list | grep Pinta
Integration with Desktop Environment
Flatpak applications integrate with your desktop environment, appearing in the application menu alongside traditionally installed programs. For optimal integration:
- Ensure desktop integration is installed:
sudo apt install xdg-desktop-portal xdg-desktop-portal-gtk - If using a non-GNOME desktop environment, install the appropriate portal package (e.g.,
xdg-desktop-portal-kdefor KDE)
Pros and Cons of Flatpak Method
Flatpak installation offers specific advantages and trade-offs:
Pros:
- Access to the latest versions from Flathub
- Strong security through sandboxing
- Consistent experience across distributions
- Multiple version installation possibility
Cons:
- Additional setup required on Ubuntu
- Larger disk space requirements
- More complex command syntax
- Potential theming inconsistencies
Method 5: Installing Pinta via PPA Repository
Personal Package Archives (PPAs) provide an alternative way to access more recent or specialized versions of software that may not be available in the standard Ubuntu repositories.
Understanding PPAs
PPAs offer several unique advantages:
- Maintained by developers or dedicated teams
- More frequent updates than official repositories
- Access to versions not yet available in official channels
- Simplified installation compared to compiling from source
- Integration with APT package management
Adding Pinta Maintainers PPA
To add the Pinta PPA to your system:
- Open a terminal window (Ctrl+Alt+T)
- Add the Pinta stable PPA:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:pinta-maintainers/pinta-stableAlternatively, for bleeding-edge development versions:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:pinta-maintainers/pinta-daily - Update your package lists:
sudo apt update
Installation Process
After adding the PPA, install Pinta:
sudo apt install pintaThe system will download and install Pinta and its dependencies automatically. You’ll see progress information in the terminal as the installation proceeds.
Verification and Testing
To verify your PPA installation:
- Check the installed version:
apt policy pintaThis shows where the package was installed from (should indicate the PPA)
- Launch Pinta from the Applications menu or terminal:
pinta
Advantages of PPA Installation
Using the PPA for installation offers several benefits:
- Access to more current versions than standard repositories
- Still integrates fully with APT package management
- Updates through standard system updates
- Smaller installation size than Snap or Flatpak
- Better system integration than universal packaging methods
Potential PPA Considerations
While PPAs are useful, be aware of these aspects:
- PPAs are third-party repositories not vetted by Ubuntu
- Repository maintenance depends on the PPA maintainers
- Adding too many PPAs can potentially cause package conflicts
- May need manual removal if you want to revert to standard packages
Method 6: Installing Pinta from Source (Tarball)
Installing from source gives you the most control over the installation process and allows you to access any specific version of Pinta, including the very latest development versions.
When to Use Source Installation
Consider source installation in these scenarios:
- When you need a specific version not available through other methods
- If you want to modify the source code or contribute to development
- When other installation methods aren’t working on your system
- If you need to customize compilation options
- For learning purposes about how the software works
Obtaining the Source Package
To obtain the Pinta source code:
- Visit the official Pinta website at https://www.pinta-project.com
- Navigate to the “Download” section and select the tarball option
- Alternatively, download directly from GitHub:
wget https://github.com/PintaProject/Pinta/releases/download/[VERSION]/pinta-[VERSION].tar.gzReplace
[VERSION]with the current version number - Verify the integrity of the downloaded tarball (if checksums are provided):
sha256sum pinta-[VERSION].tar.gz
Compilation and Installation Process
Before compiling, install required dependencies:
sudo apt install mono-complete mono-devel gtk-sharp2 gnome-sharp2 build-essentialThen proceed with extraction and compilation:
- Extract the tarball:
tar -zxf pinta-[VERSION].tar.gz - Navigate to the extracted directory:
cd pinta-[VERSION] - Configure the build environment:
./configure - Compile the program:
make - Install system-wide:
sudo make install
Troubleshooting Common Build Issues
When building from source, you might encounter these common issues:
- Missing dependencies: Install any packages reported as missing during the configure step
- Compilation errors: Check that you have the correct Mono version installed
- Path configuration problems: Ensure that installation directories are in your PATH environment variable
- Permission issues: Make sure you’re using sudo for the installation step
Benefits and Challenges
Source installation has unique characteristics:
Benefits:
- Complete control over the version and features
- Can apply custom patches or modifications
- Educational value in understanding the software
- Not dependent on package managers
Challenges:
- Most complex installation method
- Manual dependency management
- No automatic updates
- Requires more technical knowledge
- Time-consuming installation process
Launching and Configuring Pinta
Once Pinta is installed using any of the methods above, you’ll want to get it up and running with optimal settings.
Different Ways to Launch
Pinta can be launched in several ways:
- From the Applications Menu: Search for “Pinta” and click the icon
- From the Terminal: Simply type
pinta(or the appropriate command for Flatpak/Snap) - By File Association: Right-click an image file, select “Open With” and choose Pinta
- From the Dock/Panel: If pinned to your dock or panel, click the Pinta icon
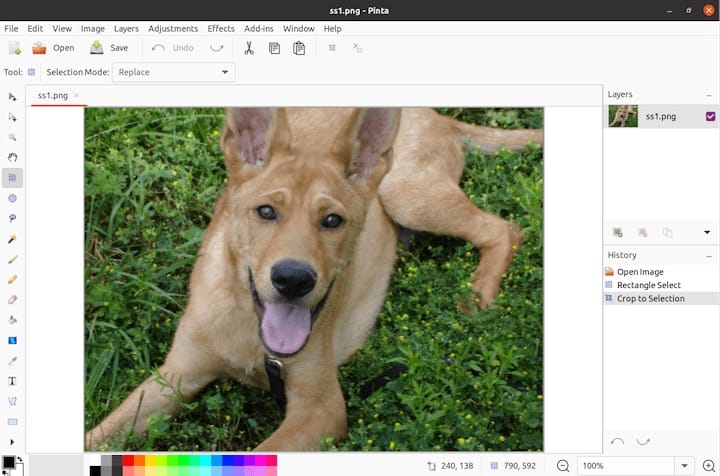
First-time Setup
When launching Pinta for the first time:
- Take note of the interface layout with tools on the left, layers and history on the right
- Access preferences from the Edit menu to adjust settings like:
- Default image size
- Canvas background color
- Auto-save frequency
- UI language settings
- Explore the available tools to familiarize yourself with Pinta’s capabilities
- Consider customizing the workspace layout to suit your workflow
Basic Functionality Testing
To ensure Pinta is working correctly, perform these basic tests:
- Create a new image (File > New) and specify dimensions
- Try drawing with different brushes and shapes
- Test layer functionality by adding and manipulating layers
- Open an existing image to test import capabilities
- Save a file in different formats to verify export functionality
Updating Pinta
Keeping Pinta updated ensures you have the latest features and security patches.
Update Methods Based on Installation Type
The update process varies by installation method:
- APT Installation:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade - Snap Installation:
sudo snap refresh pinta - Flatpak Installation:
flatpak update com.github.PintaProject.Pintaor update all Flatpak applications:
flatpak update - PPA Installation:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade - Source Installation: Requires re-downloading and compiling the new version.
Troubleshooting Common Installation Issues
Even with clear instructions, issues can arise during installation. Here are solutions to common problems.
Dependency Problems
If you encounter dependency-related errors:
- Missing Libraries: Install specific missing dependencies:
sudo apt install [package-name] - Version Conflicts: Sometimes you might need to adjust the source of the package:
sudo apt install [package-name]=specific-version - Broken Packages: Fix broken dependencies with:
sudo apt --fix-broken install
Repository Issues
For problems with repositories:
- Connection Problems: Verify your internet connection and try again later
- Authentication Errors: Update your keys:
sudo apt-key adv --refresh-keys --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com - Repository Unavailability: If Pinta is not available in the standard repository, switch to Snap, Flatpak, or PPA methods
Permission and System-Related Problems
For issues related to permissions:
- Insufficient Privileges: Ensure you’re using sudo when required
- File System Restrictions: Check if your filesystem is mounted with restrictive options
- AppArmor Conflicts: Temporarily disable specific profiles if necessary:
sudo aa-complain /etc/apparmor.d/[profile]
Graphics-Related Issues
If Pinta encounters display problems:
- Display Server Issues: Make sure your X11 or Wayland session is functioning properly
- Graphics Driver Problems: Update your graphics drivers
- Rendering Errors: Try launching with hardware acceleration disabled:
LIBGL_ALWAYS_SOFTWARE=1 pinta
Uninstalling Pinta
If you need to remove Pinta, the process depends on your installation method.
Removal Methods by Installation Type
For each installation type:
- APT Installation:
sudo apt remove pintaFor complete removal including configuration files:
sudo apt purge pinta - Snap Installation:
sudo snap remove pinta - Flatpak Installation:
flatpak uninstall com.github.PintaProject.Pinta - PPA Installation:
First remove the package:sudo apt remove pintaThen remove the PPA:
sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:pinta-maintainers/pinta-stable - Source Installation:
Navigate to the source directory and run:sudo make uninstall
Complete System Cleanup
For a thorough cleanup:
- Remove configuration files:
rm -rf ~/.config/pinta - Clean orphaned dependencies (APT):
sudo apt autoremove - Verify complete removal by checking that launching commands no longer work
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Pinta. Thanks for using this tutorial to install the latest version of Pinta drawing and image editing on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS Linux system. For additional help or useful information, we recommend you check the official Pinta website.